Barium oxalate
| Barium oxalate | |
|---|---|
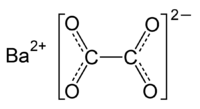 | |
| Identifiers | |
| CAS number | 516-02-9 |
| PubChem | 68201 |
| ChemSpider | 61508 |
| Jmol-3D images | {{#if:[Ba+2].[O-]C(=O)C([O-])=O|Image 1 |
| |
| |
| Properties | |
| Molecular formula | BaC2O4 |
| Molar mass | 225.346 g/mol |
| Density | 2.658 g/cm3 |
| Melting point | 400 °C (decomp) |
| Solubility in water | 0.9290 mg/L |
| Except where noted otherwise, data are given for materials in their standard state (at 25 °C (77 °F), 100 kPa) | |
| Infobox references | |
Barium oxalate, a Barium salt of oxalic acid, is a white odourless powder that is sometimes used as a green pyrotechnic colorant generally in specialized pyrotechnic compositions containing magnesium.
Though largely stable, it can be reactive with strong acids. A mild skin irritant, the substance is considered toxic when ingested, causing nausea, vomiting, renal failure and injury to the gastrointestinal tract. Its molecular structure is written as C2BaO4. The raw materials that are required to prepare Barium oxalate are oxalic acid, Barium hydroxide octahydrate, and Barium hydroxide.
It can also be prepared alternatively by using an oxalic acid solution and a Barium chloride solution, with the reaction as follows:
BaCl2 + H2C2O2 → BaC2O4↓ + 2 HCl
It is different from most pyrotechnic colorants in that it is a reducing agent, and not an oxidizing agent. It is extremely insoluble in water and converts to the oxide form when heated.
External sources
| |||||