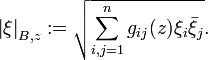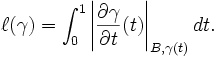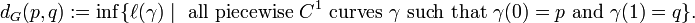Bergman metric
In differential geometry, the Bergman metric is a Hermitian metric that can be defined on certain types of complex manifold. It is so called because it is derived from the Bergman kernel, both of which are named for Stefan Bergman.
Definition
Let  be a domain and let
be a domain and let 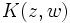 be the Bergman kernel
on G. We define a Hermitian metric on the tangent bundle
be the Bergman kernel
on G. We define a Hermitian metric on the tangent bundle 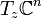 by
by
for  . Then the length of a tangent vector
. Then the length of a tangent vector  is
given by
is
given by
This metric is called the Bergman metric on G.
The length of a (piecewise) C1 curve ![\gamma \colon [0,1]\to {{\mathbb {C}}}^{n}](/2014-wikipedia_en_all_02_2014/I/media/e/6/6/a/e66a40920f9d0bcf267770a0bec43c63.png) is
then computed as
is
then computed as
The distance  of two points
of two points 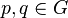 is then defined as
is then defined as
The distance dG is called the Bergman distance.
The Bergman metric is in fact a positive definite matrix at each point if G is a bounded domain. More importantly, the distance dG is invariant under
biholomorphic mappings of G to another domain 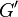 . That is if f
is a biholomorphism of G and
. That is if f
is a biholomorphism of G and 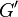 , then
, then  .
.
References
- Steven G. Krantz. Function Theory of Several Complex Variables, AMS Chelsea Publishing, Providence, Rhode Island, 1992.
This article incorporates material from Bergman metric on PlanetMath, which is licensed under the Creative Commons Attribution/Share-Alike License.