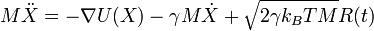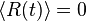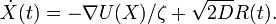Brownian dynamics
Brownian dynamics (BD) can be used to describe the motion of molecules in molecular simulation. It is a simplified version of Langevin dynamics and corresponds to the limit where no average acceleration takes place during the simulation run. This approximation can also be described as 'overdamped' Langevin dynamics, or as Langevin dynamics without inertia.
In Langevin dynamics, the equation of motion is
where 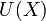 is the particle interaction potential;
is the particle interaction potential;  is the gradient operator such that
is the gradient operator such that 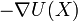 is the force calculated from the particle interaction potentials; the dot is a time derivative such that
is the force calculated from the particle interaction potentials; the dot is a time derivative such that  is the velocity and
is the velocity and  is the acceleration; T is the temperature, kB is Boltzmann's constant; and
is the acceleration; T is the temperature, kB is Boltzmann's constant; and  is a delta-correlated stationary Gaussian process with zero-mean, satisfying
is a delta-correlated stationary Gaussian process with zero-mean, satisfying
In Brownian dynamics, no acceleration is assumed to take place. Thus, the  term is neglected, and the sum of these terms is zero.
term is neglected, and the sum of these terms is zero.
Defining 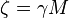 , and using the Einstein relation,
, and using the Einstein relation, 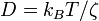 , it is often convenient to write the equation as,
, it is often convenient to write the equation as,