Barometric formula
The barometric formula, sometimes called the exponential atmosphere or isothermal atmosphere, is a formula used to model how the pressure (or density) of the air changes with altitude.
Pressure equations

There are two different equations for computing pressure at various height regimes below 86 km (or 278,400 feet). The first equation is used when the value of Standard Temperature Lapse Rate is not equal to zero; the second equation is used when standard temperature lapse rate equals zero.
Equation 1:
Equation 2:
where
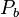 = Static pressure (pascals)
= Static pressure (pascals)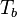 = Standard temperature (K)
= Standard temperature (K) = Standard temperature lapse rate -0.0065 (K/m) in ISA
= Standard temperature lapse rate -0.0065 (K/m) in ISA = Height above sea level (meters)
= Height above sea level (meters)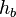 = Height at bottom of layer b (meters; e.g.,
= Height at bottom of layer b (meters; e.g.,  = 11,000 meters)
= 11,000 meters)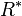 = Universal gas constant for air: 8.31432 N·m /(mol·K)
= Universal gas constant for air: 8.31432 N·m /(mol·K)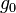 = Gravitational acceleration (9.80665 m/s2)
= Gravitational acceleration (9.80665 m/s2) = Molar mass of Earth's air (0.0289644 kg/mol)
= Molar mass of Earth's air (0.0289644 kg/mol)
Or converted to Imperial units:[1]
where
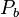 = Static pressure (inches of mercury, inHg)
= Static pressure (inches of mercury, inHg)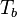 = Standard temperature (K)
= Standard temperature (K) = Standard temperature lapse rate (K/ft)
= Standard temperature lapse rate (K/ft) = Height above sea level (ft)
= Height above sea level (ft)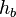 = Height at bottom of layer b (feet; e.g.,
= Height at bottom of layer b (feet; e.g.,  = 36,089 ft)
= 36,089 ft)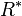 = Universal gas constant; using feet, kelvins, and (SI) moles: 8.9494596×104 lb·ft2/(lbmol·K·s2)
= Universal gas constant; using feet, kelvins, and (SI) moles: 8.9494596×104 lb·ft2/(lbmol·K·s2)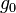 = Gravitational acceleration (32.17405 ft/s2)
= Gravitational acceleration (32.17405 ft/s2) = Molar mass of Earth's air (28.9644 lb/lbmol)
= Molar mass of Earth's air (28.9644 lb/lbmol)
The value of subscript b ranges from 0 to 6 in accordance with each of seven successive layers of the atmosphere shown in the table below. In these equations, g0, M and R* are each single-valued constants, while P, L, T, and h are multivalued constants in accordance with the table below. The values used for M, g0, and 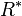 are in accordance with the U.S. Standard Atmosphere, 1976, and the value for
are in accordance with the U.S. Standard Atmosphere, 1976, and the value for 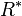 in particular does not agree with standard values for this constant.[2] The reference value for Pb for b = 0 is the defined sea level value, P0 = 101325 pascals or 29.92126 inHg. Values of Pb of b = 1 through b = 6 are obtained from the application of the appropriate member of the pair equations 1 and 2 for the case when
in particular does not agree with standard values for this constant.[2] The reference value for Pb for b = 0 is the defined sea level value, P0 = 101325 pascals or 29.92126 inHg. Values of Pb of b = 1 through b = 6 are obtained from the application of the appropriate member of the pair equations 1 and 2 for the case when  .:[2]
.:[2]
| Subscript b | Height above sea level | Static pressure | Standard temperature (K) |
Temperature lapse rate | |||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| (m) | (ft) | (pascals) | (inHg) | (K/m) | (K/ft) | ||
| 0 | 0 | 0 | 101325.00 | 29.92126 | 288.15 | -0.0065 | -0.0019812 |
| 1 | 11,000 | 36,089 | 22632.10 | 6.683245 | 216.65 | 0.0 | 0.0 |
| 2 | 20,000 | 65,617 | 5474.89 | 1.616734 | 216.65 | 0.001 | 0.0003048 |
| 3 | 32,000 | 104,987 | 868.02 | 0.2563258 | 228.65 | 0.0028 | 0.00085344 |
| 4 | 47,000 | 154,199 | 110.91 | 0.0327506 | 270.65 | 0.0 | 0.0 |
| 5 | 51,000 | 167,323 | 66.94 | 0.01976704 | 270.65 | -0.0028 | -0.00085344 |
| 6 | 71,000 | 232,940 | 3.96 | 0.00116833 | 214.65 | -0.002 | -0.0006096 |
Density equations
The expressions for calculating density are nearly identical to calculating pressure. The only difference is the exponent in Equation 1.
There are two different equations for computing density at various height regimes below 86 geometric km (84,852 geopotential meters or 278,385.8 geopotential feet). The first equation is used when the value of Standard Temperature Lapse rate is not equal to zero; the second equation is used when Standard Temperature Lapse rate equals zero.
Equation 1:
Equation 2:
where
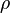 = Mass density (kg/m3)
= Mass density (kg/m3) = Standard temperature (K)
= Standard temperature (K)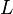 = Standard temperature lapse rate (see table below) (K/m) in ISA
= Standard temperature lapse rate (see table below) (K/m) in ISA = Height above sea level (geopotential meters)
= Height above sea level (geopotential meters)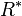 = Universal gas constant for air: 8.31432 N·m/(mol·K)
= Universal gas constant for air: 8.31432 N·m/(mol·K)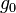 = Gravitational acceleration (9.80665 m/s2)
= Gravitational acceleration (9.80665 m/s2) = Molar mass of Earth's air (0.0289644 kg/mol)
= Molar mass of Earth's air (0.0289644 kg/mol)
Or converted to English gravitational foot-pound-second units:[1]
Where
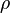 = Mass density (slug/ft3)
= Mass density (slug/ft3) = Standard temperature (kelvins)
= Standard temperature (kelvins)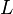 = Standard temperature lapse rate (degrees Celsius per foot)
= Standard temperature lapse rate (degrees Celsius per foot) = Height above sea level (geopotential feet)
= Height above sea level (geopotential feet) = Universal gas constant (8.9494596×104 ft2/(s·°C))
= Universal gas constant (8.9494596×104 ft2/(s·°C))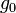 = Gravitational acceleration (32.17405 ft/s2)
= Gravitational acceleration (32.17405 ft/s2)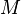 = Molar mass of Earth's air (0.0289644 kg/mol)
= Molar mass of Earth's air (0.0289644 kg/mol)
The value of subscript b ranges from 0 to 6 in accordance with each of seven successive layers of the atmosphere shown in the table below. The reference value for 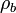 for b = 0 is the defined sea level value,
for b = 0 is the defined sea level value, 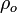 = 1.2250 kg/m3 or 0.0023768908 slug/ft3. Values of
= 1.2250 kg/m3 or 0.0023768908 slug/ft3. Values of 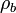 of b = 1 through b = 6 are obtained from the application of the appropriate member of the pair equations 1 and 2 for the case when
of b = 1 through b = 6 are obtained from the application of the appropriate member of the pair equations 1 and 2 for the case when  [2]
[2]
In these equations, g0, M and R* are each single-valued constants, while  , L, T and h are multi-valued constants in accordance with the table below. The values used for M, g0 and R* are in accordance with the U.S. Standard Atmosphere, 1976, and that the value for R* in particular does not agree with standard values for this constant.[2]
, L, T and h are multi-valued constants in accordance with the table below. The values used for M, g0 and R* are in accordance with the U.S. Standard Atmosphere, 1976, and that the value for R* in particular does not agree with standard values for this constant.[2]
| Subscript b | Height Above Sea Level (h) | Mass Density ( ) ) |
Standard Temperature (T') (K) |
Temperature Lapse Rate (L) | |||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| (m) | (ft) | (kg/m3) | (slugs/ft3) | (K/m) | (K/ft) | ||
| 0 | 0 | 0 | 1.2250 | 2.3768908 x 10−3 | 288.15 | -0.0065 | -0.0019812 |
| 1 | 11,000 | 36,089.24 | 0.36391 | 7.0611703 x 10−4 | 216.65 | 0.0 | 0.0 |
| 2 | 20,000 | 65,616.79 | 0.08803 | 1.7081572 x 10−4 | 216.65 | 0.001 | 0.0003048 |
| 3 | 32,000 | 104,986.87 | 0.01322 | 2.5660735 x 10−5 | 228.65 | 0.0028 | 0.00085344 |
| 4 | 47,000 | 154,199.48 | 0.00143 | 2.7698702 x 10−6 | 270.65 | 0.0 | 0.0 |
| 5 | 51,000 | 167,322.83 | 0.00086 | 1.6717895 x 10−6 | 270.65 | -0.0028 | -0.00085344 |
| 6 | 71,000 | 232,939.63 | 0.000064 | 1.2458989 x 10−7 | 214.65 | -0.002 | -0.0006096 |
Derivation
The barometric formula can be derived fairly easily using the ideal gas law:
When density is known:
And assuming that all pressure is hydrostatic:
Dividing the  by the
by the  expression we get:
expression we get:
Integrating this expression from the surface to the altitude z we get:
Assuming constant temperature, molar mass, and gravitational acceleration, we get the barometric formula:
In this formulation, 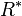 is the gas constant, and the term
is the gas constant, and the term 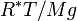 gives the scale height (approximately equal to 8.4 km for the troposphere).
gives the scale height (approximately equal to 8.4 km for the troposphere).
(For exact results, it should be remembered that atmospheres containing water do not behave as an ideal gas. See real gas or perfect gas or gas for further understanding)
Estimating the temperature
Assuming that the only energy source is from the sun, and the albedo is constant throughout the planet, we can get an estimate of a constant temperature.
The solar energy flux at a distance  can be estimated as:
can be estimated as:
where  is the solar luminosity. The actual incoming energy can be estimated as
is the solar luminosity. The actual incoming energy can be estimated as
where  is the albedo of the planet.
is the albedo of the planet.  is the radius of the planet and
is the radius of the planet and  is the distance to the Sun in astronomical units.
The outgoing energy can be estimated using the Stefan-Boltzmann's law
is the distance to the Sun in astronomical units.
The outgoing energy can be estimated using the Stefan-Boltzmann's law
where 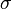 is the Stefan–Boltzmann constant and
is the Stefan–Boltzmann constant and 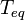 is the temperature at equilibrium.
Solving the equation:
is the temperature at equilibrium.
Solving the equation:
leads to the following estimate of a planet's temperature
which for Earth is about 255 K or −18 °C
See also
References
- ↑ 1.0 1.1 Mechtly, E. A., 1973: The International System of Units, Physical Constants and Conversion Factors. NASA SP-7012, Second Revision, National Aeronautics and Space Administration, Washington, D.C.
- ↑ 2.0 2.1 2.2 2.3 U.S. Standard Atmosphere, 1976, U.S. Government Printing Office, Washington, D.C., 1976. (Linked file is very large.)
![{P}=P_{b}\cdot \left[{\frac {T_{b}}{T_{b}+L_{b}\cdot (h-h_{b})}}\right]^{{\textstyle {\frac {g_{0}\cdot M}{R^{*}\cdot L_{b}}}}}](/2014-wikipedia_en_all_02_2014/I/media/8/d/7/d/8d7d6f94a14ff782b294356960b3c3b9.png)
![P=P_{b}\cdot \exp \left[{\frac {-g_{0}\cdot M\cdot (h-h_{b})}{R^{*}\cdot T_{b}}}\right]](/2014-wikipedia_en_all_02_2014/I/media/f/f/d/2/ffd268c00fb0afdd3ccc307436a73ebc.png)
![{\rho }=\rho _{b}\cdot \left[{\frac {T_{b}+L_{b}\cdot (h-h_{b})}{T_{b}}}\right]^{{\left(-{\frac {g_{0}\cdot M}{R^{*}\cdot L_{b}}}\right)-1}}](/2014-wikipedia_en_all_02_2014/I/media/7/4/0/2/7402c5bd4434ac8900fd9fc53e4027f8.png)
![{\rho }=\rho _{b}\cdot \exp \left[{\frac {-g_{0}\cdot M\cdot (h-h_{b})}{R^{*}\cdot T_{b}}}\right]](/2014-wikipedia_en_all_02_2014/I/media/2/8/5/2/2852fc7418a747680613fd72f376fffe.png)
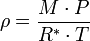
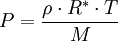
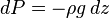
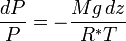

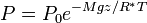
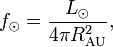



![T_{{eq}}={\sqrt[ {4}]{{\frac {L_{\odot }(1-\alpha )}{16\pi \sigma R_{{\mathrm {AU}}}^{2}}}}}](/2014-wikipedia_en_all_02_2014/I/media/9/6/a/2/96a21d5f21b6432f82879d4052fc4cc2.png)