Benzene (data page)
From Wikipedia, the free encyclopedia
This page provides supplementary chemical data on benzene.
Material Safety Data Sheet
The handling of this chemical may incur notable safety precautions. It is highly recommend that you seek the Material Safety Datasheet (MSDS) for this chemical from a reliable source such as SIRI, and follow its directions. MSDS for benzene available at AMOCO.
Structure and properties
| Structure and properties | |||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Index of refraction, nD | 1.5011 at 20°C | ||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Abbe number | ? | ||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Dielectric constant, εr | (2.274 – 0.0020ΔT) ε0 (ΔT = T – 25 °C) | ||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Bond strength | ? | ||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Bond length | 1.39 Å C-C[2] | ||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Bond angle | 120°C–C–C 120° H–C–C | ||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Magnetic susceptibility | ? | ||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Surface tension | 28.88 dyn/cm at 25°C | ||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Viscosity[1] |
| ||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
Thermodynamic properties
| Phase behavior | |
|---|---|
| Triple point | 278.5 K (5.4 °C), 4.83 kPa |
| Critical point | 562 K (289 °C), 4.89 MPa |
| Std enthalpy change of fusion, ΔfusH |
9.9 kJ/mol at 5.42 °C |
| Std entropy change of fusion, ΔfusS |
35.5 J/(mol·K) at 5.42 °C |
| Std enthalpy change of vaporization, ΔvapH |
33.9 kJ/mol at 25°C 30.77 kJ/mol at 80.1°C |
| Std entropy change of vaporization, ΔvapS |
113.6 J/(mol·K) at 25°C 87.1 J/(mol·K) at 80.1°C |
| Solid properties | |
| Std enthalpy change of formation, ΔfH |
? kJ/mol |
| Standard molar entropy, S |
45.56 J/(mol K) |
| Heat capacity, cp | 118.4 J/(mol K) at 0°C |
| Liquid properties | |
| Std enthalpy change of formation, ΔfH |
+48.7 kJ/mol |
| Standard molar entropy, S |
173.26 J/(mol K) |
| Enthalpy of combustion, ΔcH |
–3273 kJ/mol |
| Heat capacity,[1] cp | 134.8 J/(mol K) |
| Gas properties | |
| Std enthalpy change of formation, ΔfH |
+82.93 kJ/mol |
| Standard molar entropy,[3] S |
269.01 J/(mol K) |
| Heat capacity,[1] cp | 82.44 J/(mol K) at 25°C |
| van der Waals' constants[4] | a = 1823.9 L2 kPa/mol2 b = 0.1154 liter per mole |
Vapor pressure of liquid
| P in mm Hg | 1 | 10 | 40 | 100 | 400 | 760 | 1520 | 3800 | 7600 | 15200 | 30400 | 45600 |
| T in °C | –36.7(s) | –11.5(s) | 7.6 | 26.1 | 60.6 | 80.1 | 103.8 | 142.5 | 178.8 | 221.5 | 272.3 | — |
Table data obtained from CRC Handbook of Chemistry and Physics 44th ed. Note: (s) notation indicates equilibrium temperature of vapor over solid, otherwise value is equilibrium temperature of vapor over liquid.
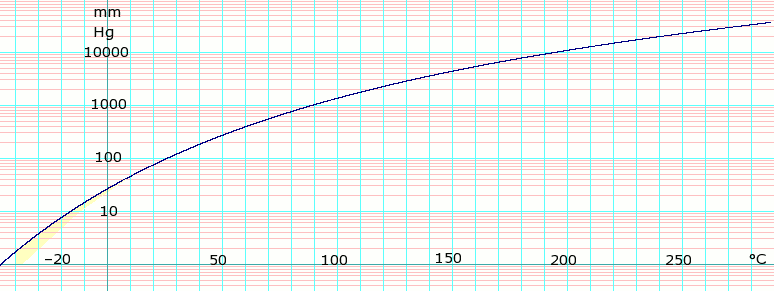
log of Benzene vapor pressure. Uses formula: 
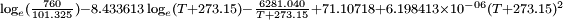 obtained from CHERIC[1] Note: yellow area is the region where the formula disagrees with tabulated data above.
obtained from CHERIC[1] Note: yellow area is the region where the formula disagrees with tabulated data above.

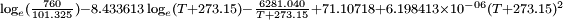 obtained from CHERIC[1] Note: yellow area is the region where the formula disagrees with tabulated data above.
obtained from CHERIC[1] Note: yellow area is the region where the formula disagrees with tabulated data above.Distillation data
|
|
|
| |||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
Spectral data
| UV-Vis | |||||||||||||||||||||||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Ionization potential | 9.24 eV (74525.6 cm−1) | ||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| S1 | 4.75 eV (38311.3 cm−1) | ||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| S2 | 6.05 eV (48796.5 cm−1) | ||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| λmax | 255 nm | ||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Extinction coefficient, ε | ? | ||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| IR | |||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Major absorption bands[6] |
| ||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| NMR | |||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Proton NMR | (CDCl3, 300 MHz) δ 7.34 (s, 6H) | ||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Carbon-13 NMR | (CDCl3, 25 MHz) δ 128.4 | ||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Other NMR data | |||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| MS | |||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Masses of main fragments |
|||||||||||||||||||||||||||


Safety data
Material Safety Data Sheet for benzene:
| Common synonyms | None |
| Physical properties | Form: colorless liquid |
| Stability: Stable, but very flammable | |
| Melting point: 5.5 C | |
| Water solubility: negligible | |
| Specific gravity: 0.87 | |
| Principal hazards | *** Benzene is a carcinogen (cancer-causing agent). |
| *** Very flammable. The pure material, and any solutions containing it, constitute a fire risk. | |
| Safe handling | Benzene should NOT be used at all unless no safer alternatives are available. |
| If benzene must be used in an experiment, it should be handled at all stages in a fume cupboard. | |
| Wear safety glasses and use protective gloves. | |
| Emergency | Eye contact: Immediately flush the eye with plenty of water. Continue for at least ten minutes |
| and call for immediate medical help. | |
| Skin contact: Wash off with soap and water. Remove any contaminated clothing. If the skin | |
| reddens or appears damaged, call for medical aid. | |
| If swallowed: Call for immediate medical help. | |
| Disposal | It is dangerous to try to dispose of benzene by washing it down a sink, since it is toxic, will cause environmental damage |
| and presents a fire risk. It is probable that trying to dispose of benzene in this way will also break local | |
| environmental rules. Instead, retain in a safe place in the laboratory (well away from any source of ignition) | |
| for disposal with other flammable, non-chlorinated solvents. | |
| Protective equipment | Safety glasses. If gloves are worn, PVA, butyl rubber and viton are suitable materials. |
References
- ↑ 1.0 1.1 1.2 1.3 "Pure Component Properties" (Queriable database). Chemical Engineering Research Information Center. Retrieved 12 May 2007.
- ↑ Brown, LeMay, Bursten (2006). Chemistry: The Central Science. Upper Saddle River, NJ: Pearson Education. p. 1067. ISBN 0-13-109686-9.
- ↑ "ETP Entropy of Benzene" (Queriable database). Dortmund Data Bank. Retrieved 7 Oct 2011.
- ↑ Lange's Handbook of Chemistry 10th ed, pp 1522-1524
- ↑ 5.0 5.1 5.2 5.3 "Binary Vapor-Liquid Equilibrium Data" (Queriable database). Chemical Engineering Research Information Center. Retrieved 12 May 2007.
- ↑ "Spectral Database for Organic Compounds" (Queriable database). Advanced Industrial Science and Technology. Retrieved 10 June 2007.
Except where noted otherwise, data relate to standard ambient temperature and pressure.
Disclaimer applies.
This article is issued from Wikipedia. The text is available under the Creative Commons Attribution/Share Alike; additional terms may apply for the media files.