Bongkrek acid
| Bongkrek acid | |
|---|---|
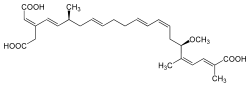 | |
| IUPAC name 20-Carboxymethyl-6-methoxy-2,5,17-trimethyldocosa-2,4,8,10,14,18,20-heptaenedioic acid | |
| Other names Bongkrekic acid | |
| Identifiers | |
| CAS number | 11076-19-0 |
| PubChem | 25463 (6R,17S) |
| ChemSpider | 4938689 (2E,4E,8E,10E,14E,18E,20E) |
| MeSH | Bongkrekic+acid |
| Jmol-3D images | {{#if:COC(CC=CC=CCCC=CCC(C)C=CC(CC(O)=O)=CC(O)=O)C(C)=CC=C(C)C(O)=OO=C(O)\C(=C\C=C(\C)[C@H](OC)C/C=C\C=C\CC/C=C/C[C@@H](/C=C/C(=C\C(=O)O)CC(=O)O)C)C|Image 1 Image 2 |
| |
| |
| Properties | |
| Molecular formula | C28H38O7 |
| Molar mass | 486.60 g mol−1 |
| Melting point | 50-60 °C |
| Except where noted otherwise, data are given for materials in their standard state (at 25 °C (77 °F), 100 kPa) | |
| Infobox references | |
Bongkrek acid is a respiratory toxin more deadly than other mitochondrial poisons cyanide or 2,4-dinitrophenol.[1] There was some dispute regarding the actual structure of bongkrek acid (also known as bongkrekic acid[2]) but this was resolved in 1973, which explains different structures appearing in the literature prior to this date.[3]
It is produced in fermented coconut contaminated by the bacterium Burkholderia gladioli pathovar cocovenenans. In particular, it has been implicated in deaths resulting from eating the soybean and coconut-based product known as tempe bongkrèk,[citation needed] which is banned in Indonesia.[citation needed]
It is highly toxic because of its effect on the ATP/ADP translocation mechanism. It shuts this system down, preventing ATP from leaving the mitochondria and providing energy to the rest of the cell.[citation needed]
References
- ↑ Henderson, P. J. F.; Lardy, H. A. (1970). "Bongkrekic Acid: An Inhibitor of Adenine Nucleotide Translocase of Mitochondria" (pdf). Journal of Biological Chemistry 245 (6): 1319–1326. PMID 4245638.
- ↑ Garcia, R. A.; Hotchkiss, J. H.; Steinkraus, K. H. (1999). "The Effect of Lipids on Bongkrekic (Bongkrek) Acid Toxin Production by Burkholderia cocovenenans in Coconut Media". Food Additives and Contaminants 16 (2): 63–69. doi:10.1080/026520399284217. PMID 10435074.
- ↑ De Bruijn, J.; Frost, D. J.; Nugteren, D. H.; Gaudemer, A.; Lijmbach, G. W. M.; Cox, H. C.; Berends, W. (1973). "Structure of Bongkrekic Acid". Tetrahedron 29 (11): 1541–1547. doi:10.1016/S0040-4020(01)83395-0.