Bifuhalol
From Wikipedia, the free encyclopedia
| Bifuhalol | |
|---|---|
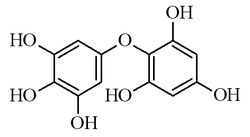 | |
| IUPAC name 2-(3,4,5-trihydroxyphenoxy)benzene-1,3,5-triol | |
| Other names 5-(2,4,6-Trihydroxyphenoxy)-1,2,3-benzenetriol | |
| Identifiers | |
| CAS number | 53254-99-2 |
| PubChem | 314874 |
| ChemSpider | 278565 |
| Jmol-3D images | Image 1 |
| |
| |
| Properties | |
| Molecular formula | C12H10O7 |
| Molar mass | 266.20 g/mol |
| Except where noted otherwise, data are given for materials in their standard state (at 25 °C (77 °F), 100 kPa) | |
| Infobox references | |
Bifuhalol is a phlorotannin. The ethanol extract of the brown alga Sargassum ringgoldianum contains phlorotannins of the bifuhalol type, which shows an antioxidative activity.[1]
References
- ↑ Phlorotannins as Radical Scavengers from the Extract of Sargassum ringgoldianum. Masaaki Nakai, Norihiko Kageyama, Koichi Nakahara, Wataru Miki, Marine Biotechnology, August 2006, Volume 8, Issue 4, pages 409-414, doi:10.1007/s10126-005-6168-9
| ||||||||||||||||||||||||||
This article is issued from Wikipedia. The text is available under the Creative Commons Attribution/Share Alike; additional terms may apply for the media files.