Brazzein
| Brazzein | |
|---|---|
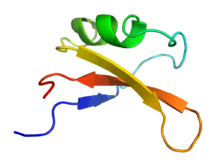 Solution NMR structure of the brazzein protein.[1] | |
| Identifiers | |
| Symbol | MONA_DIOCU |
| PDB | 1BRZ (RCSB PDB PDBe PDBj) More structures |
| UniProt | P56552 |
Brazzein is a sweet-tasting protein extracted from the West African fruit of the climbing plant Oubli (Pentadiplandra brazzeana Baillon). It was first isolated as an enzyme by University of Wisconsin–Madison in 1994.[2]
Brazzein is found in the extracellular region. It is found in the pulp tissue surrounding the seeds.
With pentadin, discovered in 1989, brazzein is the second sweet-tasting protein discovered in this African fruit.[3]
Like the other natural sweet-proteins such as monellin and thaumatin, it is highly sweet.[4]
Traditional use
The plant grows in Gabon and Cameroon, where the fruit has been consumed by the apes and local people for a long time. The berries of the plant are incredibly sweet. African locals call them "Oubli" (French for "forgot") in their vernacular language because their taste helps nursing infants forget their mother's milk,[5] as once they eat them they are said to forget to come back to the village to see their mother.[6]
Protein structure
The monomer protein, consisting of 54 amino acid residues, is the smallest of the sweet proteins with a molecular weigh of 6.5 kDa.[2] The amino acid sequence of brazzein, adapted from the Swiss-Prot biological database of protein, is as follows: QDKCKKVYEN YPVSKCQLAN QCNYDCKLDK HARSGECFYD EKRNLQCICD YCEY[7]
The structure of brazzein was determined by proton nuclear magnetic resonance (NMR) at a pH 5.2 and 22 degrees C.. Brazzein has four evenly spaced disulfide bonds and no sulfhydryl groups.
3D analysis of brazzein showed one alpha-helix and three strands of anti-parallel beta sheet. It is not similar to either of the other two sweet-tasting proteins, monellin and thaumatin.[8]
However, a recent 3D study shows that these three proteins possess similar "sweet fingers" believed to elicit the sweet taste.[9]
Residues 29–33 and 39–43, plus residue 36, as well as the C-terminus were found to be involved in the sweet tasting of the protein. The charge of the protein plays also an important role in its interaction with the sweet taste receptor.[2]
Based on this knowledge a synthesised improved brazzein, called pGlu-1-brazzein, was reported to be twice sweet as the natural counterpart.[10]
Sweetness properties
On weight basis, brazzein is 500 to 2000 times sweeter than sugar, compared to 10% sugar and 2% sugar solution respectively.[8]
Its sweet perception is more similar to sucrose than that of thaumatin with a clean sweet taste with lingering aftertaste and with a slight delay longer than aspartame in an equi-sweet solution.[11]
Brazzein is stable over a broad pH range from 2.5 to 8[12] and heat stable at 98°C for 2 hours.[2]
As a sweetener
Brazzein represents an alternative to available low calorie sweeteners. As a protein it is safe for diabetics and very soluble in water (>50 mg/mL).[12]
When blended with other sweeteners, sweeteners such as aspartame and stevia, brazzein reduces side aftertaste and complements their flavor.[13]
Unlike other natural sweeteners, apart from thaumatin, its sweet profile is closer to sucrose. Unlike other sweet-tasting proteins, it can withstand heat which makes it suitable for industrial food manufacture.[14]
Increasing interest of brazzein makes it difficult to source naturally from Gabon, but it can also be synthesised by a solid-phase method.[8] Recombinant proteins were successfully produced via E. coli.[15]
The Texas companies Prodigene and Nectar Worldwide were among the licensees to use Wisconsin Alumni Research Foundation patents on brazzein, and genetically engineer the enzyme into maize. Brazzein then can be commercially extracted from maize through ordinary milling. Approximately one ton of maize yields 1-2 kilograms of Brazzein. It can also be engineered into plants like wheat to make pre-sweetened grains, e.g. for cereals.[14]
Natur Research Ingredients intends to market brazzein under the Cweet (1000x) and (3000x) brands by 2009.[16][17]
Brazzein controversy
Despite the fact that the sweet taste of the berries was well known in West Africa, the University claims that the sweet compound (brazzein) is its own invention and admit to no connection with the Gabon.[18]
This fact, which involved appropriation of legal rights by means of patents over indigenous biomedical knowledge without compensation to the indigenous groups, is considered an act of Biopiracy by GRAIN and Green Peace.[19]
See also
References
- ↑ PDB 2brz; Caldwell JE, Abildgaard F, Dzakula Z, Ming D, Hellekant G, Markley JL (June 1998). "Solution structure of the thermostable sweet-tasting protein brazzein". Nat. Struct. Biol. 5 (6): 427–31. doi:10.1038/nsb0698-427. PMID 9628478.
- ↑ 2.0 2.1 2.2 2.3 Ming D, Hellekant G (November 1994). "Brazzein, a new high-potency thermostable sweet protein from Pentadiplandra brazzeana B". FEBS Lett. 355 (1): 106–8. doi:10.1016/0014-5793(94)01184-2. PMID 7957951.
- ↑ van der Wel H, Larson G, Hladik A, Hladik CM, Hellekant G, Glaser D (1989). "Isolation and characterization of pentadin, the sweet principle of Pentadiplandra brazzeana Baillon". Chem. Senses 14 (1): 75–79. doi:10.1093/chemse/14.1.75.
- ↑ Faus I, Sisniega H (2004). "Sweet-tasting Proteins". In Hofrichter M, Steinbüchel A. Biopolymers: Polyamides and Complex Proteinaceous Materials II (8 ed.). Weinheim: Wiley-VCH. pp. 203–209. ISBN 3-527-30223-9.
- ↑ Stein J (2002-11-04). "UW–Madison professor makes a sweet discovery". Wisconsin State Journal.
- ↑ Hladik CM, Hladik A (1988). "Sucres et "faux sucres" de la forêt équatoriale : évolution et perception des produits sucrés par les populations forestières d'Afrique". Journal d'Agriculture Tropicale et de Botanique Appliquée (FRA) 35: 51–66.
- ↑ UniProtKB/Swiss-Prot database entry #PP56552
- ↑ 8.0 8.1 8.2 Izawa H, Ota M, Kohmura M, Ariyoshi Y (July 1996). "Synthesis and characterization of the sweet protein brazzein". Biopolymers 39 (1): 95–101. doi:10.1002/(SICI)1097-0282(199607)39:1<95::AID-BIP10>3.0.CO;2-B. PMID 8924630.
- ↑ Tancredi T, Pastore A, Salvadori S, Esposito V, Temussi PA (June 2004). "Interaction of sweet proteins with their receptor. A conformational study of peptides corresponding to loops of brazzein, monellin and thaumatin". Eur. J. Biochem. 271 (11): 2231–40. doi:10.1111/j.1432-1033.2004.04154.x. PMID 15153113.
- ↑ Assadi-Porter FM, Aceti DJ, Markley JL (April 2000). "Sweetness determinant sites of brazzein, a small, heat-stable, sweet-tasting protein". Arch. Biochem. Biophys. 376 (2): 259–65. doi:10.1006/abbi.2000.1726. PMID 10775411.
- ↑ Pfeiffer JF, Boulton RB, Noble AC (2000). "Modelling the sweetness response using time-intensity data". Food Quality and Preference 11 (1): 129–138. doi:10.1016/S0950-3293(99)00036-1.
- ↑ 12.0 12.1 Birch, Gordon Gerard (2000). Ingredients Handbook - Sweeteners (Ingredients Handbook Series). Leatherhead Food Research Association. ISBN 0-905748-90-5.
- ↑ Hellekant G, Danilova V (2005). "Brazzein a Small, Sweet Protein: Discovery and Physiological Overview". Chem. Senses 30 (Supplement 1): i88–i89. doi:10.1093/chemse/bjh127. PMID 15738210.
- ↑ 14.0 14.1 US patent 5326580, Hellekant BG, Ming D, "Brazzein sweetener", issued 1994-07-05
- ↑ Assadi-Porter FM, Aceti DJ, Cheng H, Markley JL (April 2000). "Efficient production of recombinant brazzein, a small, heat-stable, sweet-tasting protein of plant origin". Arch. Biochem. Biophys. 376 (2): 252–8. doi:10.1006/abbi.2000.1725. PMID 10775410.
- ↑ Halliday J (2008-06-27). "Natural sweetener race hots up with Nutrinova break-through". www.foodnavigator.com. Retrieved 2008-11-18.
- ↑ Hills S (2008-06-24). "New sweetener to hit market hungry for alternatives". www.foodnavigator.com. Retrieved 2008-11-18.
- ↑ Select Committee on Environmental Audit (1999-11-25). "Trade Related Intellectual Property Rights (TRIPs) and Farmers' Rights". House of Commons, www.parliament.uk. Retrieved 2008-09-13.
- ↑ "The European Patent Directive: License to Plunder". Genetic Resources Action International (GRAIN). 1998-05-01. Retrieved 2008-09-13.