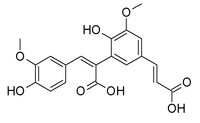
8,5'-Diferulic acid
| 8,5'-Diferulic acid | ||
|---|---|---|
 | ||
| Other names 8,5'-DiFA | ||
| Identifiers | ||
| PubChem | 10385447 | |
| ChemSpider | 8560889 | |
| Jmol-3D images | Image 1 | |
| ||
| ||
| Properties | ||
| Molecular formula | C20H18O8 | |
| Molar mass | 386.35 g mol−1 | |
| Except where noted otherwise, data are given for materials in their standard state (at 25 °C (77 °F), 100 kPa) | ||
| Infobox references | ||
8,5'-Diferulic acid is a non cyclic type of diferulic acid. It is the predominant diferulic acid in sugar beet pulp.[1] It is also found in barley,[2] in maize bran[3] and rye.[4] 8-5'-Diferulic acid has also been identified to be covalently linked to carbohydrate moieties of the arabinogalactan-protein fraction of gum arabic.[5]
See also
References
- ↑ Micard, V.; Grabber, J.H.; Ralph, J.; Renard, C.M.G.C.; Thibault, J.-F. (1997). "Dehydrodiferulic acids from sugar-beet pulp". Phytochemistry 44 (7): 1365. doi:10.1016/S0031-9422(96)00699-1.
- ↑ Hernanz, D; Nuñez, V; Sancho, AI; Faulds, CB; Williamson, G; Bartolomé, B; Gómez-Cordovés, C (2001). "Hydroxycinnamic acids and ferulic acid dehydrodimers in barley and processed barley". Journal of agricultural and food chemistry 49 (10): 4884–8. doi:10.1021/jf010530u. PMID 11600039.
- ↑ Bunzel, M; Funk, C; Steinhart, H (2004). "Semipreparative isolation of dehydrodiferulic and dehydrotriferulic acids as standard substances from maize bran". Journal of separation science 27 (13): 1080–6. doi:10.1002/jssc.200301703. PMID 15495409.
- ↑ Andreasen, MF; Christensen, LP; Meyer, AS; Hansen, A (2000). "Content of phenolic acids and ferulic acid dehydrodimers in 17 rye (Secale cereale L.) varieties". Journal of agricultural and food chemistry 48 (7): 2837–42. doi:10.1021/jf991266w. PMID 11032481.
- ↑ Renard, D; Lavenant-Gourgeon, L; Ralet, MC; Sanchez, C (2006). "Acacia senegal gum: Continuum of molecular species differing by their protein to sugar ratio, molecular weight, and charges". Biomacromolecules 7 (9): 2637–49. doi:10.1021/bm060145j. PMID 16961328.
External links
| |||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||