Bregma
| Bregma | |
|---|---|
 | |
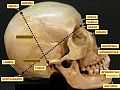
Superior view of the calvarium, bregma located at the intersection of the coronal and sagittal sutures.
(Lambda also visible at the intersection of the lambdoid suture by the sagittal suture.) | |
| Gray's | subject #32 135 |
The bregma is the anatomical point on the skull at which the coronal suture is intersected perpendicularly by the sagittal suture.
Location
The bregma is located at the intersection of the coronal suture and the sagittal suture on the superior middle portion of the calvaria. It is the point where the frontal bone and parietal bones meet.
Development
The bregma is known as the anterior fontanelle during infancy. The anterior fontanelle is membranous and closes within 4–26 months of life.
Clinical Significance
In the congenital disorder cleidocranial dysostosis, the anterior fontanelle never closes to form the bregma.
The bregma is often used as a reference point for stereotactic surgery of the brain.
Also, examination of an infant includes palpating the anterior fontanelle. A sunken fontanelle indicates dehydration, whereas a very tense or bulging anterior fontanelle indicates raised intracranial pressure.
Etymology
Bregma comes from the Greek bregma, meaning top of the head. [1]
References
- ↑ Liddell & Scott, Greek-English Lexicon
This article incorporates text from a public domain edition of Gray's Anatomy.
Additional Images
-
The bregma.Human skull.
External links
- lesson1 at The Anatomy Lesson by Wesley Norman (Georgetown University)
| ||||||||||||||||