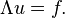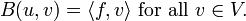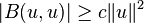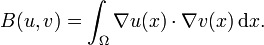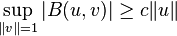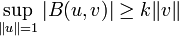Babuška–Lax–Milgram theorem
In mathematics, the Babuška–Lax–Milgram theorem is a generalization of the famous Lax–Milgram theorem, which gives conditions under which a bilinear form can be "inverted" to show the existence and uniqueness of a weak solution to a given boundary value problem. The result is named after the mathematicians Ivo Babuška, Peter Lax and Arthur Milgram.
Background
In the modern, functional-analytic approach to the study of partial differential equations, one does not attempt to solve a given partial differential equation directly, but by using the structure of the vector space of possible solutions, e.g. a Sobolev space Wk,p. Abstractly, consider two real normed spaces U and V with their continuous dual spaces U∗ and V∗ respectively. In many applications, U is the space of possible solutions; given some partial differential operator Λ : U → V∗ and a specified element f ∈ V∗, the objective is to find a u ∈ U such that
However, in the weak formulation, this equation is only required to hold when "tested" against all other possible elements of V. This "testing" is accomplished by means of a bilinear function B : U × V → R which encodes the differential operator Λ; a weak solution to the problem is to find a u ∈ U such that
The achievement of Lax and Milgram in their 1954 result was to specify sufficient conditions for this weak formulation to have a unique solution that depends continuously upon the specified datum f ∈ V∗: it suffices that U = V is a Hilbert space, that B is continuous, and that B is strongly coercive, i.e.
for some constant c > 0 and all u ∈ U.
For example, in the solution of the Poisson equation on a bounded, open domain Ω ⊂ Rn,
the space U could be taken to be the Sobolev space H01(Ω) with dual H−1(Ω); the former is a subspace of the Lp space V = L2(Ω); the bilinear form B associated to −Δ is the L2(Ω) inner product of the derivatives:
Hence, the weak formulation of the Poisson equation, given f ∈ L2(Ω), is to find uf such that
Statement of the theorem
In 1971, Babuška provided the following generalization of Lax and Milgram's earlier result, which begins by dispensing with the requirement that U and V be the same space. Let U and V be two real Hilbert spaces and let B : U × V → R be a continuous bilinear functional. Suppose also that B is weakly coercive: for some constant c > 0 and all u ∈ U,
and, for 0 ≠ v ∈ V, for some positive constant k,
Then, for all f ∈ V∗, there exists a unique solution u = uf ∈ U to the weak problem
Moreover, the solution depends continuously on the given datum:
See also
References
- Babuška, Ivo (1970/1971). "Error-bounds for finite element method". Numerische Mathematik 16: 322–333. doi:10.1007/BF02165003. ISSN 0029-599X. MR 0288971.
- Lax, Peter D.; Milgram, Arthur N. (1954). "Parabolic equations". Contributions to the theory of partial differential equations. Annals of Mathematics Studies, no. 33. Princeton, N. J.: Princeton University Press. pp. 167–190. MR 0067317.
External links
- Roşca, Ioan (2001), "Babuška–Lax–Milgram theorem", in Hazewinkel, Michiel, Encyclopedia of Mathematics, Springer, ISBN 978-1-55608-010-4