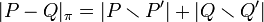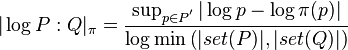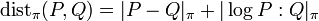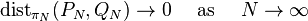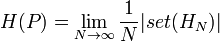Asymptotic equipartition property
In information theory, the asymptotic equipartition property (AEP) is a general property of the output samples of a stochastic source. It is fundamental to the concept of typical set used in theories of compression.
Roughly speaking, the theorem states that although there are many series of results that may be produced by a random process, the one actually produced is most probably from a loosely defined set of outcomes that all have approximately the same chance of being the one actually realized. (This is a consequence of the law of large numbers and ergodic theory.) Although there are individual outcomes which have a higher probability than any outcome in this set, the vast number of outcomes in the set almost guarantees that the outcome will come from the set. One way of intuitively understanding the property is through Cramér's large deviation theorem, which states that the probability of a large deviation from mean decays exponentially with the number of samples. Such results are studied in large deviations theory; intuitively, it is the large deviations that would violate equipartition, but these are unlikely.
In the field of pseudorandom number generation, a candidate generator of undetermined quality whose output sequence lies too far outside the typical set by some statistical criteria is rejected as insufficiently random. Thus, although the typical set is loosely defined, practical notions arise concerning sufficient typicality.
Definition
Given a discrete-time stationary ergodic stochastic process X on the probability space (Ω, B, p), AEP is an assertion that
where 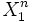 denotes the process limited to duration {1, ..., n}, and H(X) or simply H denotes the entropy rate of X, which must exist for all discrete-time stationary processes including the ergodic ones. AEP is proved for finite-valued (i.e. |Ω| < ∞) stationary ergodic stochastic processes in the Shannon-McMillan-Breiman theorem using the ergodic theory and for any i.i.d. sources directly using the law of large numbers in both the discrete-valued case (where H is simply the entropy of a symbol) and the continuous-valued case (where H is the differential entropy instead). The definition of AEP can also be extended for certain classes of continuous-time stochastic processes for which a typical set exists for long enough observation time. The convergence is proven almost sure in all cases.
denotes the process limited to duration {1, ..., n}, and H(X) or simply H denotes the entropy rate of X, which must exist for all discrete-time stationary processes including the ergodic ones. AEP is proved for finite-valued (i.e. |Ω| < ∞) stationary ergodic stochastic processes in the Shannon-McMillan-Breiman theorem using the ergodic theory and for any i.i.d. sources directly using the law of large numbers in both the discrete-valued case (where H is simply the entropy of a symbol) and the continuous-valued case (where H is the differential entropy instead). The definition of AEP can also be extended for certain classes of continuous-time stochastic processes for which a typical set exists for long enough observation time. The convergence is proven almost sure in all cases.
AEP for discrete-time i.i.d. sources
Given X is an i.i.d. source, its time series X1, ..., Xn is i.i.d. with entropy H(X) in the discrete-valued case and differential entropy in the continuous-valued case. The weak law of large numbers gives the AEP with convergence in probability,
since the entropy is equal to the expectation of
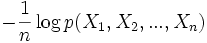 .
.
The strong law of large numbers asserts the stronger almost sure convergence,
which implies the result from the weak law of large numbers.
AEP for discrete-time finite-valued stationary ergodic sources
Consider a finite-valued sample space Ω, i.e. |Ω| < ∞, for the discrete-time stationary ergodic process  defined on the probability space (Ω, B, p). The AEP for such stochastic source, known as the Shannon-McMillan-Breiman theorem, can be shown using the sandwich proof by Algoet and Cover outlined as follows:
defined on the probability space (Ω, B, p). The AEP for such stochastic source, known as the Shannon-McMillan-Breiman theorem, can be shown using the sandwich proof by Algoet and Cover outlined as follows:
- Let x denote some measurable set x = X(A) for some A ∈ B
- Parameterize the joint probability by n and x as
- Parameterize the conditional probability by i, k and x as
- Take the limit of the conditional probability as k → ∞ and denote it as
- Argue the two notions of entropy rate
- exist and are equal for any stationary process including the stationary ergodic process X. Denote it as H.
- Argue that both
- where i is the time index, are stationary ergodic processes, whose sample means converge almost surely to some values denoted by Hk and H∞ respectively.
- Define the k-th order Markov approximation to the probability
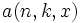 as
as
- Argue that
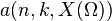 is finite from the finite-value assumption.
is finite from the finite-value assumption. - Express
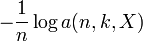 in terms of the sample mean of
in terms of the sample mean of 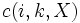 and show that it converges almost surely to Hk
and show that it converges almost surely to Hk - Define the probability measure
- Express
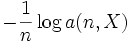 in terms of the sample mean of
in terms of the sample mean of 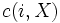 and show that it converges almost surely to H∞.
and show that it converges almost surely to H∞. - Argue that
 as k → ∞ using the stationarity of the process.
as k → ∞ using the stationarity of the process. - Argue that H = H∞ using the Lévy's martingale convergence theorem and the finite-value assumption.
- Show that
- which is finite as argued before.
- Show that
- by conditioning on the infinite past
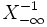 and iterating the expectation.
and iterating the expectation.
- Show that
- using the Markov's inequality and the expectation derived previously.
- Similarly, show that
- which is equivalent to
- Show that limsup of
- are non-positive almost surely by setting α = nβ for any β > 1 and applying the Borel-Cantelli lemma.
- Show that liminf and limsup of
- are lower and upper bounded almost surely by H∞ and Hk respectively by breaking up the logarithms in the previous result.
- Complete the proof by pointing out that the upper and lower bounds are shown previously to approach H as k → ∞.
AEP for non-stationary discrete-time source producing independent symbols
The assumptions of stationarity/ergodicity/identical distribution of random variables is not essential for the AEP to hold. Indeed, as is quite clear intuitively, the AEP requires only some form of the law of large numbers to hold, which is fairly general. However, the expression needs to be suitably generalized, and the conditions need to be formulated precisely.
We assume that the source is producing independent symbols, with possibly different output statistics at each instant. We assume that the statistics of the process are known completely, that is, the marginal distribution of the process seen at each time instant is known. The joint distribution is just the product of marginals. Then, under the condition (which can be relaxed) that ![{\mathrm {Var}}[\log[[p(X_{i})]]]<M](/2014-wikipedia_en_all_02_2014/I/media/4/c/4/8/4c48d24dcd30690d7d17ce1e43a81e53.png) for all i, for some M > 0, the following holds (AEP):
for all i, for some M > 0, the following holds (AEP):
where
Proof
The proof follows from a simple application of Markov's inequality (applied to second moment of  .
.
It is obvious that the proof holds if any moment ![{\mathrm {E}}\left[|\log[[p(Xi)]]|^{r}\right]](/2014-wikipedia_en_all_02_2014/I/media/6/5/9/4/6594db6b52af5372410d0843a17c44d9.png) is uniformly bounded for r > 1 (again by Markov's inequality applied to r-th moment).
is uniformly bounded for r > 1 (again by Markov's inequality applied to r-th moment). 
Even this condition is not necessary, but given a non-stationary random process, it should not be difficult to test whether the AEP holds using the above method.
Applications for AEP for non-stationary source producing independent symbols
The AEP for non-stationary discrete-time independent process leads us to (among other results) source coding theorem for non-stationary source (with independent output symbols) and channel coding theorem for non-stationary memoryless channels.
Source Coding Theorem
The source coding theorem for discrete time non-stationary independent sources can be found here: source coding theorem
Channel Coding Theorem
Channel coding theorem for discrete time non-stationary memoryless channels can be found here: noisy channel coding theorem
AEP for certain continuous-time stationary ergodic sources
Discrete-time functions can be interpolated to continuous-time functions. If such interpolation f is measurable, we may define the continuous-time stationary process accordingly as  . If AEP holds for the discrete-time process, as in the i.i.d. or finite-valued stationary ergodic cases shown above, it automatically holds for the continuous-time stationary process derived from it by some measurable interpolation. i.e.
. If AEP holds for the discrete-time process, as in the i.i.d. or finite-valued stationary ergodic cases shown above, it automatically holds for the continuous-time stationary process derived from it by some measurable interpolation. i.e.
where n corresponds to the degree of freedom in time τ. 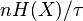 and H(X) are the entropy per unit time and per degree of freedom respectively, defined by Shannon.
and H(X) are the entropy per unit time and per degree of freedom respectively, defined by Shannon.
An important class of such continuous-time stationary process is the bandlimited stationary ergodic process with the sample space being a subset of the continuous  functions. AEP holds if the process is white, in which case the time samples are i.i.d., or there exists T > 1/2W, where W is the nominal bandwidth, such that the T-spaced time samples take values in a finite set, in which case we have the discrete-time finite-valued stationary ergodic process.
functions. AEP holds if the process is white, in which case the time samples are i.i.d., or there exists T > 1/2W, where W is the nominal bandwidth, such that the T-spaced time samples take values in a finite set, in which case we have the discrete-time finite-valued stationary ergodic process.
Any time-invariant operations also preserves AEP, stationarity and ergodicity and we may easily turn a stationary process to non-stationary without losing AEP by nulling out a finite number of time samples in the process.
Category theory
A category theoretic definition for the equipartition property is given by Gromov[1] Given a sequence of Cartesian powers  of a measure space P, this sequence admits an asymptotically equivalent sequence HN of homogenous measure spaces (i.e. all sets have the same measure; all morphisms are invariant under the group of automorphisms, and thus factor as a morphism to the terminal object) .
of a measure space P, this sequence admits an asymptotically equivalent sequence HN of homogenous measure spaces (i.e. all sets have the same measure; all morphisms are invariant under the group of automorphisms, and thus factor as a morphism to the terminal object) .
The above requires a definition of asymptotic equivalence. This is given in terms of a distance function, giving how much an injective correspondence differs from an isomorphism. An injective correspondence 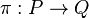 is a partially defined map that is a bijection; that is, it is a bijection between a subset
is a partially defined map that is a bijection; that is, it is a bijection between a subset  and
and 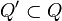 . Then define
. Then define
where |S| denotes the measure of a set S. In what follows, the measure of P and Q are taken to be 1, so that the measure spaces are probability spaces. This distance 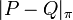 is commonly known as the earth mover's distance or Wasserstein metric.
is commonly known as the earth mover's distance or Wasserstein metric.
Similarly, define
with 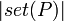 taken to be the counting measure on P. Thus, this definition requires that P be a finite measure space. Finally, let
taken to be the counting measure on P. Thus, this definition requires that P be a finite measure space. Finally, let
A sequence of injective correspondences  are then asymptotically equivalent when
are then asymptotically equivalent when
Given a sequence HN that is asymptotically equivalent to PN, the entropy H(P) of P may be taken as
See also
- Cramér's large deviation theorem
- Typical set
- Source coding theorem
- Noisy-channel coding theorem
References
- ↑ Misha Gromov, (2012) "In a Search for a Structure, Part 1: On Entropy". (See page 5, where the equipartition property is called the 'Bernoulli approximation theorem'.)
The Classic Paper
- Claude E. Shannon. "A Mathematical Theory of Communication". Bell System Technical Journal, July/October 1948.
Other Journal Articles
- Paul H. Algoet and Thomas M. Cover. "A Sandwich Proof of the Shannon-McMillan-Breiman Theorem". The Annals of Probability, 16(2): pp 899-909, 1988.
- Sergio Verdu and Te Sun Han. "The Role of the Asymptotic Equipartition Property in Noiseless Source Coding." IEEE Transactions on Information Theory, 43(3): 847-857, 1997.
Textbooks on Information Theory
- Thomas M. Cover, Joy A. Thomas. Elements of Information Theory New York: Wiley, 1991. ISBN 0-471-06259-6
- David J. C. MacKay. Information Theory, Inference, and Learning Algorithms Cambridge: Cambridge University Press, 2003. ISBN 0-521-64298-1
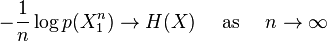
![\lim _{{n\to \infty }}\Pr \left[\left|-{\frac {1}{n}}\log p(X_{1},X_{2},...,X_{n})-H(X)\right|>\epsilon \right]=0\qquad \forall \epsilon >0.](/2014-wikipedia_en_all_02_2014/I/media/1/c/d/b/1cdbe986618f724240371d7e73350872.png)
![\Pr \left[\lim _{{n\to \infty }}-{\frac {1}{n}}\log p(X_{1},X_{2},...,X_{n})=H(X)\right]=1](/2014-wikipedia_en_all_02_2014/I/media/1/3/0/2/1302bf38b7d95ec14ed38472ae223112.png)
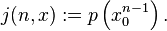

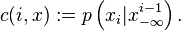
![\lim _{{n\to \infty }}{\mathrm {E}}[-\log j(n,X)]\quad {\text{and}}\quad \lim _{{n\to \infty }}{\mathrm {E}}[-\log c(n,n,X)]](/2014-wikipedia_en_all_02_2014/I/media/8/b/7/6/8b7683255186831ee1f4a6929cbee689.png)
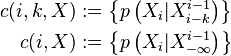

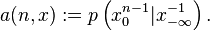
![{\mathrm {E}}\left[{\frac {a(n,k,X)}{j(n,X)}}\right]=a(n,k,X(\Omega ))](/2014-wikipedia_en_all_02_2014/I/media/d/c/9/f/dc9f948f1755a46140ce4c09c7b8b091.png)
![{\mathrm {E}}\left[{\frac {j(n,X)}{a(n,X)}}\right]=1](/2014-wikipedia_en_all_02_2014/I/media/6/2/d/e/62de02ff77780bdcc61a5dc1b940361d.png)
![\forall \alpha \in {\mathbb {R}}\ :\ \Pr \left[{\frac {a(n,k,X)}{j(n,X)}}\geq \alpha \right]\leq {\frac {a(n,k,X(\Omega ))}{\alpha }}](/2014-wikipedia_en_all_02_2014/I/media/a/2/6/4/a264fa2e0185ce6bfd3e691519ed5ebf.png)
![\forall \alpha \in {\mathbb {R}}\ :\ \Pr \left[{\frac {j(n,X)}{a(n,X)}}\geq \alpha \right]\leq {\frac {1}{\alpha }},](/2014-wikipedia_en_all_02_2014/I/media/1/3/b/a/13ba84b1bc22b43b85230adf5968070e.png)
![\forall \alpha \in {\mathbb {R}}\ :\ \Pr \left[{\frac 1n}\log {\frac {j(n,X)}{a(n,X)}}\geq {\frac {1}{n}}\log \alpha \right]\leq {\frac {1}{\alpha }}.](/2014-wikipedia_en_all_02_2014/I/media/2/7/6/6/276609976c7e3c3e12928f48fa782d71.png)
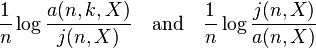
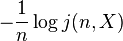
![\lim _{{n\to \infty }}\Pr \left[\,\left|-{\frac {1}{n}}\log p(X_{1},X_{2},...,X_{n})-\overline {H}_{n}(X)\right|<\epsilon \right]=1\qquad \forall \epsilon >0](/2014-wikipedia_en_all_02_2014/I/media/1/e/7/f/1e7fafc4e6121eeb3c01948175e345c4.png)

![{\begin{aligned}\Pr \left[\left|-{\frac {1}{n}}\log p(X_{1},X_{2},...,X_{n})-\overline {H}(X)\right|>\epsilon \right]&\leq {\frac {1}{n^{2}\epsilon ^{2}}}{\mathrm {E}}\left[\sum _{{i=1}}^{n}\left(\log(p(X_{i})\right)^{2}\right]\\&\leq {\frac {M}{n\epsilon ^{2}}}\to 0\ {\mbox{as}}\ n\to \infty \end{aligned}}](/2014-wikipedia_en_all_02_2014/I/media/1/2/c/4/12c4def54d8d58ee38d0aa58e93252ff.png)