Bisabolene
| Bisabolenes | |
|---|---|
 α-Bisabolene | |
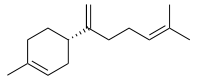 β-Bisabolene | |
 β-Bisabolene | |
 γ-Bisabolene | |
| IUPAC name (α): (E)-1-Methyl-4-(6-methylhepta-2,5-dien-2-yl)cyclohex-1-ene | |
| Identifiers | |
| CAS number | 17627-44-0 (α) |
| ChemSpider | 4509521 (α), 8279897 (β), 2298446 (γ) |
| Jmol-3D images | {{#if:(α): CC1=CCC(/C(C)=C/C/C=C(C)/C)CC1 (β): CC1=CC[C@@H](C(CC/C=C(C)/C)=C)CC1 (γ): CC(CC/1)=CCC1=C(C)/CC/C=C(C)/C|Image 1 |
| |
| |
| Properties | |
| Molecular formula | C15H24 |
| Molar mass | 204.35 g mol−1 |
| Except where noted otherwise, data are given for materials in their standard state (at 25 °C (77 °F), 100 kPa) | |
| Infobox references | |
Bisabolenes are a group of closely related natural chemical compounds which are classified as sesquiterpenes. Bisabolenes are present in the essential oils of a wide variety of plants including cubeb, lemon and oregano. Various derivates also function as pheromones in different insects, such as stink bugs[1] and fruit flies.[2]
Uses
Bisabolenes are intermediates in the biosynthesis of many other natural chemical compounds,[3] including hernandulcin, a natural sweetener. β-Bisabolene has a balsamic odor[4] and is approved in Europe as a food additive.
References
- ↑ Aldrich, J.R.; Numata, H.; Borges, M.; Bin, F.; Waite, G.K.; Lusby, W.R. (1993). "Artifacts and pheromone blends from Nezara spp. and other stink bug (Heteroptera: Pentatomidae)". Zeitschrift für Naturforschung 48C: 73–79.
- ↑ Lu, F.; Teal, P.E. (2001). "Sex pheromone components in oral secretions and crop of male Caribbean fruit flies, Anastrepha suspensa (Loew)". Arch Insect Biochem Physiol 48 (3): 144–154.
- ↑ Bisabolene derived sesquiterpenoid biosynthesis
- ↑ (-)-β-bisabolene, flavornet.org
External links
- Beta-bisabolene, NIST Chemistry WebBook listing