Benzocyclobutadiene
From Wikipedia, the free encyclopedia
| Benzocyclobutadiene | |
|---|---|
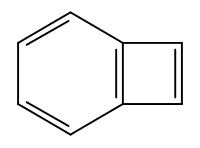 | |
| IUPAC name Bicyclo[4.2.0]octa-1,3,5,7-tetraene | |
| Identifiers | |
| CAS number | 4026-23-7 |
| PubChem | 77987 |
| ChemSpider | 70373 |
| Jmol-3D images | Image 1 |
| |
| |
| Properties | |
| Molecular formula | C8H6 |
| Molar mass | 102.13 g mol−1 |
| Except where noted otherwise, data are given for materials in their standard state (at 25 °C (77 °F), 100 kPa) | |
| Infobox references | |
Benzocyclobutadiene is the simplest polycyclic aromatic hydrocarbon, being composed of a benzene ring fused to a cyclobutadiene ring. It has chemical formula C8H6. Though the benzene ring is stabilized by aromaticity, the cyclobutadiene portion has a destabilizing effect. For this reason, benzocyclobutadiene will readily dimerize or polymerize and it reacts as a dienophile in Diels-Alder reactions.[1]
See also
References
- ↑ Carey, Francis A.; Sundberg, Richard J.; (1984). Advanced Organic Chemistry Part A Structure and Mechanisms (2nd ed.). New York N.Y.: Plenum Press. ISBN 0-306-41198-9.
This article is issued from Wikipedia. The text is available under the Creative Commons Attribution/Share Alike; additional terms may apply for the media files.