Bromoacetic acid
From Wikipedia, the free encyclopedia
| Bromoacetic acid | |
|---|---|
 |
 |
| IUPAC name 2-bromoacetic acid | |
| Other names Bromoethanoic acid, α-Bromoacetic acid, Monobromoacetic acid, Carboxymethyl bromide, UN 1938 | |
| Identifiers | |
| CAS number | 79-08-3 |
| PubChem | 6227 |
| ChemSpider | 10301338 |
| EC number | 201-175-8 |
| ChEMBL | CHEMBL60851 |
| RTECS number | AF5950000 |
| Beilstein Reference | 506167 |
| Jmol-3D images | Image 1 |
| |
| |
| Properties | |
| Molecular formula | C2H3BrO2 |
| Molar mass | 138.95 g mol−1 |
| Appearance | White to light yellow crystalline solid |
| Density | 1.934 g/mL |
| Melting point | 49 - 51 °C |
| Boiling point | 206 - 208 °C |
| Solubility in water | polar organic solvents |
| Acidity (pKa) | 2.86[1] |
| Refractive index (nD) | 1.4804 (50 °C, D) |
| Structure | |
| Crystal structure | Hexagonal or orthorhombic |
| Hazards | |
| R-phrases | R23/24/25, R36 |
| S-phrases | S36/37/39, S45 |
| Main hazards | Toxic (T), Corrosive (C) |
| NFPA 704 |
 1
3
0
|
| Flash point | 110 °C; 230 °F; 383 K |
| Except where noted otherwise, data are given for materials in their standard state (at 25 °C (77 °F), 100 kPa) | |
| Infobox references | |
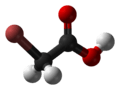
Bromoacetic acid is the chemical compound with the formula CH2BrCO2H. This colorless solid is a relatively strong alkylating agent. Bromoacetic acid and its esters are widely used building blocks in organic synthesis, for example in pharmaceutical chemistry.
The compound is prepared by bromination of acetic acid.[2]
- CH3COOH + Br2 → CH2BrCOOH + HBr
It can also be prepared by the Hell-Volhard-Zelinsky process:
- CH3COOH + Br2 + Red Phosphorus → CH2BrCOOH
See also
References
- ↑ Dippy, J.F.J., Hughes, S.R.C., Rozanski, A., J. Chem Soc., 1959, 2492.
- ↑ Natelson, S.; Gottfried, S. (1955), "Ethyl Bromoacetate", Org. Synth.; Coll. Vol. 3: 381
External links
This article is issued from Wikipedia. The text is available under the Creative Commons Attribution/Share Alike; additional terms may apply for the media files.