Bracket polynomial
In the mathematical field of knot theory, the bracket polynomial (also known as the Kauffman bracket) is a polynomial invariant of framed links. Although it is not an invariant of knots or links (as it is not invariant under type I Reidemeister moves), a suitably "normalized" version yields the famous knot invariant called the Jones polynomial. The bracket polynomial plays an important role in unifying the Jones polynomial with other quantum invariants. In particular, Kauffman's interpretation of the Jones polynomial allows generalization to invariants of 3-manifolds.
The bracket polynomial was discovered by Louis Kauffman in 1987.
Definition
The bracket polynomial of any (unoriented) link diagram L, denoted <L>, is a polynomial in the variable 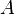 , characterized by the three rules:
, characterized by the three rules:
- <O> = 1, where O is the standard diagram of the unknot
-

-

The pictures in the second rule represent brackets of the link diagrams which differ inside a disc as shown but are identical outside. The third rule means that adding a circle disjoint from the rest of the diagram multiplies the bracket of the remaining diagram by -A2 - A-2.
Further reading
- Louis H. Kauffman, State models and the Jones polynomial. Topology 26 (1987), no. 3, 395--407. (introduces the bracket polynomial)
External links
| |||||||||||||||||||||||