Blue Banana

The Blue Banana (also known as the Hot Banana, Bluemerang, European Megalopolis or European Backbone) is a discontinuous corridor of urbanisation in Western Europe, with a population of around 110 million.[1] It stretches approximately from North West England in the north to Milan in the south.
The curvature of this corridor (hence "banana") takes in cities such as Leeds, Sheffield, Liverpool, Manchester, Nottingham, Birmingham, London, Lille, Amsterdam, The Hague, Rotterdam, Ghent, Brussels, Antwerp, Eindhoven, the Ruhr area, Düsseldorf, Cologne, Bonn, Frankfurt am Main, Luxembourg, Strasbourg, Stuttgart, Nuremberg, Munich, Zurich, Turin, Milan, Venice, and Genoa and covers one of the world's highest concentrations of people, money and industry.[2][3] The concept was developed in 1989 by RECLUS, a group of French geographers managed by Roger Brunet.[4]
List of cities and regions

The cities in the table below include their greater urban areas, clockwise from the north-west.
| City / Metropolitan Area | Country | Population (millions) |
|---|---|---|
| Liverpool / Liverpool Urban Area | United Kingdom | 1.3 |
| Newport / South Wales | United Kingdom | 1.3 |
| Cardiff / South Wales | United Kingdom | 1.3 |
| Manchester - Salford / Greater Manchester | United Kingdom | 2.5 |
| Leeds - Bradford / West Yorkshire Urban Area | United Kingdom | 1.9 |
| Sheffield / South Yorkshire | United Kingdom | 1.5 |
| Birmingham - Wolverhampton / West Midlands | United Kingdom | 2.6 |
| Nottingham - Derby | United Kingdom | 0.8 |
| London commuter belt | United Kingdom | 13.9 |
| Lille-Kortrijk-Tournai | France & Belgium | 1.8 |
| Flemish Diamond | Belgium | 5.5 |
| Randstad | Netherlands | 7.1 |
| Brabantse Stedenrij | Netherlands | 1.7 |
| Arnhem-Nijmegen | Netherlands | 0.8 |
| Euregio Enschede-Gronau | Netherlands & Germany | 3.3[5] |
| Meuse-Rhine | Belgium, Netherlands, & Germany | 3.9 |
| Rhine-Ruhr metropolitan area | Germany | 12.0 |
| Frankfurt/Rhine-Main | Germany | 5.2 |
| Nuremberg metropolitan area | Germany | 3.4[6] |
| Mannheim/Rhine-Neckar | Germany | 2.0 |
| Saarbrücken-Forbach | Germany & France | 0.7 |
| Strasbourg-Ortenau | France & Germany | 0.9 |
| Stuttgart Region/Metropolitan Region | Germany | 5.3 |
| Munich metropolitan area | Germany | 2.6 |
| Basel metropolitan area | Switzerland, France & Germany | 0.7 |
| Zurich metropolitan area | Switzerland | 3.8 |
| Milan metropolitan area | Italy | 8.1 |
| Turin metropolitan area | Italy | 2.2 |
| Genoa metropolitan area | Italy | 1.3 |
| TOTAL | 92.4 | |
History
The French geographer Roger Brunet, who wished to subdivide Europe into “active” and “passive” spaces, developed the concept of a West European “backbone” in 1989. He made reference to an urban corridor of industry and services stretching from northern England to northern Italy. Brunet did not see it as a new discovery, but as something easily predictable to anyone with "a little bit of intelligence and a feel for spatial properties."
He saw the Blue Banana as the development of historical precedents, e. g. known trade routes, or as the consequence of the accumulation of industrial capital. France, in his view, lost its links to the corridor as a result of its persecution of minorities (viz. the Huguenots) and excessive centralisation in Paris. In his analysis, Brunet artificially excluded the French conurbations, which are particularly narrowly concentrated around Paris, in order to persuade French authorities of the necessity of greater integration of business into the centre of Europe.
| “ | The name was added by the media: the banana shape was pointed out at a press-conference by Jacques Chérèque, a government minister; the colour was then given to it by an artist at the Nouvel Observateur, in an article by Josette Alia three days later which baptised the banane bleue. | ” |
It is said that the banana was rendered as blue because it represented the core of Europe, and the flag of Europe is largely blue.[citation needed] Other sources claim that the colour refers to the clothing of industrial workers (“blue collar”).[citation needed]
Its existence is sometimes attributed to the redrawing of the map of Europe after World War II, which led to the creation of a north-south axis (of which the highly developed infrastructure of the Rhine valley provides an example), while east-west relationships were enfeebled.[citation needed] On the other hand, large centres already existed long before that time (Randstad, the Ruhr, Manchester) so it was only natural that development would occur in areas that lay between these powerhouses, and that large populations would follow.
Criticism
Because of its simplicity and memorability, the term was rapidly adopted by the media, and became subject to promotional manipulation. Local authorities within the Blue Banana tried to redefine it as the best place for business investment. This gave other interested parties good reason to blur the boundaries to include regions they wished to promote. This was the opposite of Brunet's intention.
Detractors have pointed out that similar corridors of importance can be found along the Danube and on the Baltic and Mediterranean coasts, and that conurbations exist around Berlin, Paris, Budapest and Warsaw. More importantly, the Blue Banana includes vast tracts of sparsely populated area (the North Sea and the Alps), and does not take into account the difficulties that have been experienced by Wallonia, Lorraine, the Ruhr, and Saarland in trying to adjust to economic changes.
Implications
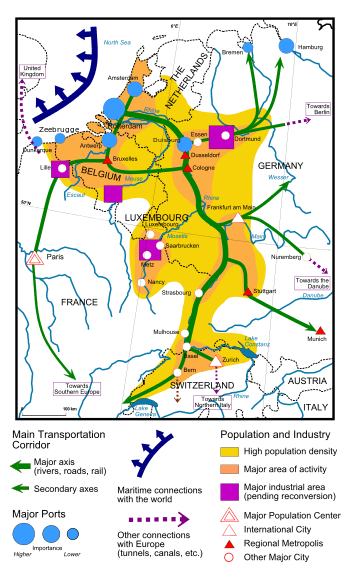
The Blue Banana holds an economically advantageous position through its population density, which is at an urban level for long stretches; and its infrastructure, although more industrial than IT in character, is above average throughout. The region is of interest to multinational companies, not only for its good transport infrastructure, e.g. ports (Rotterdam, Antwerp) or airports (London, Frankfurt, Amsterdam), but also for its convenience as a centre of operations. The region contains the main offices of several international organisations, such as the International Court in The Hague, the European Parliament in Strasbourg, and NATO headquarters in Brussels.
The more southerly Golden Banana is known for its modern industries, such as electronics, aeroplane manufacture, and research centres.
Development
Brunet's intention was to criticise French policies and his ideas were taken on board, so that today the Blue Banana model is no longer accurate: the former conurbations have grown several new branches, including one stretching from Paris to southern Spain[citation needed], and the last few years have seen so much expansion that one might speak of a Blue Star — although the Blue Banana remains at its core.
New regions that have been compared to the Blue Banana can be found on the Mediterranean coast between Valencia and Genoa, as part of the Golden Banana, or "European Sunbelt", paralleling that of America (where a pleasant climate draws newer industries), and in the north of Germany, where another conurbation lies on the North Sea coast, stretching into Denmark and from there into southern Scandinavia.
An influx of immigrants, who move by preference to the more prosperous, densely inhabited regions, has resulted in a disequilibrium in growth that is so severe that it may lead to polarisation within Europe, and a fragmentation into economic "winners" (inhabitants of the Blue Banana) and "losers" (rural areas, remote towns, and Eastern Europe in general)[citation needed]. The most serious problems lie with the people in outlying regions, who face a vicious circle of administrative neglect and gradual depopulation[citation needed], thus becoming increasingly dependent.[citation needed] In addition, the fact that high-speed train services are only viable in wealthy and heavily populated areas[citation needed] means that peripheral towns face yet more competitive disadvantages in comparison to urban centres.
See also
- List of metropolitan areas in the European Union by GDP
- Location of European Union institutions
- Megalopolis (city type)
- Northeast megalopolis
- North Western Metropolitan Area - EU designated region
- Quebec City-Windsor Corridor
- Taiheiyō Belt
References
- ↑ "The European Blue Banana". Eu-partner.com. 2011-03-03. Retrieved 2013-09-14.
- ↑ Gert-Jan Hospers (2002). "Beyond the Blue Banana? Structural Change in Europe's Geo-Economy" (PDF). 42nd EUROPEAN CONGRESS of the Regional Science Association Young Scientist Session - Submission for EPAINOS Award 27–31 August 2002. Dortmund, Germany. Retrieved 2006-09-27.
- ↑ Gert-Jan Hospers (2003). "Beyond the Blue Banana? Structural Change in Europe's Geo-Economy" (PDF). Intereconomics 38 (2): 76–85. doi:10.1007/BF03031774. Retrieved 2006-09-27.
- ↑ Brunet, Roger (1989). Les villes europeénnes: Rapport pour la DATAR (in French). Montpellier: RECLUS. ISBN 2-11-002200-0.
- ↑ EUREGIO (2004) (PDF). Demographische Daten EUREGIO (Report). http://www.euregio.de/cms/publish/content/downloaddocument.asp?document_id=437. Retrieved 2011-12-15.
- ↑ http://www.nuernberg.de/imperia/md/wirtschaft/dokumente/englische_versionen/key_data_for_investors_nuremberg.pdf
- Brunet, Roger (April 2002). "Lignes de force de l'espace Européen". Mappemonde (in French) (66): 14–19.