Buccinator muscle
| Buccinator muscle | |
|---|---|
 | |
| Buccinator outlined in red. | |
| Latin | musculus buccinator |
| Gray's | p.384 |
| Origin | from the alveolar processes of the maxillary bone and mandible, temporomandibular joint |
| Insertion | in the fibers of the orbicularis oris |
| Artery | buccal artery |
| Nerve | buccal branch of the facial nerve (VII cranial nerve) |
| Actions | The buccinator compresses the cheeks against the teeth and is used in acts such as blowing. It is an assistant muscle of mastication (chewing) and in neonates it is used to suckle. |
The buccinator (/ˈbʌksɪneɪtər/[1][2] ) is a thin quadrilateral muscle, occupying the interval between the maxilla and the mandible at the side of the face. It forms the anterior part of the cheek or the lateral wall of the oral cavity. [3]
Action
Its purpose is to pull back the angle of the mouth and to flatten the cheek area, which aids in holding the cheek to the teeth during chewing. This action causes the muscle to keep food pushed back on the occlusal surface of the posterior teeth, as when a person chews. By keeping the food in the correct position when chewing, the buccinator assists the muscles of mastication. [3]
It aids whistling and smiling, and in neonates it is used to suckle.
Origin and insertion
It arises from the outer surfaces of the alveolar processes of the maxilla and mandible, corresponding to the three pairs of molar teeth; and behind, from the anterior border of the pterygomandibular raphé which separates it from the constrictor pharyngis superior.
The fibers converge toward the angle of the mouth, where the central fibers intersect each other, those from below being continuous with the upper segment of the orbicularis oris, and those from above with the lower segment; the upper and lower fibers are continued forward into the corresponding lip without decussation.
Innervation
Motor innervation is from the buccal branch of the facial nerve (cranial nerve VII). Sensory innervation is supplied by the buccal branch (one of the muscular branches) of mandibular nerve (cranial nerve V3).
Additional images
-

-

-

-

-

Left maxilla. Outer surface.
-

Mandible. Outer surface. Side view.
-
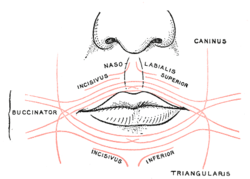
Scheme showing arrangement of fibers of Orbicularis oris.
-

The internal carotid and vertebral arteries. Right side.
-
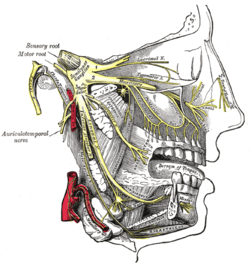
Distribution of the maxillary and mandibular nerves, and the submaxillary ganglion.
-
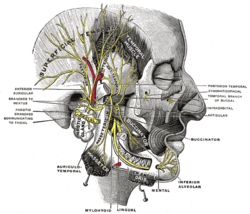
Mandibular division of the trifacial nerve.
-

The mouth cavity. The cheeks have been slit transversely and the tongue pulled forward.
-

Position of buccinator muscle (red).
-

Position of buccinator muscle (red).
-

Position of buccinator muscle (red).
-
Buccinator muscle
References
- ↑ OED 2nd edition, 1989.
- ↑ Entry "buccinator" in Merriam-Webster Online Dictionary.
- ↑ 3.0 3.1 Illustrated Anatomy of the Head and Neck, Fehrenbach and Herring, Elsevier, 2012, page 91
External links
| Wikimedia Commons has media related to Buccinator muscles. |
- -845545395 at GPnotebook
- LUC buc
- Buccinator+muscle at eMedicine Dictionary
- Roche Lexicon - illustrated navigator, at Elsevier 05287.011-1
- Roche Lexicon - illustrated navigator, at Elsevier 25420.000-1
- An anatomical study of the buccinator muscle fibres that extend to the terminal portion of the parotid duct, and their functional roles in salivary secretion, Kang, et al, J Anat. 2006 May; 208(5): 601–607 at http://www.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/pmc/articles/PMC2100218/
This article incorporates text from a public domain edition of Gray's Anatomy.
| |||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
