5-Methylcytidine
From Wikipedia, the free encyclopedia
| 5-Methylcytidine | |
|---|---|
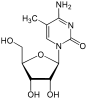 | |
| 3-[(4S,2R,3R,5R)-3,4-Dihydroxy-5-(hydroxymethyl)oxolan-2-yl]-6-amino-5-methyl-3-hydropyrimidin-2-one | |
| Other names m5C | |
| Identifiers | |
| CAS number | 2140-61-6 |
| PubChem | 92918 |
| ChemSpider | 83877 |
| Jmol-3D images | {{#if:O=C1/N=C(/N)\C(=C/N1[C@@H]2O[C@@H]([C@@H](O)[C@H]2O)CO)C|Image 1 |
| |
| |
| Properties | |
| Molecular formula | C10H15N3O5 |
| Molar mass | 257.24 g mol−1 |
| Except where noted otherwise, data are given for materials in their standard state (at 25 °C (77 °F), 100 kPa) | |
| Infobox references | |
5-Methylcytidine is a modified nucleoside derived from 5-methylcytosine. It is found in ribonucleic acids of animal, plant, and bacterial origin.[1]
References
- ↑ Dunn, D. B. (1960). "Isolation of 5-methylcytidine from ribonucleic acid". Biochimica et Biophysica Acta 38: 176–178. doi:10.1016/0006-3002(60)91219-1. PMID 13818675.
This article is issued from Wikipedia. The text is available under the Creative Commons Attribution/Share Alike; additional terms may apply for the media files.