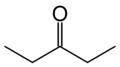
3-Pentanone
| 3-Pentanone | |
|---|---|
 | |
 | |
| Pentan-3-one | |
| Other names diethyl ketone, diethylketone, 3-pentanone, dimethyl acetone, propione, DEK, metacetone, methacetone | |
| Identifiers | |
| CAS number | 96-22-0 |
| ChemSpider | 7016 |
| UNII | 9SLZ98M9NK |
| ChEMBL | CHEMBL45315 |
| Jmol-3D images | Image 1 |
| |
| |
| Properties | |
| Molecular formula | C5H10O |
| Molar mass | 86.13 g mol−1 |
| Appearance | Colorless liquid[1] |
| Odor | Acetone-like |
| Density | 0.815 g/cm³ |
| Melting point | −39 °C; −38 °F; 234 K |
| Boiling point | 100–102 °C |
| Solubility in other solvents | water: 50 g/L (20 °C) |
| Hazards | |
| Flash point | 12.78 °C; 55.00 °F; 285.93 K |
| Autoignition temperature | 425 °C; 797 °F; 698 K |
| Except where noted otherwise, data are given for materials in their standard state (at 25 °C (77 °F), 100 kPa) | |
| Infobox references | |
3-Pentanone (also known as diethyl ketone) is a simple, symmetrical dialkyl ketone. It is a colorless liquid ketone with an odor like that of acetone. It is soluble in about 25 parts water, but miscible with organic solvents. It is mainly used as a solvent in paint and a precursor to vitamin E.[2] It is easily soluble in diethyl ether and partially soluble in acetone, methanol, and water.[3] Two related and more important ketones are 2-pentanone and methyl isopropyl ketone.
3-Pentanone is produced industrially from propionic acid using metal oxide catalysts:
- 2 CH3CH2CO2H → (CH3CH2)2CO + CO2 + H2O
It can also be prepared from ethylene, CO, and H2[2] or by ketonic decarboxylation of propanoic acid over a manganese(II) oxide catalyst in a tube furnace.[4]
Safety
The TLV value for 3-pentanone is 200 ppm (705 mg/m3).[2] 3-pentanone can be hazardous if it comes in contact with the skin or eyes, and can cause irritation of the skin and redness, watering, and itching of the eyes. This chemical can also cause nervous system or organ damage if ingested. Although considered stable, 3-pentanone is extremely flammable if exposed to flame, sparks, or another source of heat. For safety, it should be stored in a flammable materials cabinet away from heat or sources of ignition, preferably in a cool, well-ventilated area.[3]
References
- ↑ NIOSH Pocket Guide to Chemical Hazards, Centers for Disease Control and Prevention, updated 11/7/2013
- ↑ 2.0 2.1 2.2 Hardo Siegel, Manfred Eggersdorfer "Ketones" in Ullmann's Encyclopedia of Industrial Chemistry Wiley-VCH, 2002 by Wiley-VCH, Wienheim. doi:10.1002/14356007.a15_077
- ↑ 3.0 3.1 Chemicals & Laboratory Equipment, Material Safety Data Sheet for 3-pentanone, ScienceLab.com, updated 11/06/2008
- ↑ Furniss, Brian; Hannaford, Antony; Smith, Peter; and Tatchell, Austin (1996). Vogel's Textbook of Practical Organic Chemistry 5th Ed.. London: Longman Science & Technical. p. 613. ISBN 9780582462366.