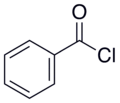
Benzoyl chloride
| Benzoyl chloride | |
|---|---|
 | |
 |
 |
| IUPAC name Benzoyl chloride | |
| Identifiers | |
| CAS number | 98-88-4 |
| PubChem | 7412 |
| ChemSpider | 7134 |
| KEGG | C19168 |
| RTECS number | DM6600000 |
| Jmol-3D images | Image 1 Image 2 |
| |
| |
| Properties | |
| Molecular formula | C7H5ClO |
| Molar mass | 140.57 g mol−1 |
| Appearance | colorless liquid |
| Density | 1.21 g/mL, liquid |
| Melting point | −1 °C; 30 °F; 272 K |
| Boiling point | 197.2 °C; 387.0 °F; 470.3 K |
| Solubility in water | reacts |
| Hazards | |
| MSDS | Oxford MSDS |
| EU classification | |
| R-phrases | R34 |
| S-phrases | (S1/2) S26 S45 |
| Flash point | 72 °C; 162 °F; 345 K |
| Related compounds | |
| Related compounds | benzoic acid, benzoic anhydride, benzaldehyde |
| Except where noted otherwise, data are given for materials in their standard state (at 25 °C (77 °F), 100 kPa) | |
| Infobox references | |
Benzoyl chloride, also known as benzenecarbonyl chloride, is an organochlorine compound with the formula C6H5COCl. It is a colourless, fuming liquid with an irritating odour. It is mainly useful for the production of peroxides but is generally useful in other areas such as in the production of dyes, perfumes, pharmaceuticals, and resins.
Preparation
Benzoyl chloride is produced from benzotrichloride using either water or benzoic acid:[1]
- C6H5CCl3 + H2O → C6H5COCl + 2 HCl
- C6H5CCl3 + C6H5CO2H → 2 C6H5COCl + HCl
As for other acyl chlorides, it can be generated from the parent acid and other chlorinating agents phosphorus pentachloride or thionyl chloride. It was first prepared by treatment of benzoic acid with chlorine.[2]
Reactions
Benzoyl chloride is a typical acyl chloride. It reacts with alcohols and amines to give the corresponding esters and amides. It undergoes the Friedel-Crafts acylation with arenes to give the corresponding benzophenones. Similarly, it reacts with water to produce hydrochloric acid and benzoic acid:
- C6H5COCl + H2O → C6H5CO2H + HCl
Benzoyl peroxide is industrially synthesised by reacting benzoyl chloride with hydrogen peroxide and sodium hydroxide:[3]
- 2 C6H5COCl + H2O2 + 2 NaOH → (C6H5CO)2O2 + 2 NaCl + 2 H2O
References
- ↑ Takao Maki, Kazuo Takeda “Benzoic Acid and Derivatives” Ullmann's Encyclopedia of Industrial Chemistry 2002, Wiley-VCH, Weinheim. doi: 10.1002/14356007.a03_555
- ↑ Friedrich Wöhler, Justus von Liebig (1832). "Untersuchungen über das Radikal der Benzoesäure". Annalen der Pharmacie 3 (3): 249–282. doi:10.1002/jlac.18320030302.
- ↑ El-Samragy, Yehia (2004). Chemical and Technical Assessment (PDF). "Benzoyl Peroxide". 61st JECFA (Technical report) (Joint FAO/WHO Expert Committee on Food Additives): 1. Retrieved 31 October 2013.