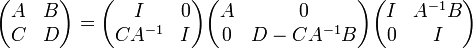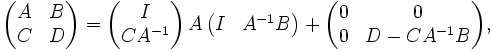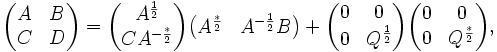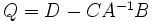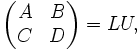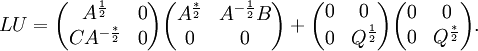Block LU decomposition
In linear algebra, a Block LU decomposition is a matrix decomposition of a block matrix into a lower block triangular matrix L and an upper block triangular matrix U. This decomposition is used in numerical analysis to reduce the complexity of the block matrix formula.
Block LU decomposition
Block Cholesky decomposition
Consider a block matrix:
where the matrix 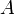 is assumed to be non-singular,
is assumed to be non-singular,
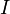 is an identity matrix with proper dimension, and
is an identity matrix with proper dimension, and  is a matrix whose elements are all zero.
is a matrix whose elements are all zero.
We can also rewrite the above equation using the half matrices:
where the Schur complement of 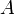 in the block matrix is defined by
in the block matrix is defined by
and the half matrices can be calculated by means of Cholesky decomposition or LDL decomposition. The half matrices satisfy that
Thus, we have
where
The matrix 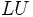 can be decomposed in an algebraic manner into
can be decomposed in an algebraic manner into