2-Hexanol
From Wikipedia, the free encyclopedia
| 2-Hexanol[1] | |
|---|---|
 | |
/-/(R)-Hexan-2-ol_3D_ball.png) | |
| Hexan-2-ol | |
| Identifiers | |
| CAS number | 626-93-7 |
| PubChem | 12297 |
| ChemSpider | 11794 |
| ChEMBL | CHEMBL45425 |
| Jmol-3D images | Image 1 |
| |
| |
| Properties | |
| Molecular formula | C6H14O |
| Molar mass | 102.174 g/mol |
| Density | 0.81 g/mL |
| Boiling point | 140 °C; 284 °F; 413 K |
| Solubility in water | 14 g/L |
| Solubility | soluble in ethanol, diethyl ether |
| Thermochemistry | |
| Std enthalpy of formation ΔfH |
-392.0 kJ·mol-1 (liquid) -333.5 kJ·mol-1 (gas) |
| Except where noted otherwise, data are given for materials in their standard state (at 25 °C (77 °F), 100 kPa) | |
| Infobox references | |
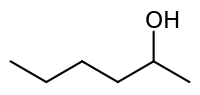
2-Hexanol (or hexan-2-ol) is a six carbon alcohol in which the OH group is located on the second carbon atom. Its chemical formula is C6H14O or C6H13OH. It is an isomer of the other hexanols. 2-Hexanol has a chiral center and can be resolved into enantiomers.
References
| |||||||||||||||||
This article is issued from Wikipedia. The text is available under the Creative Commons Attribution/Share Alike; additional terms may apply for the media files.