Brigadier general
Brigadier general is a senior rank in the armed forces. It is the lowest ranking general officer in some countries, usually sitting between the ranks of colonel and major general. When appointed to a field command, a brigadier general is typically in command of a brigade consisting of around 4,000 troops (four battalions). In some countries a brigadier general is informally designated as a one-star general.
In some countries, this rank is given the name of brigadier, which is often considered to not be a general-officer rank, but is usually equivalent to brigadier general in the armies of nations that use the rank.
The rank can be traced back to the militaries of Europe where a brigadier general, or simply a brigadier, would command a brigade in the field. An alternative rank of "brigade general" was first used in the French revolutionary armies.
In the first quarter of the 20th century, British and Commonwealth armies used the rank of brigadier general as a temporary appointment, or as an honorary appointment on retirement; in the 1920s this practice changed to the use of brigadier, which was not classed as a general officer.
Brazil and a few other countries use major general as the equivalent of brigadier general. Some of these countries then use the rank of colonel general to make four general-officer ranks.[citation needed]
The naval equivalent is usually commodore.[1]
Insignia
Army insignia
-

Australian Army:
(until 1922)
Brigadier general -

Belgium:
Général de brigade /
Brigadegeneraal -

Canadian Forces:
Brigadier general /
Brigadier-général -

Colombia:
brigadier general -

Royal Danish Army:
Hæren -

Egyptian Armed Forces:
Brigadier General
(Arabic: عميد) -

Estonia:
Brigaadikindral -
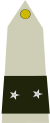
France:
général de brigade -

Germany:
Brigadegeneral Bundeswehr -

Greece:
Ταξίαρχος
(Taxiarchos) -

Hungary:
Dandártábornok -

Iran:
Sartip (Persian:سرتیپ)
Brigadier Gegenral -
.svg.png)
Italy:
Generale di brigata (Brigadiere generale) -

Macedonia:
бригаден генерал (brigaden general) -

Royal Netherlands Army:
Brigadegeneraal -

Portuguese Army:
Brigadeiro-general -

Romania:
General de brigadă -
Serbia:
Бригадни Генерал / Brigadni general -

U.S. Army:
Brigadier general
Air Force insignia
This gallery displays Air Force brigadier general insignia if they are different from the Army brigadier general insignia. (They usually are.)
Note that in many Commonwealth countries, the equivalent air force rank is Air Commodore (and in the Netherlands, it is simply Commodore).
-

Canada
-

Denmark:
Flyvevåbnet -

France:
Général de brigade aérienne -

Greece:
Ταξίαρχος -

Hungary:
Dandártábornok -

Italy:
Generale di Brigata Aerea -
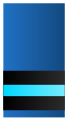
Royal Netherlands Air Force:
Commodore -

Poland
-
Romania:
General de flotilă aeriană -
Serbia:
Бригадни Генерал / Brigadni general -
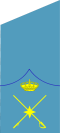
Spain
-

U.S. Air Force:
Brigadier General
Other insignia
-

French Gendarmerie: général de brigade
-

French Foreign Legion: général de brigade[1]
-

Germany
Cite error: There are <ref> tags on this page, but the references will not show without a {{reflist}} template (see the help page).
Brigadier general ranks by country
Argentina
The rank of brigadier general (with some local variations) is used in the Argentine Air Force. Unlike other armed forces of the World, the rank of brigadier general is actually the highest rank in the Air Force. This is due to the use of the rank of brigadier and its derivatives to designate all general officers in the Air Force: brigadier (lowest general officer); brigadier-major (middle); and brigadier-general (highest). The rank of brigadier general is reserved for the Chief General Staff of the Air Force, as well as the Chief of the Joint General Staff if he should be an Air Force officer.
The Argentine Army does not use the rank of brigadier-general, instead using brigade general ( Spanish: General de brigada ) which in turn is the lowest general officer before Divisional General ( Spanish: General de Division ) and Lieutenant General ( Spanish: Teniente General ). See also Argentine Army officer rank insignia.
Australia
In the Australian Imperial Force during World War I, the rank of brigadier general was always temporary and held only while the officer was posted to a particular task, typically the command of a brigade. When posted elsewhere, the rank would be relinquished and the former rank resumed. This policy prevented an accumulation of high-ranking general officers brought about by the relatively high turnover of brigade commanders. Brigadier general was also used as an honorary rank on retirement. The rank insignia was like that of the current major general, but without the star/pip[2] - example.
As in the United Kingdom, the rank was later replaced by brigadier. Hence, prior to 1922, a "brigadier general" was a "general officer"; subsequently, brigadiers were not "generals"; this is shown by the rank insignia being like that of a colonel, but with an extra (third) star/pip[2] - example.
(See also Australian Army officer rank insignia and List of Australian generals and brigadiers.)
Bangladesh
Prior to 2001, the Bangladesh Army rank was known as brigadier, in conformity with the rank structure of the Commonwealth Nations. In 2001 the Bangladesh Army introduced the rank of brigadier general, however "the grade stayed equivalent to brigadier".
It is the lowest ranking general officer, between the ranks of Colonel and Major General. Brigadier General is equivalent to commodore of the Bangladesh Navy and air commodore of the Bangladesh Air Force. It is still more popularly called brigadier (one-star general).
Belgium
The Belgian Army uses the rank of général de brigade (French) and brigadegeneraal (Dutch) (Brigade General). However, in this small military there are no permanent promotions to this rank, and it is only awarded as a temporary promotion to a full colonel who assumes a post requiring the rank, notably in an international context (e.g. as Military Attaché in a major embassy).
Brazil
General de Brigada (Brigade General) is the lowest rank amongst general officers of the Brazilian Army. A General de Brigada wears two stars as this is the entry level for general officers in the Brazilian Army. In the Brazilian Air Force, the two-star, three-star and four-star ranks are known as Brigadeiro (Brigadier), Major-Brigadeiro (Major-Brigadier) and Tenente-Brigadeiro-do-Ar (Lieutenant-Air-Brigadier) respectively. See Military ranks of Brazil and Brigadier#Officer rank in Latin America for more information.
Canada
In the Canadian Forces, the rank of brigadier-general (BGen) (brigadier-général or bgén in French) is an Army or Air Force rank equal to a commodore of the Navy. A brigadier-general is the lowest rank of General Officer. A brigadier-general is senior to a colonel or naval captain, and junior to a major-general or rear admiral.
The rank title "brigadier-general" is still used notwithstanding that brigades in the army are now commanded by colonels. Until the late 1990s brigades were commanded by brigadier-generals. In the air force context, brigadier-generals used to command air force "Groups" until these bodies were abolished in the late 1990s.
The rank insignia for a brigadier-general is a single gold maple leaf beneath crossed sword and baton, all surmounted by St. Edward's Crown, worn on the shoulder straps of the service dress jacket, and on slip-ons on other uniforms. The service dress jacket also features a wide strip of gold braid around the cuff. On the visor of the service cap are two rows of gold oak leaves; the air force wedge cap features gold braid on the edges of the ear flaps. The cap insignia for a general officer is a modified version of the Canadian Forces insignia; the collar insignia (Army generals only) is two crossed sabres. Some brigadier-generals, by nature of holding a branch-specific appointment, may continue to wear the insignia of their personnel branch; for example, the chaplain-general wears the general officer's cap insignia with the collar insignia of the Chaplain Branch,[3] while the surgeon-general continues to wear the cap and collar insignia of the Canadian Forces Medical Service.[4]
Brigadier-generals are initially addressed verbally as "General" and name; thereafter by subordinates as "Sir" or "Ma'am" in English or "mon général" in French. They are normally entitled to staff cars.
Note: Before unification in 1968 of the Royal Canadian Air Force, Canadian Army, and the Royal Canadian Navy, rank structure and insignia followed the British pattern. In army usage, the term "brigadier" was used to denote what is now known as a brigadier-general while the air force used the rank of Air Commodore.
China
Chinese rank of (Da-Xiao 大校) or Senior Colonel is a direct equivalent of a brigadier. It ranks above colonel (Shang-Xiao 上校) and below major general (Shao-Jiang 少将). A brigadier is commonly in command of a division (Shi 师) or a brigade (Lu 旅). Divisional commanders are seldom general officers.
Colombia
The rank of brigadier general is the first general officer rank in the Fuerzas Militares,[5] and the National Police.[6]
Denmark
Same as most NATO nations - first of general ranks - usually a brigade commander. Since Denmark is a NATO member (and as of this writing the NATO secretary general being the former Danish prime minister) Denmark has for many, many years been following NATO standards and adapting its rank system to closely relate.
Estonia
In the Estonian military, the rank is called Brigaadikindral.
France
France uses the rank of "brigade general" (général de brigade). It formerly used the historic rank, until 1793, of brigadier des armées ("brigadier of the armies"). The rank contrasts with the French sub-officer rank of brigadier. As with all French general officers, a French brigade general is titled "general" without any implication that he is an army general; for instance General Charles de Gaulle never rose higher than brigade general.
Until 1793, a rank of brigadier des armées ("brigadier of the armies") existed in the French Army, which could be described as a senior colonel or junior brigade commander. The normal brigade command rank was field marshal (maréchal de camp) (which elsewhere is a more senior rank). A "brigadier of the armies" wore one-star and a "field marshal" wore two stars. During the French Revolution, the revolutionaries' drive to rationalise the state led to a change in the system of ranks. The rank of "brigadier of the armies" was abolished and the normal brigade command rank, field marshal, was replaced by brigade general. The rank of brigade general inherited the two stars of the rank of field marshal, explaining the absence since 1793 of a French rank with only one star.
Nowadays, a French général de brigade generally commands a brigade, which is the biggest permanent formation in the French army. The rank can also be awarded in an honorary fashion to retiring colonels. The insignias are two stars, worn on the shoulder are at the sleeve of the uniform, depending on the dress. Two different kepis are issued : the service kepi sports the two stars, while the formal kepi features a large band of oak leaves (the kepi of a division general has two smaller such bands).
Charles de Gaulle held the rank of brigade general. He was given a temporary promotion to this rank in May 1940 as commander of the 4th Armoured Reserve Division (4ème division cuirassée de réserve). However his authority as head of the Free French really came from being the only cabinet member outside occupied France, not from his military rank. As a reminder of his war position, he refused any further promotion.
Germany
The equivalent modern German rank is Brigadegeneral. The concept of a brigadier general rank is relatively new, as prior to 1945 the lowest German general officer rank was Generalmajor, which was often considered equivalent to brigadier general in other armies.
Greece
Hungary
In Hungary the brigadier general is a relatively new military rank used from 1992. The army and the air force insignia are not different.
Indonesia
In Indonesia, brigadir jenderal (abbreviated as "brigjen") is the fourth highest rank and the lowest general rank both in Polri and TNI. The insignia is a gold star.
Iran
The equivalent rank for brigadier general in the Iranian army and air force is called sar-tip. In Persian the word tip means brigade, and sar means head or commander. After 1987 the rank sar-tip dovom (second brigadier general) was introduced between sar-tip and sar-hang (colonel or literally head of regiment). There is no equivalent for sar-tip dovom in other countries. The rank above sar-tip is sar-lashkar. Lashkar means division so, sar-lashkar means divisional general (major general).
The Iranian Revolutionary Guards also use this rank; the difference is in salutation. One refers an army or air force brigadier general as "amir sar-tip", while a revolutionary guard general is referred to as "sardar sar-tip".
Major general is the highest Iranian military rank, and therefore brigadier general is considered to be second highest rank. It is equivalent to the rank of the commander of the air force, and commodore of the Navy.
Ireland
The country is divided into two areas for administrative and operational reasons, and in each area there is an infantry Brigade. The two brigade group structure envisages distinct operational areas of responsibility for each of the brigades and is supported in its responsibilities by the Naval Service and Air Corps. Each of the Brigade formations and the Air Corps are commanded by a Brigadier General while the Naval Service is commanded by a Commodore. See also Brigade Commanders.
Israel
In the Israel Defense Forces, the rank of brigadier general is called tat aluf and is the third highest rank, below aluf (major general) and rav aluf (lieutenant general or general), and above aluf mishne (colonel).
Jordan
In the Jordanian military, the rank of brigadier general is known as amid, and it is higher than colonel (akeed) and lower than major general (liwa).
South Korea
The rank of brigadier general is known in South Korea as junjang (Korean: 준장; hanja: 准將)[7] and is a direct equivalent to the United States one-star rank, with very similar insignia. The military of North Korea does not technically maintain a brigadier general rank, but the rank of senior colonel (대좌, taejwa) which is above colonel (상좌, sangjwa) and below major general (소장, Sojang) is the effective equivalent.
Burma (Myanmar)
The rank of brigadier general is known in Burma as bo mhu gyoke and is often the deputy commander of one of Burma's Regional Military Commands, commander of the light infantry division (LID) or Military Operation Commands. In civil service, a brigadier general often holds the office of deputy minister or director general of certain ministries.
Mexico
In Mexico, brigade general is the rank below divisional general and, confusingly, the rank above brigadier general. A Mexican brigade general wears as rank insignia the arms of Mexico above two stars. (A Mexican brigadier general wears the arms of Mexico above one star.)
Poland
Prior to 2002, the Polish rank of generał brygady was equivalent to both the ranks of major general and brigadier general.
Portugal
In the Portuguese Army and Air Force, brigadeiro-general is a temporary general rank for the colonels that have to exercise a special command. It is the equivalent of the commodore rank in the Portuguese Navy.
The rank was reintroduced in 1999. Before that, simply as brigadeiro, it existed from 1707 to 1864 and again from 1929 to 1947, not being considered a general rank. From 1947 to 1999, brigadeiro become the two-star general rank in the Portuguese Army. As two-star rank, it was substituted by the rank of major-general in 1999.
Spain
In the Spanish Army and Spanish Air Force, general de brigada is the lowest rank of general officers. Its equivalent in the Navy is contraalmirante.
Sweden
In the Swedish Army and Swedish Air Force, brigadgeneral is the lowest rank of general officers. Its equivalent in the Navy is flottiljamiral.
Turkey
In the Turkish Army and the Turkish Air Force, the equivalent rank is tuğgeneral (the Turkish Navy equivalent would be tuğamiral). The name is derived from tugay, the Turkish word for a brigade. Both tugay and tuğ- as military terms may owe their origins to the older Turkish word tuğ, meaning horsetail, which was used as a symbol of authority and rank in Ottoman and pre-Ottoman times.
United Kingdom
-2.png)
Brigadier-general was formerly a rank or appointment in the British Army and Royal Marines, and briefly in the Royal Air Force. It first appeared in the army in the reign of James II,[8] but did not exist in the Royal Marines until 1913.[9] In the 1740s, the substantive rank of brigadier-general was suppressed,[10] and thereafter brigadier-general was a temporary appointment only, bestowed on a colonel or lieutenant-colonel (or on a colonel commandant in the Royal Marines) for the duration of a specific command.
The appointment was abolished in both the Army and the Marines in 1922, being replaced in the Army by the appointments of colonel-commandant (which already existed as a rank in the Marines) and colonel on the staff. Colonel-commandant was in turn replaced by the appointment of brigadier in the Army in 1928, and later, at some time between World War II and 1957, in the Marines.[11][12] From the formation of the Royal Air Force on 1 April 1918 until 31 July 1919, it used the appointment of brigadier-general. This was superseded by the rank of air commodore on the following day.
The rank insignia for appointment of the brigadier-general was a crossed sword and baton; the insignia for higher grades of general consist of this device, with the addition of a star (major general), crown (lieutenant general), or both ("full" general). The equivalent naval appointment was commodore.
Brigadier is the highest field officer rank (hence the absence of the word "general"), whereas brigadier-general was the lowest general officer "rank". However, the two ranks are considered equal.
United States
In the United States Army, United States Air Force and United States Marine Corps, a brigadier general is a one-star general officer. It is equivalent to the rank of rear admiral (lower half) in the other uniformed services.
See also
- British Army officer rank insignia
- Comparative military ranks
- History of Russian military ranks
- Military unit
- NATO Air Force officers
- NATO Army officers
- U.S. Army officer rank insignia
- United Kingdom and United States military ranks compared
- Wiktionary definition of General.
References and notes
- ↑ In the U.S., the rank of commodore has been redesignated as rear admiral (lower half).
- ↑ 2.0 2.1 Australian Army rank insignia for 2LT, LT, CAPT, LTCOL, COL, BRIG, MAJGEN and GEN use the Order of the Bath star, which is commonly referred to as a "pip".
- ↑ "Layout 1" (PDF). Retrieved 2010-06-19.
- ↑ "Canadian Surgeon General". Forces.gc.ca. 2008-07-17. Retrieved 2010-06-19.
- ↑ Decreto 1428 de 2007
- ↑ DECRETO 1791 DE 2000 (septiembre 14)
- ↑ (Korean) Empas hanja dictionary, Junjang entry
- ↑ John J. McGrath; Combat Studies Institute (U.S.) (2009). The Brigade: A History, Its Organization and Employment in the US Army. DIANE Publishing. ISBN 1-4289-1022-0. Retrieved 2010-06-19.
- ↑ Senior RM Officers - Promotion, London Gazette
- ↑ Beatson, Robert (1788). A Political Index to the Histories of Great Britain and Ireland: Or, A Complete Register of the Hereditary Honours, Public Offices, and Persons in Office, from the Earliest Periods to the Present Time. G. G. J. & J. Robinson. p. 387.
- ↑ "World War II RN Pay Tables". Retrieved 2010-06-19.
- ↑ Scribbles (April 1956). "Pay and Allowances of Officers - RN, RM, WRNS, QARNNS and VAD". Pbenyon.plus.com. Retrieved 2010-06-19.


