2,6-Xylidine
From Wikipedia, the free encyclopedia
| 2,6-Xylidine | |
|---|---|
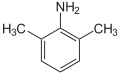 | |
| 2,6-dimethylbenzene-1-amine | |
| Other names 2,6-dimethylaniline, 2,6-dimethylbenzenamine, 2,6-dimethylphenylamine | |
| Identifiers | |
| CAS number | 87-62-7 |
| ChemSpider | 6630 |
| KEGG | C11004 |
| ChEBI | CHEBI:28738 |
| Jmol-3D images | Image 1 |
| |
| |
| Properties | |
| Molecular formula | C8H11N |
| Molar mass | 121.18 g mol−1 |
| Appearance | Clear to yellow reddish liquid |
| Density | 0.9842 g/mL |
| Melting point | 11.45 °C; 52.61 °F; 284.60 K |
| Boiling point | 215 °C; 419 °F; 488 K |
| Refractive index (nD) | 1.5601 |
| Except where noted otherwise, data are given for materials in their standard state (at 25 °C (77 °F), 100 kPa) | |
| Infobox references | |
2,6-Xylidine is an aromatic amine with the chemical formula (CH3)2C6H3NH2. It is an isomer of 2,4-xylidine and 3,4-xylidine. It is a clear to yellow-red liquid which darkens upon exposure to air and light.
2,6-Xylidine may be used to synthesize lidocaine:[1]
References
- ↑ T. J. Reilly (1999). "The Preparation of Lidocaine". J. Chem. Ed. 76 (11): 1557. doi:10.1021/ed076p1557.
This article is issued from Wikipedia. The text is available under the Creative Commons Attribution/Share Alike; additional terms may apply for the media files.
