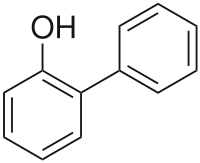
2-Phenylphenol
| 2-Phenylphenol | |
|---|---|
 | |
 | |
| 2-phenylphenol | |
| Other names o-phenylphenol | |
| Identifiers | |
| CAS number | 90-43-7 |
| ChemSpider | 13839012 |
| UNII | D343Z75HT8 |
| KEGG | D08367 |
| ChEBI | CHEBI:17043 |
| ChEMBL | CHEMBL108829 |
| ATC code | D08 |
| Jmol-3D images | Image 1 |
| |
| |
| Properties | |
| Molecular formula | C12H10O |
| Molar mass | 170.21 g mol−1 |
| Density | 1.293 g/cm³ |
| Melting point | 55.5 to 57.5 °C; 131.9 to 135.5 °F; 328.6 to 330.6 K |
| Boiling point | 280 to 284 °C; 536 to 543 °F; 553 to 557 K |
| Except where noted otherwise, data are given for materials in their standard state (at 25 °C (77 °F), 100 kPa) | |
| Infobox references | |
2-Phenylphenol, or o-phenylphenol, is an organic compound that consists of two linked benzene rings and a phenolic hydroxyl group.[1][2] It is a white or buff-colored, flaky crystalline solid with a melting point of about 57 °C. It is a biocide used as a preservative under the trade names Dowicide, Torsite, Preventol, Nipacide and many others.
History
2-Phenylphenol (ortho-phenylphenol, OPP), and sodium o-phenylphenate, SOPP, were first evaluated by the 1962 JECFA for their use for the post-harvest treatment of fruits and vegetables to protect against microbial damage during storage and distribution in commerce.[3]
Uses
The primary use of 2-phenylphenol is as an agricultural fungicide. It is generally applied post-harvest. It is a fungicide used for waxing citrus fruits. It is no longer a permitted food additive in the European Union, but is still allowed as a post harvest treatment.
It is also used for disinfection of seed boxes. It is a general surface disinfectant, used in households, hospitals, nursing homes, farms, laundries, barber shops, and food processing plants. It can be used on fibers and other materials. It is used to disinfect hospital and veterinary equipment. Other uses are in rubber industry and as a laboratory reagent. It is also used in the manufacture of other fungicides, dye stuffs, resins and rubber chemicals.
2-Phenylphenol is found in low concentrations in some household products such as spray disinfectants and aerosol or spray underarm deodorants.
Eye contact can cause severe irritation and burns with possible eye damage. For some individuals, 2-phenylphenol can also irritate the skin. It is one of the chemicals that the Hyperactive Children's Support Group recommends be eliminated from the diet of children.[4]
The sodium salt of orthophenyl phenol, sodium orthophenyl phenol, is a preservative,[5] used to treat the surface of citrus fruits to prolong shelf life.[3]
Orthophenyl phenol is also used as a fungicide in food packaging and may migrate into the contents.[6]
References
- ↑ M.J.O'Neil, ed. by (2001). Merck Index : an encyclopedia of chemicals, drugs, & biologicals : 13th ed. (13. ed. ed.). United States: MERCK & CO INC. p. 7388. ISBN 0911910131.
- ↑ Budavari, Susan (1997). The Merck index an encyclopedia of chemicals, drugs, and biologicals (12. ed., 2. printing ed.). Whitehouse Station, NJ: Merck. p. 7458. ISBN 0911910123.
- ↑ 3.0 3.1 "2-PHENYLPHENOL AND ITS SODIUM SALT". Food and Agriculture Organization of the United Nations.
- ↑ "Right to Know Hazardous Substance Fact Sheet". New Jersey Department of Health and Senior Services. Retrieved 2 June 2012.
- ↑ "Environmental Fate and Exposure Potential". 2-Phenylphenol - Substance Summary. National Center for Biotechnology Information, U.S. National Library of Medicine. Retrieved 2 June 2012.
- ↑ Mehmet Coelhan, Karl-Heinz Bromig, Karl Glas, and A. Lynn Roberts (2006). "Determination and Levels of the Biocide ortho-Phenylphenol in Canned Beers from Different Countries". J. Agric. Food Chem. 54 (16): 5731–5735. doi:10.1021/jf060743p. PMID 16881670.
External links
- List of brand name products which contain 2-phenylphenol
- National Center for Biotechnology Information 2-Phenylphenol - Substance Summary