Beek
| Beek Baek | |||
|---|---|---|---|
| Municipality | |||
 | |||
| |||
.svg.png) | |||
| Coordinates: 50°56′N 5°48′E / 50.933°N 5.800°ECoordinates: 50°56′N 5°48′E / 50.933°N 5.800°E | |||
| Country | Netherlands | ||
| Province | Limburg | ||
| Government[1] | |||
| • Body | Municipal council | ||
| • Mayor | Ralf Krewinkel (PvdA) | ||
| Area[2] | |||
| • Total | 21.03 km2 (8.12 sq mi) | ||
| • Land | 21.03 km2 (8.12 sq mi) | ||
| • Water | 0.00 km2 (0.00 sq mi) | ||
| Elevation[3] | 81 m (266 ft) | ||
| Population (November 2013)[4] | |||
| • Total | 16,300 | ||
| • Density | 775/km2 (2,010/sq mi) | ||
| Demonym | Bekenaar | ||
| Time zone | CET (UTC+1) | ||
| • Summer (DST) | CEST (UTC+2) | ||
| Postcode | 6176, 6190–6199 | ||
| Area code | 046 | ||
| Website | www.gemeentebeek.nl | ||
 Beek (
Beek (![]() pronunciation (help·info)) (Limburgish: Baek) is a town and municipality in the southeastern Netherlands, in the province of Limburg. As of 2012, Beek has a population of about 16,400, of which about 8,800 live in the town of Beek.
pronunciation (help·info)) (Limburgish: Baek) is a town and municipality in the southeastern Netherlands, in the province of Limburg. As of 2012, Beek has a population of about 16,400, of which about 8,800 live in the town of Beek.
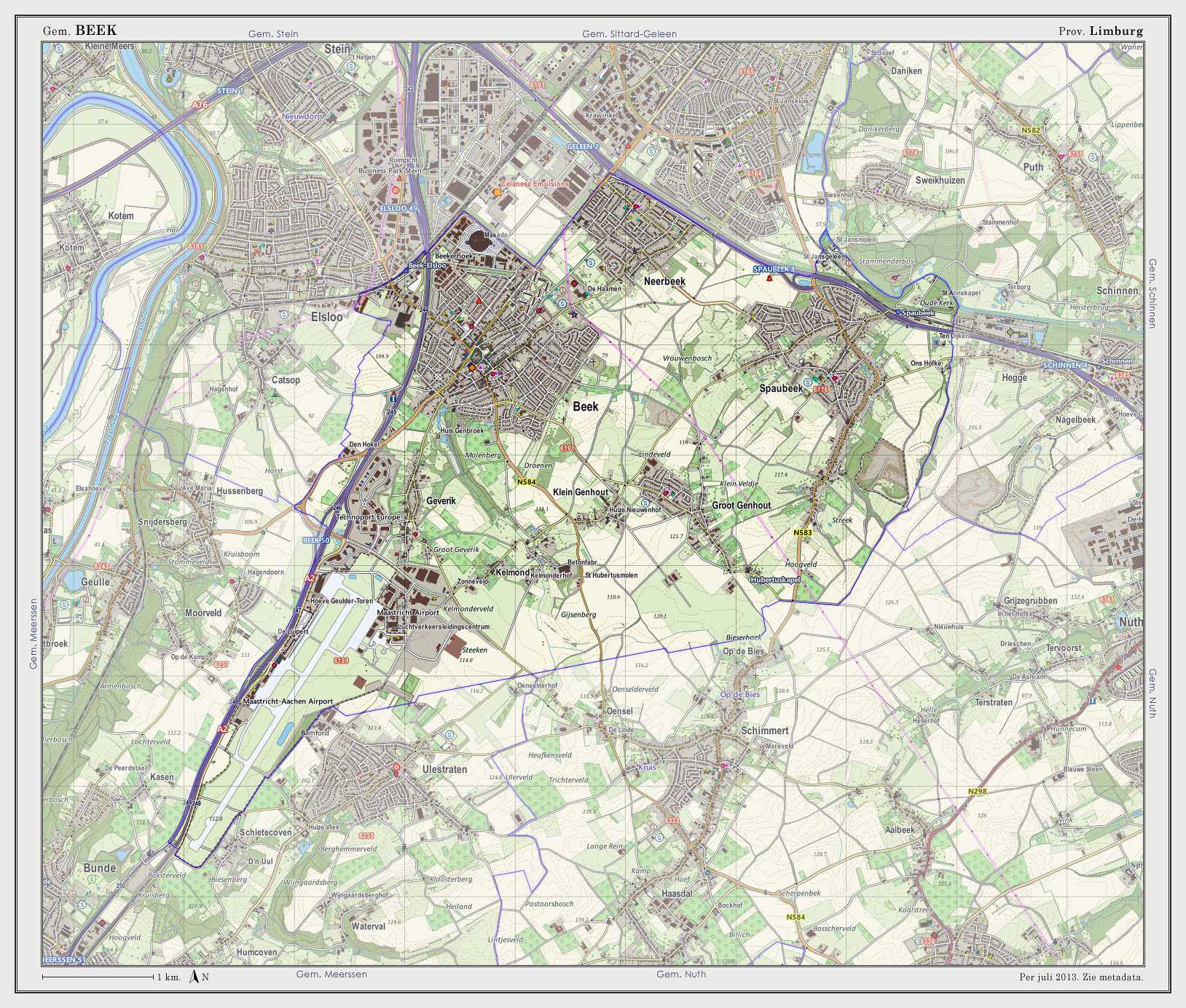
The municipality of Beek makes part of the region of South Limburg and lies between the city of Geleen in the north and Maastricht in the south, and lies furthermore southeast of interchange Kerensheide and the chemical industries of Chemelot. It has a slightly hilly landscape with altitudes differing between 70 and 120 metres (230 and 390 ft) above sea level, and has two small forests: Kelmonderbos between Beek and Kelmond, and Spaubekerbos near Spaubeek. The Keutelbeek flows through and has its source in the municipality of Beek.
Population centres
Settlements in the municipality of Beek (population within brackets on January 1, 2005).
Town:
- Beek (8,770)
|
Villages:
|
Hamlets:
|
History
In 1982, Spaubeek merged with Beek and the municipality got his current size. In 2005, an archaeological site was found between Beek and Neerbeek, consisting of the remainings of a settlement from 5,000 BC. Because of this, Beek is considered the eldest village in the Netherlands.
Buildings
Noteworthy buildings:
- Sint-Hubertusmolen (Mill of Saint Hubertus) in Klein Genhout, dated 1801-1802
- Sint-Hubertuskerk (Church of Saint Hubertus) in Groot Genhout, by architect Alphons Boosten
- Kasteel Genbroek, a castle near Geverik
Transportation
The municipality of Beek is surrounded by A2 motorway (Amsterdam-Belgian border) in the west and A76 motorway (Belgian border-German border) in the north.
The municipality has two railway stations:
- Beek-Elsloo railway station in the west
- Spaubeek railway station in the east
Beek also contains an airport:
- Maastricht Aachen Airport in the south
Economy
When KLM exel operated, its head office was on the grounds of Maastricht Aachen Airport in Beek.[5] When V Bird operated, its head office was on the grounds of the airport.[6]
Politics
The municipal council of Beek has 17 seats.
| Municipal council seats | |||||||||||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Party | 2010 | ||||||||||||||
| BBB-NDB[7] | 7 | ||||||||||||||
| CDA | 4 | ||||||||||||||
| Progressief Beek[8] | 4 | ||||||||||||||
| VVD | 2 | ||||||||||||||
| Total | 17 | ||||||||||||||
The executive board (2010-2014) consists of four persons:
- Ralf Krewinkel (PvdA) since May 1, 2011
Aldermen:
- Jan Bijen (Progressief Beek)
- Thijs van Es (BBB-NDB)
- Maurice Wierikx (BBB-NDB)
References
- Notes
- ↑ "Samenstelling en taakverdeling college van B&W" [Members and tasks of the board of mayor and aldermen] (in Dutch). Gemeente Beek. Retrieved 13 October 2013.
- ↑ "Kerncijfers wijken en buurten" [Key figures for neighbourhoods]. CBS Statline (in Dutch). CBS. 2 July 2013. Retrieved 11 July 2013.
- ↑ "Postcodetool for 6191KA". Actueel Hoogtebestand Nederland (in Dutch). Het Waterschapshuis. Retrieved 13 October 2013.
- ↑ "Bevolkingsontwikkeling; regio per maand" [Population growth; regions per month]. CBS Statline (in Dutch). CBS. 23 December 2013. Retrieved 24 December 2013.
- ↑ "Directory: World airlines." Flight International. 23–29 March 2004. 94.
- ↑ "Contact." V Bird. 24 June 2004. Retrieved on 18 July 2010.
- ↑ Burger Belangen Beek - Nieuwe Democraten Beek (BBB-NDB) is a local party.
- ↑ Literally translated: Progressive Beek, a cooperation of PvdA, GreenLeft, and D66.
- Bibliography
- (Dutch) Nederland Dichterbij: Limburg, Reader's Digest, 1995
External links
 Media related to Beek, Limburg at Wikimedia Commons
Media related to Beek, Limburg at Wikimedia Commons- Official website (Dutch)
 |
Stein | Sittard-Geleen |  | |
| |
Schinnen | |||
| ||||
| | ||||
| Meerssen | Nuth |
.svg.png)

