Boeing 717
The Boeing 717 is a twin-engine, single-aisle jet airliner, developed for the 100-seat market. The airliner was designed and marketed by McDonnell Douglas as the MD-95, a third-generation derivative of the DC-9. Capable of seating of up to 117 passengers, the 717 has design range of 2,060 nautical miles (3,820 km). The aircraft is powered by two Rolls-Royce BR715 turbofan engines.
The first order was placed in October 1995; McDonnell Douglas and Boeing merged in 1997[2] prior to production, and the first planes entered service in 1999 as the Boeing 717. Production ceased in May 2006 after 156 were produced.[3]
Development
Background
Douglas Aircraft developed the DC-9 to be a short-range companion to their larger four engined DC-8 in the early 1960s. The DC-9 was an all-new design, using two rear fuselage-mounted Pratt & Whitney JT8D turbofan engines, a small, highly efficient wing, and a T-tail. The DC-9 first flew in 1965 and entered airline service later that year. When production ended in 1982 a total of 976 DC-9s had been produced.
The McDonnell Douglas MD-80 series was introduced into airline service in 1980. The design was the second generation of the DC-9. It was a lengthened DC-9-50 with a higher maximum take-off weight (MTOW) and higher fuel capacity, as well as next-generation Pratt and Whitney JT8D-200 series engines. Nearly 1,200 MD-80s were delivered from 1980 to 1999.
The MD-90 was developed from the MD-80 series. It was launched in 1989 and first flew in 1993. The MD-90 was longer, and featured a glass cockpit (electronic instrumentation) and more powerful, quieter, fuel efficient IAE V2525-D5 engines, with the option of upgrading that to an IAE V2528 engine. Only 117 MD-90 airliners were built.
MD-95
The MD-95 traces its history back to 1983 when McDonnell Douglas outlined a study named the DC-9-90. During the early 1980s, as production of the DC-9 family moved away from the smaller Series 30 towards the larger Super 80 (later redesignated MD-80) variants, Douglas proposed a smaller version of the DC-9 to fill the gap left by the DC-9-30. Dubbed the DC-9-90, the aircraft was revealed in February 1983 and was to be some 25 ft 4 in (7.72 m) shorter than what was then the DC-9-81 giving it an overall length of 122 ft 6 in (37.34 m) The aircraft was proposed with a 17,000 lbf (76 kN) thrust version of the JT8D-200 series engine, although the CFM56-3 was also being considered. Sized to seat up to 117 passengers, the DC-9-90 was to be equipped with the DC-9's wing with 2 ft (0.61 m) tip extensions, rather than the more heavily modified increased area of the MD-80. The aircraft had a design range of around 1,500 nmi (2,800 km), with an option to increase to 2,000 nmi (3,700 km), and a gross weight of 112,000 lb (51,000 kg). The DC-9-90 was designed to meet the needs of the newly deregulated air transport industry in the United States, however, the development of the short fuselage MD-80 was postponed as a result of the downturn in business in the recession of the early 1980s. When McDonnell Douglas did develop a smaller version of the MD-80, it simply shrunk the aircraft to create the MD-87, rather than offer a lower thrust lighter aircraft that was more comparable to the DC-9-30. With its relatively high MTOW and powerful engines, the MD-87 essentially became a special mission aircraft and could not compete with the all new 100-seaters that were being developed. Although an excellent aircraft for specialized roles, the MD-87 has not really sold on its own, and tends to rely heavily on its commonality factor which has generally limited sales to existing MD-80 operators.[4]
During early 1991, McDonnell Douglas revealed that it was again considering the development of a specialized 100-seat version of the MD-80 family, which was initially dubbed the MD-87-105 (105 seats). The new lighter aircraft was to be some 8 ft (2.4 m) shorter than the MD-87, and would be powered by engines in the 16,000–17,000 lbf (71–76 kN) thrust class.[4]
McDonnell Douglas, Pratt & Whitney, and the China National Aero-Technology Import Export Agency signed a memorandum of understanding to develop a 105-seat version of the MD-80. Then at the 1991 Paris Airshow, McDonnell Douglas announced the development of the new 105-seat version, now designated MD-95.[4] The "MD-95" name was selected to reflect the anticipated year deliveries would begin.[5] McDonnell Douglas first offered the airliner for sale in 1994.[5][6] With an overall length of 122 ft 5 in (37.31 m), and a maximum takeoff weight (MTOW) of 118,400 lb (53,700 kg), what McDonnell Douglas was proposing at that stage was very similar to the DC-9-90 design of 1983.
In early 1994, the MD-95 re-emerged as quite similar to the DC-9-30. Indeed the aircraft's specification in terms of weight, dimensions, and fuel capacity are almost identical. The major changes included a fuselage "shrink" back to 119 ft 4 in (36.37 m) length (same as the DC-9-30), and the reversion to the original DC-9 wing of 93 ft 5 in (28.47 m) span. At the time of the redefinition, McDonnell Douglas said that it expected the MD-95 to grow into a family of aircraft with the capability of increased range and seating capacity.[4]
The MD-95 was developed to satisfy the market need to replace early DC-9 models, then approaching 30 years old. The MD-95 project was a complete overhaul of the system, going back to the original DC-9-30 design and reinventing it for modern transport with new engines, cockpit and other more modern systems.[5] Historically, aircraft shrinks have sold poorly; examples of such aircraft in addition to the MD-87 include the Boeing 747SP, Boeing 737-600, Airbus A318, and Airbus A340-200.
Longtime McDonnell Douglas customer Scandinavian Airlines System (SAS) chose the Boeing 737-600 for its 100-seater over the MD-95 in March 1995.[5] Then in October 1995, United States discount carrier ValuJet signed an order for 50 MD-95s, plus 50 options.[5] McDonnell Douglas president Harry Stonecipher felt that launching MD-95 production on the basis of this small order was only a small risk, explaining that further orders would "take a while longer".[7] The ValuJet order was the only order received for some two years.[8]
Engines
As first proposed, the MD-95 was to be powered by a 16,500 lbf (73,000 N) thrust derivative of the JT8D-200 series, and the Rolls-Royce Tay 670 was also considered as an alternative. This was confirmed in January 1992, when Rolls-Royce and McDonnell Douglas signed a memorandum of understanding concerning the Tay-powered MD-95. McDonnell Douglas said that the MD-95 project would cost only a minimal amount to develop, as it was a direct offshoot of the IAE-powered MD-90.[4]
During 1993 McDonnell Douglas seemed to be favoring a life extension program of the DC-9-30, under the program name DC-9X, to continue its presence in the 100-120 seat market, rather than concentrating on the new build MD-95. During its evaluation of the various engines available for the proposed re-engining component of DC-9X, McDonnell Douglas found the BMW Rolls-Royce BR700 engine an ideal candidate and the BMW Rolls-Royce BR700 engine was selected to power the aircraft on February 23, 1994.[4]
Production
McDonnell Douglas was planning for all MD-95 assembly to be undertaken in China, as an offshoot of the Trunkliner program, for which McDonnell Douglas had been negotiating to have up to 150 MD-90s built in China. The MD-90 Trunkliner deal was finalized in June 1992, but the contract was for a total of 40 aircraft, including 20 MD-80Ts and 20 -90Ts. The MD-80 has been license built in Shanghai since the 1980s. However in early 1993, MDC said that it was considering sites outside China, and was later seeking alternative locations for the assembly line. In 1994, McDonnell Douglas sought global partners to share development costs. It also began a search for a low-cost final assembly site. Halla Group in South Korea was selected to make the wings; Alenia of Italy the entire fuselage; Aerospace Industrial Development Corp. of Taiwan, the tail; ShinMaywa of Japan, the horizontal stabilizer; and a manufacturing division of Korea Air Lines, the nose and cockpit.[4]
In an unprecedented move, McDonnell Douglas announced on November 8, 1994 that final assembly would be taken away from the longtime Douglas plant in Long Beach, California. Instead, it tapped a modifications and maintenance operation, Dalfort Aviation in Dallas, Texas, to assemble the MD-95. In early 1995, management and unions in Long Beach reached an agreement to hold down wage costs for the life of the MD-95 program and McDonnell Douglas canceled the preliminary agreement with Dalfort.[9]
Rebranding

After McDonnell Douglas merged with Boeing in August 1997,[10] most industry observers expected that Boeing would cancel development of the MD-95. However, Boeing decided to go forward with the design under a new name, Boeing 717. Some believed Boeing had skipped the 717 model designation when the 720, and then the 727 followed the 707. The 717 name had actually been used within the company to refer to the KC-135 Stratotanker. 717 had also been used to promote an early design of the 720 to airlines before it was modified to meet market demands. A Boeing historian notes that the Air Force plane had the designation "717-100" and the commercial airliner had the designation "717-200".[11] The lack of a widespread use of the 717 name left it available to rebrand the MD-95.
At first Boeing had no more success selling the 717 than McDonnell Douglas. Even the original order for 50 was no certainty in the chaotic post-deregulation United States airline market. Assembly started on the first 717 in May 1997.[12] The aircraft had its roll out ceremony on June 10, 1998. The 717's first flight took place on September 2, 1998. Following flight testing, the airliner was awarded a type certification on September 1, 1999. Its first delivery was to AirTran Airways in September 1999 and entered commercial service the following month.
Boeing's decision to go ahead with the 717 slowly began to pay off. Early 717 operators were delighted with the reliability and passenger appeal of the type and ordered more.[citation needed] The small Australian regional airline Impulse took a long-term lease on five 717s in early 2000 to begin an expansion into mainline routes. The ambitious move could not be sustained in competition with the majors, and Impulse sold out to Qantas in May 2001. This left Qantas with a more-or-less unwanted handful of 717s to spoil the efficiency of its fleet of large Boeing and small BAe 146 jets.
Within a few months, however, the abilities of the 717 became clear. It is roomier and faster than the BAe 146, cheaper to operate, and achieved a higher dispatch reliability, over 99%, than competing aircraft.[13] Maintenance costs are very low: a C check inspection, for example, takes three days and is required once in 6,000 flying hours.[citation needed] (For comparison, its predecessor, the DC-9 needed 21 days for a C check.) The new Rolls-Royce BR715 engine design is highly modular: none of the line-replaceable units takes more than an hour to exchange.[citation needed] Many 717 operators, even accidental ones like Qantas, become converts to the plane. Qantas bought more 717s, and other significant orders came from Hawaiian Airlines and Midwest Airlines.
Boeing actively marketed the 717 to a number of large airlines, including Lufthansa and Northwest (who already operated a large fleet of DC-9 aircraft). Boeing also studied a stretched, higher-capacity version of the 717, to have been called 717-300, but decided against proceeding with the new model, fearing that it would encroach on the company's 737-700 model. Production of the original 717 continued. Boeing continued to believe that the 100-passenger market would be lucrative enough to support both the 717 and the 737-600, the smallest of the Next-Generation 737 series. While the aircraft were similar in overall size, the 737-600 was better suited to long-distance routes, while the lighter 717 was more efficient on shorter, regional routes.

The 100-seat market was overcrowded until 2001, but several potential competitors disappeared. BAe canceled its Avro RJX (an updated BAe 146 with modern engines); Fairchild Dornier closed its doors, taking the 728/928 project with it; and Bombardier canceled its new BRJ in favor of a less ambitious stretched 90-seat CRJ900. The remaining players are Boeing, Airbus with the A318, and Embraer with the E-195. The worldwide fleet was then largely made up of aging twinjets with relatively high operating costs, notably the DC-9, early model 737s, and the Fokker 100, plus the newer four-engined BAe 146, which is a prime prospect for refurbishment.
In 2001, Boeing began implementing a moving assembly line for production of the 717 and 737.[14] The moving line greatly reduced production time, which led to lower production costs.[15]
Following the slump in airline traffic caused by reaction to the September 11, 2001 attacks in the United States, Boeing announced a review of the type's future. After much deliberation, it was decided to continue with production. Despite the lack of orders, Boeing had confidence in the 717's fundamental suitability to the 100-seat market, and in the long-term size of that market. After 19 worldwide 717 sales in 2000, and just 6 in 2001, Boeing took 32 orders for the 717 in 2002, despite the severe industry downturn. Additionally, the former Douglas facility at Long Beach was producing only 717s and C-17s at this time.
End of production

Increased competition from regional jets manufactured by Bombardier and Embraer took a heavy toll on sales during the airline slump after 2001. The beginning of the end came in December 2003 when Boeing lost a US$2.7 billion contract from Air Canada, who chose the Embraer E-Jets and Bombardier CRJ over the 717.[16] In January 2005, citing slow sales, Boeing announced that it planned to end production of the 717 after it had met all of its outstanding orders.[17]
The 156th and final 717 rolled off the assembly line in April 2006 for AirTran Airways, which was the 717's launch customer as well as its final customer. The final two Boeing 717s were delivered to customers AirTran and Midwest Airlines on May 23, 2006.[3] The 717 was the last commercial airplane produced at Boeing's Long Beach facility in Southern California.[3]
Program milestones
- Announced: June 16, 1991 at the Paris Airshow as MD-95 program by McDonnell Douglas.[18]
- Approval to offer: July 22, 1994 Douglas got MDC board approval to offer the aircraft.[4][19]
- First order: October 19, 1995 from ValuJet (later to become AirTran Airways) for 50 firm and 50 options for BR715-powered MD-95s.[19]
- Roll out: June 10, 1998 at Long Beach, California.[20]
- First flight: September 2, 1998.
- FAA certification: September 1, 1999.[21]
- EASA (JAA) certification: September 16, 1999.[22]
- Entry into service: October 12, 1999 with AirTran Airways on Atlanta-Washington DC route.
- 100th aircraft delivery: June 12, 2002 to AirTran Airways.
- Last delivery: May 23, 2006 to AirTran Airways.[23]
Design

The 717 features a two-crew cockpit that incorporates six interchangeable liquid-crystal-display units and advanced Honeywell VIA 2000 computers. The cockpit design is called Advanced Common Flightdeck (ACF) and is shared with the MD-11. Flight deck features include an Electronic Instrument System, a dual Flight Management System, a Central Fault Display System, and Global Positioning System. Category IIIb automatic landing capability for bad-weather operations and Future Air Navigation Systems are available. The 717 shares the same type rating as the DC-9 such that FAA approved transition courses for DC-9 and analog MD-80 pilots can be completed in 11 days.[24]
In conjunction with Parker Hannifin, MPC Products of Skokie, Illinois designed a fly-by-wire technology mechanical control suite for the 717 flight deck. The modules replaced much cumbersome rigging that had occurred in previous DC-9/MD-80 aircraft. The Rolls-Royce BR715 engines are completely controlled by an electronic engine system (FADEC — Full Authority Digital Engine Control) developed by BAE Systems, offering improved controllability and optimization over its predecessors.
Like its DC-9/MD-80/MD-90 predecessors, the 717 has a 2+3 seating arrangement in coach, providing only one middle seat per row, whereas other single-aisle twin jets often have 3+3 arrangement with two middle seats per row. Unlike its predecessors, McDonnell Douglas decided not to offer the MD-95/717 with the boarding flexibility of aft airstairs, with the goal of maximizing fuel efficiency through the reduction and simplification of as much auxiliary equipment as possible.
Variants
Three initial variants were proposed by McDonnell Douglas in 1993:[4]
- MD-95-30: Baseline aircraft with 100 seats.
- MD-95-30ER: extended range (with additional fuel), and
- MD-95-50: a slightly larger with standard capacity for 122 passengers.
Boeing 717 Business Express
Boeing 717 Business Express was a proposed corporate version of 717-200, unveiled at EBACE Convention in Geneva, Switzerland in May 2003. Configurable for 40 to 80 passengers in first and/or business class interior (typically, 60 passengers with seat pitch of 52 inch, 132 cm). Maximum range in HGW configuration with auxiliary fuel and 60 passengers was 3,140 nmi (5,815 km; 3,613 mi). The version complements BBJ family.[25]
Undeveloped variants
Boeing 717-100 (-100X): Proposed 86-seat version, formerly MD-95-20; four frames (6 ft 3 in, 1.9 m) shorter. Renamed -100X; wind tunnel tests began in early 2000; revised mid-2000 to eight-frame (12 ft 8 in, 3.86 m) shrink. Launch decision was deferred in December 2000 and again thereafter to an undisclosed date. Shelved by mid-2003.[26]
Boeing 717-100X Lite: Proposed 75-seat version, powered by Rolls-Royce Deutschland BR 710 turbofans; later abandoned.[26]
Boeing 717-300X: Proposed stretched version, formerly MD-95-50; studies suggest typical two-class seating for 130 passengers, with overall length increased to 138 ft 4 in (42.16 m) by addition of nine frames (five forward and four aft of wing); higher MTOW and space-limited payloads weights; additional service door aft of wing; and 21,000 lb (93.4 kN) BR 715C1-30 engines. AirTran expressed interest in converting some -200 options to this model. Was under consideration late 2003 by Star Alliance Group (Air Canada, Austrian Airlines, Lufthansa and SAS); interest was reported from Delta, Iberia and Northwest Airlines.[26]
Operators


In July 2013, 148 Boeing 717-200s were in airline service with Southwest Airlines (88), Hawaiian Airlines (18), Volotea (14), QantasLink (13), Blue1 (9), and Turkmenistan Airlines (6).[27] Following Southwest's merger with AirTran Airways, Delta Air Lines is to lease AirTran's 88 717s from Southwest Airlines in 2013.[28]
Incidents
As of March 2009, the Boeing 717 has been involved in 5 incidents,[29] with no hull-loss accidents and no fatalities.[30] The incidents included an on-ground collision, a hard landing and one attempted hijacking.[29]
Specifications
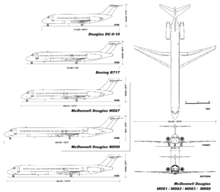
| 717-200 Basic Gross Weight |
717-200 High Gross Weight | |
|---|---|---|
| Cockpit crew | Two | |
| Seating capacity | 117 (1-class, typical) 106 (2-class, typical) | |
| Seat pitch | 32 in (81 cm) (1-class, typical) 36 in (91 cm) & 32 in (81 cm) (2-class, typical) | |
| Length | 124 ft 0 in (37.8 m) | |
| Wingspan | 93 ft 5 in (28.47 m) | |
| Tail height | 29 ft 1 in (8.92 m) | |
| Cabin width, external | 131.6 in (334.2 cm) | |
| Cabin width, internal | 123.8 in (314.5 cm) | |
| Max takeoff weight | 110,000 lb (49,900 kg) | 121,000 lb (54,900 kg) |
| Cargo capacity | 935 ft³ (26.5 m³) | 730 ft³ (20.7 m³) |
| Ceiling | 37,100 feet (11,300 m) maximum altitude 34,100 feet (10,400 m) typical altitude | |
| Typical cruising speed | Mach 0.77 (504 mph, 438 knots, 811 km/h) at altitude of 34,100 feet (10,400 m) | |
| Max. range | 1,430 nmi (2,645 km) | 2,060 nmi (3,815 km) |
| Max. fuel capacity | 3,673 US gal (13,903 L) | 4,403 US gal (16,665 L) |
| Powerplants (2x) | Rolls Royce BR715-A1-30 | Rolls Royce BR715-C1-30 |
| Engine thrust | 18,500 lbf (82.3 kN) | 21,000 lbf (93.4 kN) |
Sources: Boeing 717 Characteristics[31] 717 Airport planning report[32] Boeing 717 Specifications[33]
Orders and deliveries
Orders
| 2004 | 2003 | 2002 | 2001 | 2000 | 1999 | 1998 | 1997 | 1996 | 1995 |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| 8 | 8 | 32 | 3 | 21 | 0 | 50 | 0 | 0 | 50 |
Deliveries
| 2006 | 2005 | 2004 | 2003 | 2002 | 2001 | 2000 | 1999 | 1998 | 1997 |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| 5 | 13 | 12 | 12 | 20 | 49 | 32 | 12 | 0 | 0 |


See also
- Related development
- Aircraft of comparable role, configuration and era
- Airbus A318
- Antonov An-148-158
- Avro RJ series
- Boeing 737-600
- Bombardier CRJ1000
- Bombardier CSeries
- Comac ARJ21-900
- Embraer 190/195
- Fokker 100
- Sukhoi Superjet 100-95
- Tupolev Tu-334
- Yakovlev Yak-42D
References
- ↑ 1.0 1.1 "The Boeing 717". Boeing Commercial Airplanes. Retrieved January 4, 2011.
- ↑ Boeing Chronology, 1997-2001, Boeing
- ↑ 3.0 3.1 3.2 "Boeing Delivers Final 717s; Concludes Commercial Production in California" (Press release). Boeing. May 23, 2006. Retrieved December 9, 2010.
- ↑ 4.0 4.1 4.2 4.3 4.4 4.5 4.6 4.7 4.8 Airclaims Jet Programs 1995
- ↑ 5.0 5.1 5.2 5.3 5.4 Norris, Guy; Wagner, Mark (1999). Douglas Jetliners. MBI Publishing. ISBN 0-7603-0676-1.
- ↑ Becher 2002, p. 106.
- ↑ Lopez, Ramon and Guy Norris. "MD-95 Launched with ValuJet". Flight International, October 25–31, 1995.
- ↑ Becher 2002, p. 107.
- ↑ Parallels in production: 7E7 and 717
- ↑ "The Boeing Company ... The Giants Merge", Boeing history.
- ↑ "Aerospace Notebook: Orphan 717 isn't out of sequence", seattlepi.com, December 22, 2004.
- ↑ Flight International Commercial Aircraft Page 45 (3 Sep 1997)
- ↑ Boeing 717: Designed for Airline Profitability
- ↑ Boeing 2001 Annual report
- ↑ 717 innovations live on long after production. Boeing
- ↑ "Air Canada buying 90 jets from Bombardier, Embraer". CBC News (CBC). December 19, 2003. Retrieved December 30, 2009.
- ↑ "Boeing to Recognize Charges for USAF 767 Tanker Costs and Conclusion of 717 Production" (Press release). Boeing. January 15, 2005. Retrieved December 30, 2009.
- ↑ "MDC Steps into 100-seat arena with MD-95". Flight International - Paris Show Report 1991, 26 June 1991, p. 13.
- ↑ 19.0 19.1 Flight International 1 April 1998 - Page 31 "Classic takes shape"
- ↑ Boeing Rolls Out First 717-200 Passenger Jet. Boeing
- ↑ FAA Type Certificate Data Sheets A6WE
- ↑ EASA Type Certificate Data Sheets IM.A.211
- ↑ Boeing delivers final 717 to AirTran, ending Douglas era
- ↑ Flying the 717-200, Airline Pilot, Retrieved 15 December 2007.
- ↑ Boeing Introduces 717 Business Express at EBACE 2003
- ↑ 26.0 26.1 26.2 Jane's All World Aircraft 2005
- ↑ "World Airliner Census". Flight International, August 13–19, 2013.
- ↑ Delta to Add Boeing 717 Aircraft to its Fleet
- ↑ 29.0 29.1 Boeing 717 incidents, Aviation-Safety.net, March 22, 2009 .
- ↑ Boeing 717 summary, Aviation-Safety.net, 2008.
- ↑ 717-200 Technical Characteristics
- ↑ "717-200 Airplane Characteristics for Airport Planning". Boeing, May 2011. Retrieved: June 19, 2012.
- ↑ "Boeing 717 Specifications"
- Becher, Thomas. Douglas Twinjets, DC-9, MD-80, MD-90 and Boeing 717. The Crowood Press, 2002. ISBN 1-86126-446-1.
External links
| Wikimedia Commons has media related to: |
- Boeing 717 web page
- Boeing 717 on Aircraft-Info.net
- Boeing 717 profile on gizmohighway.com
- 717 List on plane-spotters.net
| |||||||||||||||||
| Boeing 7x7 aircraft production timeline, 1955–present | ||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| 1950s | 1960s | 1970s | 1980s | 1990s | 2000s | 2010s | ||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| 5 | 6 | 7 | 8 | 9 | 0 | 1 | 2 | 3 | 4 | 5 | 6 | 7 | 8 | 9 | 0 | 1 | 2 | 3 | 4 | 5 | 6 | 7 | 8 | 9 | 0 | 1 | 2 | 3 | 4 | 5 | 6 | 7 | 8 | 9 | 0 | 1 | 2 | 3 | 4 | 5 | 6 | 7 | 8 | 9 | 0 | 1 | 2 | 3 | 4 | 5 | 6 | 7 | 8 | 9 | 0 | 1 | 2 | 3 |
| Boeing 707 | ||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Boeing 717 (MD-95) | ||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Boeing 727 | ||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Boeing 737 | ||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Boeing 747 | ||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Boeing 757 | ||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Boeing 767 | ||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Boeing 777 | ||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Boeing 787 | ||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| = Narrow-body | = Wide-body | |||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| |||||||||||
| ||||||||||||||
| ||||||||||||||