Battle of Juncal
| Battle of Juncal | |||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Part of Cisplatine War | |||||||

|
|||||||
|
|||||||
| Belligerents | |||||||
| Commanders and leaders | |||||||
| Strength | |||||||
| 1 Brigantine 11 Schooners | 1 Brigantine 5 Schooners |
||||||
| Casualties and losses | |||||||
| 12 ships captured 3 burnt casualties unknown | no ships lost 17 killed in action[1] |
||||||
The naval Battle of Juncal took place between a squadron of the newly independent United Provinces of the River Plate under command of William Brown and a squadron belonging to the Brazilian Empire, commanded by Sena Pereira. It spanned two days, from the 8th to the 9th of February, 1827, in the waters of the Rio de la Plata.
The two squadrons were initially of roughly equal strength, but because of superior command and control, and artillery training,[citation needed] the Argentines scored a decisive victory: out of 17 Brazilian vessels, 12—including the flagship with its admiral—were captured and 3 were burnt. Not a single Argentine vessel was lost.
In the aftermath of the battle, the Third Division, the arm of the Brazilian fleet tasked with controlling the Uruguay River and thus disrupting communications with the Argentine army then operating in the Banda Oriental, was completely destroyed. The result was the biggest naval victory for Argentina in the Cisplatine War
The situation before the battle
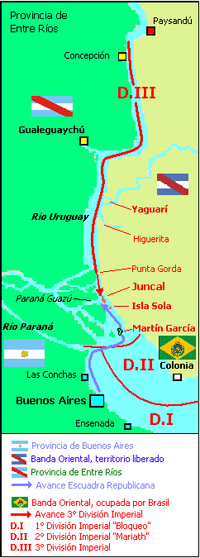
The division of the imperial fleet
During the second year of the Argentina-Brazil War, the Brazilians took advantage of their numerical superiority and divided their naval forces operating in the Rio de la Plata sector into three squadrons, or "divisions".
- The first division, "Bloqueo", was placed under the command of John Charles Pritz. It was tasked with blockading traffic to and from the principle port of Buenos Aires and secondary departure points such as Las Conchas, Ensenada de Barragán, and the mouth of the Salado River.
- The second division, named "Oriental" or "Mariath", was tasked with securing the Uruguayan coast from the mouth of the Uruguay River to the River Plate. The bulk of this division put under the command of the Frederico Mariath, who would later support the Third Division.
- The "Third Division", under the command of Jacinto Roque de Sena Pereira, was to remain in the Uruguay River in order to divide the Argentine front and exploit political fault lines between the province of Entre Ríos and Buenos Aires that had been exacerbated by the passing of the Unitary Constitution of 1826. By controlling the Uruguay River, the supply lines to an Argentine expeditionary force in the contested territory of Banda Oriental (modern Uruguay) would be cut, and the Brazilians would have freedom of maneuver for a later attack on the Argentine flank.
|
First Argentine advance
To confront the three threats, each of similar or superior strength to his own forces, William Brown acted rapidly to organize a squadron to advance past the mouth of the Uruguay, then find and destroy the Third Division.

Typical of Brown's audacity, the force he dispatched was in the best case only the equal of the Third Division, while the defense of Buenos Aires was clearly imperiled.
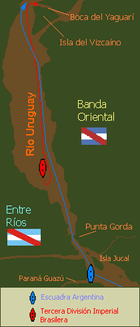
Impeded from gaining access to the narrow channel, Brown withdrew to the south towards Punta Gorda to wait for the Brazilians. He landed a small force on Vizcaino Island to secure it and send instructions to the militia of Santo Domingo de Soriano to cut supplies to the Brazilian fleet.[2] In response, the Brazilians withdrew further north to Concepción del Uruguay (then still usually called "Arroyo de la China") where they could secure supplies.
Worried about the menace that the Mariath Division posed to his rear, Brown decided to fully return to Buenos Aires in search of reinforcements for Martin Garcia Island. He ordered Rosales to return the Goleta Sarandi to Uruguay via the Paraná de las Palmas[3] while he finished the preparations, after which he rejoined the fleet by travelling aboard a small whaler.[4]
Preparations
On the 6th of January the fortification work was begun. The Mariath Division launched an advance on the island with the corvette Maceio and 9 other gunships. On the 18th Brown twice ordered his forces out to meet the Brazilian squadron and both times the Brazilians withdrew after an exchange of cannon fire.
Brown wanted on one side to lure the Third Division into combat, yet at the same time he didn't want the Mariath Division to join the Third or attack his rear. Helping him navigate the delicate situation was an excellent intelligence network which gave him daily updates on the movement of the Imperial fleet. Essentially, the emissary carrying Rodrigo Pinto Guedes' orders to Sena Periera had been co-opted by Argentine patriots in Montevideo, and as a result Brown received timely news of the Imperial fleet's intentions.[5] Thus, he took notice when Pinto Guerdes communicated to Sena Pereira the orders given to Mariath to advance towards the south. Brown deduced that the Third Division would descend the river on February 7 in order to link up with Mariath. Brown believed that the fortifications and batteries of Martin Garcia would be prepared by then, allowing him to block the Mariath Division while forcing the Third Division into battle.
The work at the new fort was duly accelerated; Brown himself worked as a master mason in the hold of the Santa Barbara.[5] On the 5th, the works were ready and in a solemn ceremony Brown named the fort "Constitución". In his speech to the garrison, he informed them that he expected the Argentine squadron to meet Sena Pereira within the next couple days.[6]
At the beginning of February there was word that the Third Division was taking on provisions at Arroyo de la China; by the third it had passed Paysandú and on the 6th it approached Higuerita (today's Nueva Palmira, where it arrived the next day. That same day, Brown outlined his plan and assigning each ship a role in the battle. At 10 that night, the vanguard of the Argentine fleet reached the mouth of the Paraná Guazú River and waited for the rest of the fleet to arrive.[6]
The battle
Combatants
Argentina (Brown)
15 vessels, 73 guns, approximately 750 men
- Sarandi 7 (Coe)
- Balcarce 23 (Seguí)
- Maldonado 8 (Drummond)
- Pepa 2 (Silva)
- Guanaco 8 (Granville)
- Union 10 (Malcolm)
- Uruguay 7 (Mason)
- 8 1-gun launches
Brazil (Pereira)
17 vessels, about 750 men
- Oriental 11 (flag) - Captured
- Januaria 14 - Captured
- Bertioga 8 - Captured
- 4 2-gun schooners - Captured
- 4 2-gun gunboats - Captured
- ? - Captured
- 3 vessels - Burnt
- 2 others

The Argentine squadron numbered 15 vessels, including three major ships: the flagship goleta Sarandí under the direct command of Brown, the goleta Maldonado under the command of the young Francisco Drummond—fiance of Brown's daughter—and the Bergantín Balcarce, with 14 cannons and under the command of Francisco José Seguí. Rounding out the squadron were the schooners La Pepa, under Calixto Silva, Guanaco (Guillermo Enrique Granville), Unión (Shannon Malcolm), the smack Uruguay (Guillermo Mason), and 8 gunboats. In total, 69 cannons and a crew of approximately 750 men.
The Brazilian squadron included 17 vessels: the flagship goleta Oriental under command of Jacinto Roque de Sena Pereira, the Bergantín Dona Januária under Pedro Antonio Carvalho, the goleta Bertioga under Lieutenant George Broom, the Liberdade do Sul under Lieutenant Augusto Venceslau da Silva Lisboa, the 12 de Outubro, the goleta Fortuna (a hospital ship), the Goleta Vitoria de Colonia, the goleta Itapoã under the command of lieutenant Germano Máximo de Souza Aranha, the goleta 7 de Março, the goleta Brocoió under Francisco de Paula Osório, the goleta 9 de Janeiro, the goleta 7 de Setembro, two gun schooners (the Atrevida and the Paraty) and the cañoneras Cananéia, Paranaguá, and Iguapé. In total, 65 guns and approximately 750 men. For the first and only time during the war, there was relative parity between the forces, or at least, the Brazilian advantage was not so great.[7]
Approach of the fleets
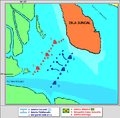
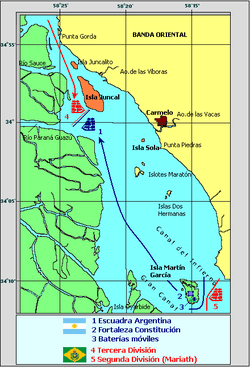
The Argentine squadron spent the night of February 7 anchored between Juncal Island and the west bank of the river. At dawn on the 8th the sails of the Brazilians were spotted descending the river, taking advantage of a gentle north wind. Brown gave the order to weigh anchors and place his ships in a line of battle arrayed obliquely to the southeast from Juncal Island. The goleta Sarandi formed the center of the line, with Maldonando in the vanguard and Balcarce in the rear.
The Brazilian fleet continued its advance until the wind died down around 11:30, at which point it anchored some 1,000 yards from the Argentine line, with the flagship Oriental in the center.
Beginning of the battle
The weather on the 8th was stormy, hot and humid, with light and variable winds; typical for that time of year in the litoral regions.
Sena Pereira anchored his ships and unleashed a fire ship toward the enemy fleet. However, this was promptly sunk by Argentine gunfire.[citation needed]
At noon Brown ordered forward a detachment of 6 of his gunboats, which could fire at a longer range than his other vessels with their 18 pounder guns. However the Argentine long guns had longer range and were manned by superior gunners. After exchanging fire for approximately two hours, a sudden sudestada(Sudestada (Southeast blow) is the Spanish name for a climatic phenomenon common to the Río de la Plata) separated the fleets and forced them to suspend the battle.
The Brazilians maintained the dominant, windward position; because the wind was blowing towards the Argentines, the Brazilians had the initiative. Sena Pereira duly tried to stage his ships in an attack line. However, the maneuvers of the vessels was disastrous: the goleta Liberdade do Sul grounded, while the Dona Januária left the formation and strayed within range of the fire of General Balcarce, the Sarandí, and 3 gunboats.

At 3 in the afternoon the wind again died down, and the action was again reduced to a long range artillery duel. Visibility was steadily reduced by the smoke of the guns, which were audible as far away as Buenos Aires and Colonia del Sacramento.
Once again a severe storm rolled in and the fleets struggled fruitlessly to maintain their positions. The General Balcarce began to settle, but succeeded in remaining afloat. Eventually the storm died down and was replaced by a northeast breeze. Sena Pereira attempted to take advantage of the new wind by retiring to the north to take up better positions.
Once again, the resulting maneuver was poor. The 12 de Outubro could only be saved by the help of the remaining ships, while the hospital ship Fortuna was unable to anchor and was blown towards the Argentine lines, where she was captured. As a result of the "Fortuna's" capture John Halstead Coe (comodoro Juan Coe) was freed after having been a prisoner on board since December 1826. It was midnight before the Brazilian squadron was fully reunited in a disorderly anchorage near Sola Island.[8][9]
|
Second day

Exhausted, the Brazilians were not able to lay any plans that night. At dawn, the captains of the fleet boarded the Oriental to decided the plan of battle; basically, to choose between fighting while maneuvering or to remain anchored. Sena Pereira did not make a decision and opted to choose his tactics as the situation developed.
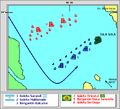
For his part, Brown was ready. At 8 am, with a southeast breeze, he ordered the Sarandí to run up a red flag, the signal for the Argentines to occupy the windward position, marshal into a battle line, and advance towards the Brazilians.
In response, Sena Pereira gave the order to form a battle line and drop anchor. However, once again, the result was confusion and disorder: some of the gunboat drifted out of formation and downwind. Sena Pereira, shouting ineffectively with a megaphone, tried to restore order. With the Argentines closing quickly and in good order, he changed his decision, now ordering his fleet to raise anchors and attempt to maneuver.
The Dona Januária, the Bertioga and the Oriental duly advanced on the approaching Argentines, but without the support of the rest of the squadron, which remained dispersed behind them. The three ships were quickly engaged by the General Balcarce and the Argentine vanguard. The Argentine fire was effective: a shot from the General Balcarce soon destroyed the Januária's bowsprit, and another knocked down her foremast, causing such disruption that she was on the point of foundering. Sena Pereira ordered the small schooner Vitoria de Colonia to take Januária under tow, but the schooner Uruguay blocked the way.
The attack was so rapid and devastating that the captain of the Januária, Lieutenant Pedro Antonio Carvalho, ordered his cannons to concentrate on the Argentine artillery while a team remained to attempt to scuttle the ship and he departed with the crew in boats towards the east.[10]
For his part, Drummond, commander of the Maldonado, attacked the Bertioga, under the command of his old comrade, Lieutenant George Broom. An accurate shot from a heavy Argentine gun knocked down the main mast of the Bertioga and the ship, now unable to maneuver, was forced to surrender after a half hour of combat.

Throughout this time, the General Balcarce under Francisco Seguí led a combined attack against the Oriental. The intense crossing fire knocked out the Oriental's cannons, half of its carronades, and caused 37 casualties, including Sena Pereira.
Despite the losses the Brazilians refused to strike their colors, which had been nailed to the mast. Finally the ship was boarded and Seguí accepted the sword of the Brazilian commander as a sign of surrender.
With the surrender of the Oriental, the remaining vessels of the Brazilian fleet disengaged and attempted to flee, turning the Argentine victory into a rout.
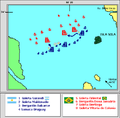
Brown transferred his flag to the General Balcarce and ordered the Sarandí and the gunboats to give chase to the broken Brazilian squadron. He boarded the surrendered Brazilian flagship and was presented with the sword of the Brazilian commander, at which he commended Francisco Seguí with the words "Usted es el héroe" ("You are the hero").
Brown retired with four of the prizes towards Martín García to repair damages, write his report, and prepare for the eventual attempt of the Mariath Division, stationed to the south of the island, to force its way north.
|
Martín García

Mariath's orders were to use his 10 vessels to overcome the fortifications at Martín García, attack the Argentine rear, and reinforce the Third Division.[11]
Although he could already hear cannon fire in the distance, Mariath moved slowly and with great caution. As the main Argentine battery (consisting of 9 24 pounders) were on the west side, covering the Grand Canal, Mariath sent a schooner down the Canal del Infierno, the passage to the east of the island, in order to determine if the water was deep enough for his squadron. In response, the garrison moved its mobile battery (consisting of 2 12 pounders and a Congreve rocket launcher) to the east to defend against a possible landing.[12]
The move proved unnecessary, however, as the Brazilian vessel ran hard aground. Mariath was thus dissuaded from taking the eastern route, although his pilot thought it still possible. He commenced an artillery duel with the main batteries, until the storm obliged him to suspend the indecisive action.
At this point, Mariath believed that the shallow water, the unpredictable weather, and the formidable batteries at Martín García made passing the island too risky. Thus, on the 9th, while the Third Division was being destroyed, the Mariath Division remained in the distance as a spectator. On the 10th, Mariath finally decided to withdraw in the direction of Colonia de Sacramento, where he arrived a week later.
The first news of the defeat reached the Brazilians on the morning of February 12, when 8 survivors of the Oriental arrived. Their stories were confirmed by the boat of Lieutenant Carvalho, and later, on the 14th, by the arrival of the only survivors, the schooner Vitoria de Colonia and a gunboat, escorted by the frigate Dona Paula.[13]
The chase
On the day following the battle, the schooner Brocoio was pursued and captured, in addition to two gunboats (the Paraty and the Iguape) that ran aground in the mouth of the Paraná River and were likewise made Argentine prizes.
At this point the Third Division was reduced to the schooners Liberdade do Sul, Itapoã, 7 de Março, 9 de Janeiro and 7 de Setembro, the gunboats Cananéia y Paranaguá, and an assortment of smaller launches. All of these surviving and functioning vessels were in full flight north up the Uruguay River. The German skipper of the schooner Itapoã, a Lieutenant Souza Aranha, took command of the reduced squadron, which soon suffered further setbacks: the schooners Liberdade do Sul, the Itapoã and the 7 de Março all ran aground and were burnt to prevent capture.[14] The dwindling fleet continued north with a total of 351 officers and crew piled aboard, with the intent of surrendering to the authorities of the Province of Entre Ríos.
Rapidly completing the reorganization of his forces, and in face of the withdrawal of the Mariath Division, Brown quickly returned his attention to the survivors of Juncal. Already on the 14th he had returned to the Uruguay River in the Maldonado, accompanied by some 6 other vessels. On the 15th he arrived at Fray Bentos and received the news that Souza Aranha, after casting his cannons into the sea, had surrendered his ships to the governor of Entre Ríos. Brown anchored outside Gualeguaychú and asked for the handover of the ships and prisoners. However, the Entre Ríos authorities resisted these demands, foreseeing that such a capitulation would have grave results for their own cherished autonomy. In response to this rebuff Brown mounted a successful combined land and sea operation which resulted in the final capture of the Brazilian fleet.
| Vessels of the Third Division | ||
|---|---|---|
| Name of Vessel | Result of Battle | Final disposition |
| Goleta Oriental | Captured | Renamed 29 de Diciembre |
| Goleta Bertioga | Captured | Renamed 9 de Febrero |
| Bergantín Dona Januária | Captured | Renamed 8 de Febrero |
| Goleta Brocoió | Captured in the Paraná | Renamed 30 de Julio |
| Cañonera Paraty | Captured in the Paraná | Renamed Cañonera N° 13 |
| Cañonera Iguapé | Captured in the Paraná | Renamed Cañonera N° 4 |
| Goleta 12 de Outubro | Captured at Entre Ríos | Renamed Goleta 18 de Enero |
| Goleta 9 de Janeiro | Captured at Entre Ríos | Renamed 11 de Junio |
| Goleta 7 de Setembro | Captured at Entre Ríos | Renamed 25 de Febrero |
| Cañonera Cananéia | Captured at Entre Ríos | Renamed Cañonera N° 7 |
| Cañonera Paranaguá | Captured at Entre Ríos | Renamed Cañonera N° 6 |
| Goleta Libertade do Sul | Burnt | - |
| Goleta Itapoã | Burnt | - |
| Goleta 7 de Março | Burnt | - |
| Goleta Fortuna | Captured | Recaptured by Brazilian forces |
| Goleta Vitoria de Colonia | Survivor | - |
| Cañonera Atrevida | Survivor | - |
Aftermath

With 12 vessels captured, three burnt, and only two survivors, the battle imposed a significant loss on the Brazilians and represented the greatest triumph of the Argentine fleet.
In the larger scope of the war, the victory frustrated the Brazilian attempt to cut the lines of communication to the expeditionary force. In addition, it denied the Brazilians use of the Uruguay River to stage an offensive against the Argentine litoral, an offensive which at a minimum could have detached the litoral provinces from the Confederation and at worst may have threatened its existence.
In Buenos Aires, Brown was received with bonfires and orchestras. He was elevated to most popular figure of the Republic.
Sena Pereira remained a prisoner of Brown, who recognized his valor and commended him to the Argentine government "for his brave and intrepid defense, performed by a soldier". However, Pereira refused to give any pledge and eventually escaped. At the beginning of 1829, he would be one of those who handed over the plaza of Montevideo to the westerners.
The republican naval victory off Juncal was rapidly followed on land by Ituzaingó (20 Feb) and Carmen de Patagones (28 Feb). After this, the conflict ground to a halt, as the Brazilian Empire had been defeated in various fronts while Argentina was incapable of taking advantage of the situation given that the Naval blockade still persisted, especially after the Battle of Monte Santiago which almost fully destroyed the Navy of the United Provinces of the Rio de la Plata, and also given that Montevideo and Colonia, the two largest cities in the Banda Oriental, were still under control by the Empire of Brazil.
This situation would continue until the Preliminary Peace Convention, by which Oriental Province became the independent Western State of Uruguay.
References
Notes
- ↑ 1.0 1.1 1.2 El País (Uruguay) (2005). "Batallas que hicieron historia", Juncal. Cañonazos en la tormenta. Montevideo.
- ↑ Carranza, Ángel Justiniano Campañas Navales de la República Argentina, Volumen IV (Notas Complementarias a Tomos 3 y 4, 2nd Edition, Secretaria de Estado de Marina, Buenos Aires, 1962. pp232 and 298.
- ↑ Carranza, Ángel Justiniano Campañas Navales de la República Argentina, Volumen IV (Notas Complementarias a Tomos 3 y 4, 2nd Edition, Secretaria de Estado de Marina, Buenos Aires, 1962. p298. Also, Rodríguez, Horacio. Leonardo Rosales .
- ↑ Carranza, Ángel Justiniano Campañas Navales de la República Argentina, Volumen IV (Notas Complementarias a Tomos 3 y 4, 2nd Edition, Secretaria de Estado de Marina, Buenos Aires, 1962. p234.
- ↑ 5.0 5.1 Carranza, Ángel Justiniano Campañas Navales de la República Argentina, Volumen IV (Notas Complementarias a Tomos 3 y 4, 2nd Edition, Secretaria de Estado de Marina, Buenos Aires, 1962. p235
- ↑ 6.0 6.1 Carranza, Ángel Justiniano Campañas Navales de la República Argentina, Volumen IV (Notas Complementarias a Tomos 3 y 4, 2nd Edition, Secretaria de Estado de Marina, Buenos Aires, 1962. p236
- ↑ Carranza. Campañas Navales. Buenos Aires, 1962. pp. 185-186, 236-238, 247, 300-302. See also, Toscano, Jorge, Victoria Argentina en el Juncal, Boletín del Centro Naval N° 815, 2006, páginas 473-477. as well as Historical Handbook of World Navies and Navíos de Guerra, en naval.com.br .
- ↑ A number of sources--primarily Brian Vale's work and those which cite him--refer to "Isla Solís" instead of "Isla Sola". However, Solís is much farther south in the Rio de la Plata, further south even than Martín García. (34°13′58″S 58°19′36″W / 34.23278°S 58.32667°W) Due to the distance and the strategy of the Brazilian command its very likely that this is a mistake. Moreover, first person accounts, such as that of D. Francisco Seguí (found in Carraza, Campañas Navales. p237.) clearly indicate Sola Island.
- ↑ For accounts of the actions of the first day, see Carranza pp236 and 299. and Toscano, Jorge, Victoria Argentina en el Juncal, Boletín del Centro Naval N° 815, 2006, p474.
- ↑ (Toscano, Jorge, obra citada, página 477).
- ↑ For a description of Mariath's actions during the battle and the days preceding, see Carranza, pp234 and 299-300, and Toscano, Jorge, p476.
- ↑ This was the greatest fear of the Argentine garrison. While the cannons of the Brazilian squadron would have enough range to bombard the fort from the far side of the island, it would be difficult to transverse the fortification's fixed batteries and return effective fire. In addition, the garrison's infantry forces were limited and inexperienced, numbering around 100 (From Diario de Noticias del Comandante del Puerto de Buenos Aires, Archivo General de la Nación VII-7-6-D), and the land defenses were incomplete, lacking a ditch or moat for two of the walls. Mariath knew the limitations of the Argentine artillery and counted on his superior firepower, his ability to block access to Buenos Aires, and his capability to land a veteran force 2 to 3 times larger than the Argentine garrison. See also Carranza, p300.
- ↑ See Toscano, Jorge, p477. With respect to Dona Paula, a frigate with 36 heavy cannons: although it is mentioned in some sources, she is not believed to have participated in the battle or to have played a role in the Third Division.
- ↑ In respect to the Brazilian ships burnt, see Carranza, pp237-239 and 300-301 and Toscano, Jorge p477.
Bibliography
- Carranza, Ángel Justiniano, Campañas Navales de la República Argentina, Volumen IV (Notas Complementarias a Tomos 3 y 4, 2° Edición, Secretaria de Estado de Marina, Buenos Aires, 1962
- Arguindeguy, Pablo E. CL, y Rodríguez, Horacio CL; Buques de la Armada Argentina 1810-1852 sus commandos y operaciones, Buenos Aires, Instituto Nacional Browniano, 1999
- Vale, Brian, Una guerra entre ingleses, Instituto De Publicaciones Navales, 2005, ISBN 950-899-057-0
- Toscano, Jorge, Victoria Argentina en el Juncal, Boletín del Centro Naval N° 815, 2006
- Castagnin, Daniel Ítalo, Visión estratégica del teatro de operaciones platense (1814–1828), Revista del Mar N° 162, Instituto Nacional Browniano, 2007
External links
- Ships of the United Provinces of the Rio de la Plata (Spanish)
- Historical Handbook of World Navies
- Ships of War (Portuguese)
- Article on the foreign origin of sailors involved in the Argentina-Brazil War (Spanish)
- Official site of the Argentine Navy (Spanish)
- Official site of Brazilian Navy (Portuguese)