Brin-class submarine
From Wikipedia, the free encyclopedia
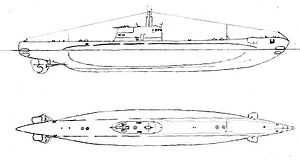 Archimede in Bordeaux | |
| Class overview | |
|---|---|
| Name: | Brin-class submarines |
| Builders: | Tosi |
| Operators: |
|
| Preceded by: | Marcello-class submarine |
| Completed: | 5 |
| Lost: | 4 |
| General characteristics | |
| Type: | Submarine |
| Displacement: |
1,016 tons (surfaced) 1,266t (submerged) |
| Length: | 72.5m |
| Beam: | 6.7m |
| Draught: | 4.5m |
| Propulsion: |
(surfaced/submerged) diesel / electric , 2 shafts 3,200 hp / 1,200 hp |
| Speed: | 17 / 8 knots (surfaced/submerged) |
| Range: | 18,000nm at 10 kts |
| Complement: | 58 |
| Armament: |
1 x 120mm gun 4 x 13.2mm anti-aircraft 8 x 21" torpedo tubes (4 bow, 4 stern) 14 torpedoes |
The Brin-class submarines were five Italian submarines that served in the Regia Marina during World War II. All ships were built by Tosi. Two boats were replacements for Archimede-class submarines secretly transferred to the Nationalists during the Spanish Civil War in 1937. The class were partially double hulled. The deck gun was initially mounted in the conning tower (to enable surface action during Indian ocean Monsoon). The gun was re-sited on the forward deck later in the war in surviving boats and the large conning tower was re-built to a smaller design.
Ships
| Ship | Namesake | Launched | Fate |
|---|---|---|---|
| Brin | Benedetto Brin | 3 April 1938 | Surrendered to the Allies in 1943, discarded Feb 1948 |
| Galvani | Luigi Galvani | 22 May 1938 | Sunk by British sloop HMS Falmouth near Persian Gulf 26 June 1940 |
| Guglielmotti | 5 March 1939 | Sank the Greek cargo ship Atlas in the Red Sea on 6 September 1940. Torpedoed by HMS Unbeaten 17 March 1942 | |
| Archimede | Archimedes | 5 March 1939 | Escaped from East Africa in 1941 to Bordeaux, Sunk by US Navy Catalina flying boat off Brazil 16 March 1943 |
| Torricelli | Evangelista Torricelli | 26 March 1939 | Sunk in the Red Sea, 23 June 1940 by British destroyers HMS Kandahar, HMS Khartoum, HMS Kingston and sloop HMS Shoreham, The submarine was commanded by Salvatore Pelosi |
See also
References
Ireland, Bernard (1996). Warships of World War II. Glasgow: Harper Collins & Jane's. pp. 74–75.
- Conway's All the World's Fighting Ships 1922-1947
| |||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
This article is issued from Wikipedia. The text is available under the Creative Commons Attribution/Share Alike; additional terms may apply for the media files.