Bogacki–Shampine method
The Bogacki–Shampine method is a method for the numerical solution of ordinary differential equations, that was proposed by Przemyslaw Bogacki and Lawrence F. Shampine in 1989 (Bogacki & Shampine 1989). The Bogacki–Shampine method is a Runge–Kutta method of order three with four stages with the First Same As Last (FSAL) property, so that it uses approximately three function evaluations per step. It has an embedded second-order method which can be used to implement adaptive step size. The Bogacki–Shampine method is implemented in the ode23 function in MATLAB (Shampine & Reichelt 1997).
Low-order methods are more suitable than higher-order methods like the Dormand–Prince method of order five, if only a crude approximation to the solution is required. Bogacki and Shampine argue that their method outperforms other third-order methods with an embedded method of order two.
The Butcher tableau for the Bogacki–Shampine method is:
| 0 | |||||
| 1/2 | 1/2 | ||||
| 3/4 | 0 | 3/4 | |||
| 1 | 2/9 | 1/3 | 4/9 | ||
| 2/9 | 1/3 | 4/9 | 0 | ||
| 7/24 | 1/4 | 1/3 | 1/8 |
Following the standard notation, the differential equation to be solved is 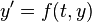 . Furthermore,
. Furthermore,  denotes the numerical solution at time
denotes the numerical solution at time  and
and  is the step size, defined by
is the step size, defined by  . Then, one step of the Bogacki–Shampine method is given by:
. Then, one step of the Bogacki–Shampine method is given by:
Here, 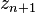 is a second-order approximation to the exact solution. The method for calculating
is a second-order approximation to the exact solution. The method for calculating 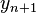 is due to Ralston (1965). On the other hand,
is due to Ralston (1965). On the other hand, 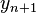 is a third-order approximation, so the difference between
is a third-order approximation, so the difference between 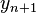 and
and 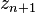 can be used to adapt the step size. The FSAL—first same as last—property is that the stage value
can be used to adapt the step size. The FSAL—first same as last—property is that the stage value 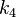 in one step equals
in one step equals 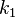 in the next step; thus, only three function evaluations are needed per step.
in the next step; thus, only three function evaluations are needed per step.
References
- Bogacki, Przemyslaw; Shampine, Lawrence F. (1989), "A 3(2) pair of Runge–Kutta formulas", Applied Mathematics Letters 2 (4): 321–325, doi:10.1016/0893-9659(89)90079-7, ISSN 0893-9659.
- Ralston, Anthony (1965), A First Course in Numerical Analysis, New York: McGraw-Hill.
- Shampine, Lawrence F.; Reichelt, Mark W. (1997), "The Matlab ODE Suite", SIAM Journal on Scientific Computing 18 (1): 1–22, doi:10.1137/S1064827594276424, ISSN 1064-8275.
