Bistriflimide

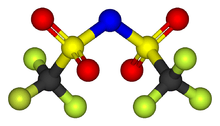
Bistriflimide, systematically known as bis(trifluoromethane)sulfonimide and colloquially as TFSI, is a non-coordinating anion with the chemical formula [(CF3SO2)2N]-. The anion is widely used in ionic liquids, since it is less toxic and more stable than more "traditional" counterions such as tetrafluoroborate. Developing an IUPAC name for bistriflimide that indicates the structure and reactivity is challenging, and changes to current names have been proposed.[1]
This anion is also of importance in lithium-ion and lithium metal batteries because of its high dissociation and conductivity. It has the added advantage of suppressing crystallinity in poly(ethylene oxide), which increases the conductivity of that polymer below its melting point at 50C.
The conjugate acid of bistriflimide is a superacid. It is a crystalline compound, but is extremely hygroscopic and deliquescent. Its pKa value in water cannot be accurately determined but in acetonitrile it has been estimated as 0.3 and in 1,2-dichloroethane -11.9 (relative to the pKa value of 2,4,6-trinitrophenol, arbitrarily taken as zero).[citation needed]
References
- ↑ Wilson, Gregory J.; Hollenkamp, Anthony F.; Pandolfo, Anthony G. (July-August 2007). "Resolving Ambiguous Naming for an Ionic Liquid Anion". Chemistry International (IUPAC) 29 (4). Retrieved 2008-01-08.