Biurea
From Wikipedia, the free encyclopedia
| Biurea | |
|---|---|
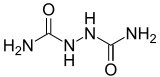 | |
| Hydrazine-1,2-dicarboxamide[citation needed] | |
| Systematic name (Carbamoylamino)urea[1] | |
| Other names
| |
| Identifiers | |
| CAS number | 110-21-4 |
| PubChem | 8039 |
| ChemSpider | 7748 |
| EC number | 203-747-2 |
| Jmol-3D images | {{#if:[nH2]:c(:[o]):[nH]:[nH]:c(:[nH2]):[o]NC(=O)NNC(N)=O|Image 1 Image 2 |
| |
| |
| Properties | |
| Molecular formula | C2H6N4O2 |
| Molar mass | 118.09 g mol−1 |
| Appearance | White crystals |
| Thermochemistry | |
| Std enthalpy of formation ΔfH |
−499.9–−497.5 kJ mol−1 |
| Std enthalpy of combustion ΔcH |
−1.1471–−1.1447 MJ mol−1 |
| Related compounds | |
| Related compounds | |
| Except where noted otherwise, data are given for materials in their standard state (at 25 °C (77 °F), 100 kPa) | |
| Infobox references | |
Biurea is a chemical compound with the molecular formula C2H6N4O2. It is produced in food products containing azodicarbonamide, a common ingredient in bread flour, when they are cooked.[2] Upon exposure, biurea is rapidly eliminated from the body through excretion.[3]
Biurea is produced from urea and hydrazine.[4] Its major use is as a chemical intermediate in the production of azodicarbonamide.[4]
References
- ↑ "Biurea - Compound Summary". PubChem Compound. USA: National Center for Biotechnology Information. 26 March 2005. Identification. Retrieved 27 June 2012.
- ↑ Azodicarbonamide, FAO Nutrition Meetings, Report Series No. 40A,B,C
- ↑ Mewhinney, JA; Ayres, PH; Bechtold, WE; Dutcher, JS; Cheng, YS; Bond, JA; Medinsky, MA; Henderson, RF; Birnbaum, LS (1987). "The fate of inhaled azodicarbonamide in rats". Fundamental and applied toxicology : official journal of the Society of Toxicology 8 (3): 372–81. PMID 3569707.
- ↑ 4.0 4.1 Kirk-Othmer Encyclopedia of Chemical Technology. 4th ed. Volumes 1: New York, NY. John Wiley and Sons, 1991-Present., p. V13 590
External links
This article is issued from Wikipedia. The text is available under the Creative Commons Attribution/Share Alike; additional terms may apply for the media files.