Bronopol
| Bronopol | |
|---|---|
 | |
 | |
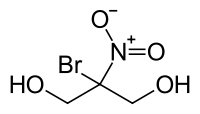
| IUPAC name 2-bromo-2-nitropropane-1,3-diol | |
| Identifiers | |
| CAS number | 52-51-7 |
| ChemSpider | 2356 |
| UNII | 6PU1E16C9W |
| KEGG | D01577 |
| ATCvet code | QD01 |
| Jmol-3D images | {{#if:[O-][N+](=O)C(Br)(CO)CO|Image 1 |
| |
| |
| Properties | |
| Molecular formula | C3H6BrNO4 |
| Molar mass | 199.989 g/mol |
| Appearance | white |
| Melting point | 130 °C |
| Boiling point | 140 °C (decomposes) |
| Except where noted otherwise, data are given for materials in their standard state (at 25 °C (77 °F), 100 kPa) | |
| Infobox references | |
Bronopol (INN) is an organic compound that is used as an antimicrobial. It is a white solid although commercial samples appear yellow.
Bronopol was invented by The Boots Company PLC in the early 1960s and first applications were as a preservative for pharmaceuticals. Owing to its low mammalian toxicity (at in-use levels) and high activity against bacteria (especially the troublesome Gram-negative species), bronopol became popular as a preservative in many consumer products such as shampoos and cosmetics. It was subsequently adopted as an antimicrobial in other industrial environments such as paper mills, oil exploration and production facilities, as well as cooling water disinfection plants. It is used at concentrations of 0.0025% (25 parts per million).
Production
Bronopol is produced by the bromination of di(hydroxymethyl)nitromethane, which is derived from nitromethane.[1]World production increased from the tens of tonnes in the late 1970s to current estimates in excess of 5,000 tonnes. Manufacturing today is the business of low cost producers, mainly in China.
Applications
Bronopol is used in consumer products as an effective preservative agent, as well as a wide variety of industrial applications (almost any industrial water system is a potential environment for bacterial growth, leading to slime and corrosion problems - in many of these systems Bronopol can be a highly effective treatment).
The use of Bronopol in personal care products (cosmetics, toiletries) has declined since the late 1980s due to the potential formation of nitrosamines.
Nitrosamine problem
Although ubiquitous in our diet and the environment, and even produced within the stomach from various foodstuffs, many nitrosamines are known or suspect carcinogens and therefore should be avoided in manufactured goods. Nitrosamines are relatively easily produced from secondary amines and amides in the presence of nitrite ions (this is why they are formed in-vivo from foodstuffs).
While Bronopol is not in itself a nitrosating agent, under conditions where it decomposes (alkaline solution and/or elevated temperatures) it can liberate nitrite and low levels of formaldehyde and these decomposition products can react with any contaminant secondary amines or amides in a personal care formulation to produce significant levels of nitrosamines (due to the toxicity of thes substances, the term 'significant' means levels as low as 10s of parts per billion).
Manufacturers of personal care products are therefore instructed by regulatory authorities to 'avoid the formation of nitrosamines' which might mean removing amines or amides from the formulation, removing Bronopol from a formulation, or using nitrosamine inhibitors.
This ingredient has been restricted for use in cosmetics in Canada.[2]
Physical and chemical properties
Appearance
Bronopol is supplied as crystals or crystalline powder, which may vary from white to pale yellow in colour depending on the grade. The yellow colouration is due to chelation of iron during the manufacturing process.
Melting point
As a pure material, Bronopol has a melting point of about 130°C. However due to its polymorphic characteristics, Bronopol undergoes a lattice rearrangement at 100 to 105°C and this can often be wrongly interpreted as the melting point.
At temperatures above 140°C Bronopol decomposes exothermically releasing Hydrogen bromide and oxides of Nitrogen.
Solubility
Bronopol is readily soluble in water; the dissolution process is endothermic. Solutions containing up to 28% w/v are possible at ambient temperature.
Bronopol is poorly soluble in non-polar solvents but shows a high affinity for polar organic solvents.
| Solvent | %w/v |
|---|---|
| Water | 28 |
| Methanol | 89 |
| Ethanol | 56 |
| Isopropanol | 41 |
| Liquid Paraffin | <0.5 |
Partition coefficient
Study of the solubility data clearly shows that Bronopol has a high affinity for polar rather than non-polar environments. In two phase systems, Bronopol partitions preferentially into the polar (usually aqueous) phase.
| Solvent Combination | Partition Co-efficient |
|---|---|
| Hexanol/Water | 0.74 |
| Alkane|Liquid Paraffin/Water | 0.043 |
| Chloroform/Water | 0.068 |
Stability in aqueous solution
In aqueous solutions, Bronopol is most stable when the pH of the system is on the acid side of neutral. Temperature also has a significant effect on stability in alkaline systems.
Degradation
When conditions are such that Bronopol decomposes in aqueous solution, very low levels of formaldehyde are produced. Liberated formaldehyde is not responsible for the biological activity associated with Bronopol.
Amongst other decomposition products detected after Bronopol breakdown are, bromide ion, nitrite ion, Bromonitroethanol and 2-Hydroxymethyl-2-nitropropane-1,3-diol.
See also
References
- ↑ Sheldon B. Markofsky "Nitro Compounds, Aliphatic" in Ullmann's Encyclopedia of Industrial Chemistry, 2012, Wiley-VCH, Weinheim. doi:10.1002/14356007.a17_401.pub2
- ↑ http://www.goodguide.com/ingredients/50954-bromo-nitropropane-diol