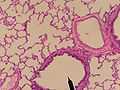
Bronchiole
| Bronchiole | |
|---|---|
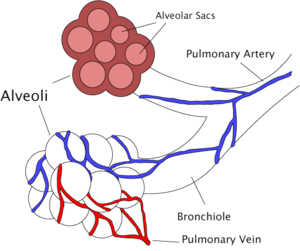 | |
| Diagram of the alveoli with both cross-section and external view. | |
| Latin | Bronchioli |
| Gray's | subject #240 1098 |
| Code | TH H3.05.02.0.00005 |
The bronchioles or bronchioli are the passageways by which the air passes through the nose or mouth to the air sacs of the lungs in which branches no longer contain cartilage or glands in their submucosa. They are branches of the bronchi. The bronchioles terminate by entering the circular sacs called alveoli.
Structure
A pulmonary lobule is the portion of the lung ventilated by one bronchiole. Bronchioles are approximately 1mm or less in diameter and their walls consist of ciliated cuboidal epithelium and a layer of smooth muscle. Bronchioles divide into even smaller terminal bronchioles that are 0.5mm or less in diameter. Terminal bronchioles in turn divide into respiratory bronchioles which divide into alveolar ducts. Terminal bronchioles mark the end of the conducting division of air flow in the respiratory system while respiratory bronchioles are the beginning of the respiratory division where actual gas exchange takes place.
The diameter of the bronchioles plays an important role in air flow. The bronchioles change diameter to either increase or reduce air flow. An increase in diameter is called bronchodilation and is stimulated by either epinephrine or sympathetic nerves to increase air flow. A decrease in diameter is called bronchoconstriction and is stimulated by histamine, parasympathetic nerves, cold air, chemical irritants and other factors to decrease air flow.
Primary bronchioles
The primary bronchioles arise from the tertiary bronchi. They are histologically distinct from the tertiary bronchi in that their walls do not have hyaline cartilage and they have club cells in their epithelial lining. The epithelium starts as a simple ciliated columnar epithelium and changes to simple ciliated cuboidal epithelium as the primary bronchiole decreases in size. The diameter of the primary bronchioles is often said to be less than 1 mm, though this value can actually range from 5 mm to 0.3 mm. As stated, these bronchioles do not have hyaline cartilage to maintain their patency. Instead, they rely on elastic fibers attached to the surrounding lung tissue for support. The inner lining (lamina propria) of these bronchioles is thin with no glands present, and is surrounded by a layer of smooth muscle. As the primary bronchioles get smaller they divide into terminal bronchioles.
Pathology
Bronchospasm, a potentially life-threatening situation, occurs when the smooth muscular tissue of the bronchioles constricts, severely narrowing their diameter. The most common cause of this is asthma. Bronchospasm is commonly treated by oxygen therapy and bronchodilators.
The medical condition of inflammation of the bronchioles is termed bronchiolitis. Diseases of the bronchioles include asthma, bronchiolitis obliterans, respiratory syncytial virus infections, and influenza.
Additional images
-
Cross sectional cut of primary bronchiole
-

Bronchi, bronchial tree, and lungs
-

1. Trachea
2. Mainstem bronchus
3. Lobar bronchus
4. Segmental bronchus
5. Bronchiole
6. Alveolar duct
7. Alveolus
References
1.Saladin, Kenneth S. Anatomy & Physiology: the Unity of Form and Function. New York, NY: McGraw-Hill, 2007.
- Dudek, Ronald W. High-Yield Histology, 3rd ed. (2004). ISBN 0-7817-4763-5
- Gartner, Leslie P. and James L. Hiatt. Color Atlas of Histology, 3rd ed. (2000). ISBN 0-7817-3509-2
- Gartner, Leslie P. and James L. Hiatt. Color Textbook of Histology (2001). ISBN 0-7216-8806-3