Białołęka
| Białołęka | |||
|---|---|---|---|
| Dzielnica of Warsaw | |||
 | |||
| |||
 | |||
| Coordinates: 52°11′34.37″N 20°53′23.03″E / 52.1928806°N 20.8897306°ECoordinates: 52°11′34.37″N 20°53′23.03″E / 52.1928806°N 20.8897306°E | |||
| Country |
| ||
| Voivodeship | Masovian | ||
| County/City | Warsaw | ||
| Government | |||
| • Mayor | Adam Grzegrzółka | ||
| Area | |||
| • Total | 73.04 km2 (28.20 sq mi) | ||
| Population (2011) | |||
| • Total | 92,768 | ||
| • Density | 1,300/km2 (3,300/sq mi) | ||
| Time zone | CET (UTC+1) | ||
| • Summer (DST) | CEST (UTC+2) | ||
| Area code(s) | +48 22 | ||
| Website | bialoleka.waw.pl | ||
Białołęka (Polish pronunciation: [bʲawɔˈwɛŋka], from biały - white and łąka - meadow) is one of 18 districts of Warsaw, located in the northern part of the city. Until October 27, 2002 Białołęka was a gmina. The name Białołęka comes from a nobleman Białołęcki, who bought the area before the First World War.
According to the Central Statistical Office data, the district's area is 73.04 square kilometres (28.20 square miles) and 92 768 people inhabit Białołęka.
History
On the fields of Białołęka, one of the battles with the Swedish on July 28–30, 1656 took place. On February 25, 1831 one of the battles of the November Uprising - Battle of Białołęka - took place.
- In 1425, the Białołęka village came into being and belonged to the Gołyński family.
- In the interwar period the only part of today's Białołęka area which was included in Warsaw was the Różopol subdivision.
- In 1938 Białołęka had 900 inhabitants and belonged to the Bródno municipality.
- In 1951 a group of villages (including Białołęka) joined Warsaw as result of the new administrative division of Warsaw.
- In 1976, during the next border changes, another villages joined Warsaw and the north-eastern border of Warsaw reached the point where it remains today.
- In 1994, the Białołęka subdivision gave its name to the new gmina Warsaw-Białołęka. In respect of area, the gmina was the third out of eleven Warsaw gminas, taking 15% of the whole city's area.
- In 2002, the territorial division of Warsaw changed, and gminas were replaced with dzielnicas.
Division
The area of the division is subdivided into following parts:
- industrial, where many industries are located in central, southern and southern-western parts: Żerań CHP Station (Elektrociepłownia Żerań), Polfa Tarchomin (a pharmaceutical company), Czajka sludgeworks, printing site of Agora SA publisher, factories of L'Oréal and the Coca-Cola Company, PKP rail sites, and many building companies
- housing estates with high density housing located in the central-western part (Nowy Tarchomin, Nowodwory and Nowe Świdry)
- housing estates with prevalent detached housing - northern and central-northern parts (Choszczówka, Białołęka Dworska, Płudy, Henryków and others)
- housing estates in village areas and arable lands (Brzeziny, Lewandów, Kobiałka, Białołęka Szlachecka, Mańki-Wojdy and others)
Subdivisions of Białołęka
Białołęka is divided into smaller subdivisions (osiedles). Here's a list of them (the italic names are the ones which are not taken into account by the TERYT).

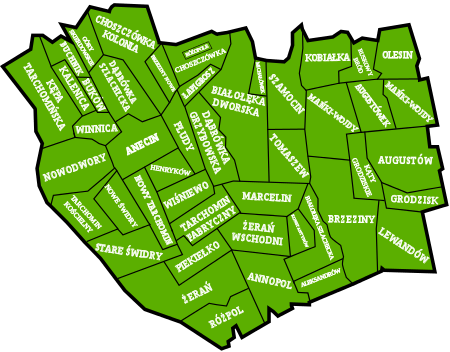
|
West
|
Middle west
|
Middle east
|
East
|
Other subdivisions:
- Szylówek
Green Białołęka


- Parks:
- Henrykowski Park – 30 056 m²
- "Picassa" Park – 36 700 m²
- Squares
- By Botewa/Talarowa streets – 5088 m²
- Next to Picassa housing estate – 32 900 m²
- Around the town hall – 4560 m²
- By Światowida street – 4600 m²
- Flowerbeds
- Area of flowerbeds – 250 m²
- Area of rose-gardens – 177 m²
- Surface waters
- Vistula river – 10 123 m
- Henrykowski canal – 9638 m
- Żerański canal – 9240 m
- Długa river + Markowski canal – 5450 m
- Bródnowski canal – 3600 m
- Dyke B – 3270 m
- Dyke A – 2640 m
- Jabłonna stream – 1838 m
- Natural reserves
- Ławice Kiełpińskie natural reserve – fauna natural reserve near the border of Warsaw, which function is to protect places where water-mud birds make nests. Area - 803 hectares.
- Łęgi Czarnej Strugi natural reserve – situated in the north-west part of Nieporęt gmina. Area - 39,53 hectares.
There are also many different-sized forests in Białołęka.
Monuments of Białołęka
- Court on Mehoffera street
- It consists of a court from 18th century, a palace from the beginning of the 19th century, built by Tadeusz Mostowski and a park.

- Church of St James the Great
- 2, Mehoffera street
- Church of St James the Great on Mehoffera street is the only Gothic temple in Warsaw, which is still looking nearly the same today as when it was built. The architectural details from 16th century are still readable. The church is made from brick and it's from the beginning of 16th century.
- Church of Birth of the Blessed Virgin Lady
- 21, Klasyków street
- Church built from 1908 to 1913 in the style of Vistula Neo-Gothic. It was consecrated on September 8, 1913, and on September 16, 1949 it was given the name by Stefan Wyszyński.
- Church of Michelangelo
- 119, Głębocka street
- One of the oldest wooden churches in Warsaw, probably funded by Bona Sforza in 1534.
Transport in Białołęka
The main street where all transport goes is the Modlińska street (extension of Jagiellońska), which is a part of trunk road 61 to Gdańsk and Masuria; and the Toruńska route, part of trunk road 8 to Białystok. Płochocińska street is also an important transport route as a fragment of the 633 voivodeship road to Nieporęt.
There are also plans of creating whole-city-long routes including Białołęka's routes:
- Maria Skłodowska-Curie Bridge route
- Vistula route
- Olszynka Grochowska route
- extension of Marywilska street to the borders of Warsaw
A railroad to Działdowo goes through the district. There are three stops on the railroad, on which the Koleje Mazowieckie passenger trains, going from Warszawa Gdańska and Warszawa Wola (now as Warszawa Zachodnia's eighth platform) stations, going to Legionowo, Nasielsk, Ciechanów and Działdowo, stop.
Borders
Białołęka borders:
- Targówek on south through Toruńska Route
- Bielany and Łomianki on west through Vistula
- Jabłonna and Nieporęt on north
- Marki on east
External links
| Wikimedia Commons has media related to Białołęka. |

