Biorthogonal system
From Wikipedia, the free encyclopedia
In mathematics, a biorthogonal system is a pair of indexed families of vectors
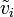 in E and
in E and  in F
in F
such that
where E and F form a pair of topological vector spaces that are in duality, ⟨,⟩ is a bilinear mapping and 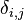 is the Kronecker delta.
is the Kronecker delta.
A biorthogonal system in which <var>E</var> = <var>F</var> and 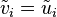 is an orthonormal system.
is an orthonormal system.
An example is the pair of sets of respectively left and right eigenvectors of a matrix, indexed by eigenvalue.[citation needed]
Projection
Related to a biorthogonal system is the projection
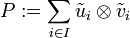 ,
,
where 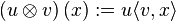 ; its image is the linear span of
; its image is the linear span of  , and the
kernel is
, and the
kernel is  .
.
Construction
Given a possibly non-orthogonal set of vectors 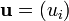 and
and  the projection related is
the projection related is
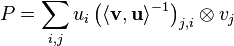 ,
,
where 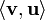 is the matrix with entries
is the matrix with entries  .
.
-
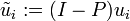 , and
, and 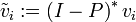 then is an orthogonal system.
then is an orthogonal system.
See also
References
This article is issued from Wikipedia. The text is available under the Creative Commons Attribution/Share Alike; additional terms may apply for the media files.
