Beta-Carboline
| β-Carboline | |
|---|---|
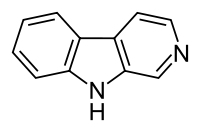 | |
| IUPAC name 9H-β-carboline | |
| Other names 9H-pyrido[3,4-b]indole | |
| Identifiers | |
| CAS number | 244-63-3 |
| PubChem | 64961 |
| ChemSpider | 58486 |
| MeSH | norharman |
| ChEBI | CHEBI:109895 |
| ChEMBL | CHEMBL275224 |
| Jmol-3D images | Image 1 |
| |
| |
| Properties | |
| Molecular formula | C11H8N2 |
| Molar mass | 168.20 g/mol |
| Except where noted otherwise, data are given for materials in their standard state (at 25 °C (77 °F), 100 kPa) | |
| Infobox references | |
β-Carboline (9H-pyrido[3,4-b]indole) also known as norharmane is a nitrogen containing heterocycle. It is also the prototype of a class of compounds known as β-carbolines.
Pharmacology
β-Carboline alkaloids are widespread in plants and animals, and frequently act as benzodiazepine inverse agonists. As components of the liana Banisteriopsis caapi, the β-carbolines harmine, harmaline, and tetrahydroharmine play a pivotal role in the pharmacology of the indigenous psychedelic drug ayahuasca by preventing the breakdown of dimethyltryptamine in the gut by inhibiting monoamine oxidase, thus making it psychoactive upon oral administration. Some β-carbolines, notably tryptoline and pinoline, are formed naturally in the human body. The latter is implicated along with melatonin in the role of the pineal gland in regulating the sleep-wake cycle.[citation needed] β-carboline is a benzodiazepine receptor inverse agonist and can therefore have convulsive, anxiogenic and memory enhancing effects.[1]
Structure
β-Carboline belongs to the group of indole alkaloids and consist of pyridine ring that is fused to an indole skeleton.[2] The structure of β-carboline is similar to that of tryptamine, with the ethylamine chain re-connected to the indole ring via an extra carbon atom, to produce a three-ringed structure. The biosynthesis of β-carbolines is believed to follow this route from analogous tryptamines.[3] Different levels of saturation are possible in the third ring, which is indicated here in the structural formula by colouring the optionally double bonds red and blue:
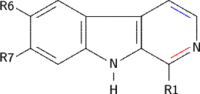
Examples of β-carbolines
Some of the more important β-carbolines are tabulated by structure below.
| Short Name | R1 | R6 | R7 | Structure | ||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| β-Carboline |  | |||||
| Tryptoline | .svg.png) | |||||
| Pinoline | .svg.png) | |||||
| Harmane | | | .svg.png) | |||
| Harmine | | | | .svg.png) | ||
| Harmaline | | | .svg.png) | |||
| Tetrahydroharmine | | .svg.png) |
Occurrence in nature
Eight plant families are known to express 64 different kinds of β-carboline alkaloids. By dry weight, the seeds of Peganum harmala (Syrian Rue) contain between 0.16%[4] and 5.9%[5] β-carboline alkaloids.
As a result of the presence of β-carbolines in the cuticle of scorpions, their skin is known to fluoresce when exposed to certain wavelengths of ultraviolet light such as that produced by a blacklight.[6]
A group of β-carboline derivatives, termed eudistomins were extracted from ascidians (marine tunicates of the family Ascidiacea), like Ritterella sigillinoides,[7] Lissoclinum fragile [8] or Pseudodistoma aureum.[9] Nostocarboline was isolated from freshwater cyanobacterium.
See also
References
- ↑ Venault P, Chapouthier G (2007). "From the behavioral pharmacology of beta-carbolines to seizures, anxiety, and memory". ScientificWorldJournal 7: 204–23. doi:10.1100/tsw.2007.48. PMID 17334612.
- ↑ The Encyclopedia of Psychoactive Plants: Ethnopharmacology and its Applications. Ratsch, Christian. Park Street Press c. 2005
- ↑ Baiget, Jessica; Llona-Minguez, Sabin; Lang, Stuart; MacKay, Simon P; Suckling, Colin J; Sutcliffe, Oliver B (2011). "Manganese dioxide mediated one-pot synthesis of methyl 9H-pyrido[3,4-b]indole-1-carboxylate: Concise synthesis of alangiobussinine". Beilstein Journal of Organic Chemistry 7: 1407–11. doi:10.3762/bjoc.7.164. PMC 3201054. PMID 22043251.
- ↑ Hemmateenejad B, Abbaspour A, Maghami H, Miri R, Panjehshahin MR (Aug 2006). "Partial least squares-based multivariate spectral calibration method for simultaneous determination of beta-carboline derivatives in Peganum harmala seed extracts". Anal Chim Acta 575 (2): 290–9. doi:10.1016/j.aca.2006.05.093. PMID 17723604.
- ↑ Herraiz T, González D, Ancín-Azpilicueta C, Arán VJ, Guillén H. (2010). "beta-Carboline alkaloids in Peganum harmala and inhibition of human monoamine oxidase (MAO)". Food Chem Toxicol. 48 (3): 839–43. doi:10.1016/j.fct.2009.12.019. PMID 20036304.
- ↑ Stachel SJ, Stockwell SA, Van Vranken DL (August 1999). "The fluorescence of scorpions and cataractogenesis". Chem. Biol. 6 (8): 531–9. doi:10.1016/S1074-5521(99)80085-4. PMID 10421760.
- ↑ Lake RJ, Blunt JW, Munro MHG (1989). "Eudistomins From the New Zealand Ascidian Ritterella sigillinoides". Aust. J. Chem. 42 (7): 1201–1206. doi:10.1071/CH9891201.
- ↑ Badre A, Boulanger A, Abou-Mansour E, Banaigs B, Combaut G, Francisco C (April 1994). "Eudistomin U and Isoeudistomin U, New Alkaloids from the Caribbean Ascidian Lissoclinum fragile". J. Nat. Prod. 57 (4): 528–533. doi:10.1021/np50106a016.
- ↑ Davis RA, Carroll AR, Quinn RJ (June 1998). "Eudistomin V, a New β-Carboline from the Australian Ascidian Pseudodistoma aureum". J. Nat. Prod. 61 (7): 959–960. doi:10.1021/np9800452.
External links
- Beta-Carbolines at the US National Library of Medicine Medical Subject Headings (MeSH)
- TiHKAL #44
- TiHKAL in general
- Beta-carbolines in Coffee
- Farzin D, Mansouri N (July 2006). "Antidepressant-like effect of harmane and other beta-carbolines in the mouse forced swim test". Eur Neuropsychopharmacol 16 (5): 324–8. doi:10.1016/j.euroneuro.2005.08.005. PMID 16183262.