2,6-Di-tert-butylphenol
| 2,6-Di-tert-butylphenol | |
|---|---|
 | |
| Other names 2,6-bis(1,1-dimethylethyl)phenol, dibutylphenol, 2,6-bis(tert-butyl)phenol, and 2,6-di(1,1-dimethylethyl) phenol, 2,6-DTBP, Ethanox 701, Ethyl 701, Ethyl AN 701, Irganox L 140, Isonox 103, TK 12891 | |
| Identifiers | |
| CAS number | 128-39-2 |
| ChemSpider | 29135 |
| ChEMBL | CHEMBL281071 |
| Jmol-3D images | Image 1 |
| |
| |
| Properties | |
| Appearance | Low-melting colourless solid |
| Melting point | 34-36 °C |
| Boiling point | 253 °C |
| Hazards | |
| R-phrases | R22 R36 R37 R38 |
| S-phrases | S22 S36 |
| Except where noted otherwise, data are given for materials in their standard state (at 25 °C (77 °F), 100 kPa) | |
| Infobox references | |
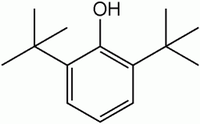
2,6-Di-tert-butylphenol is an organic compound with the structural formula 2,6-((CH3)3C)2C6H3OH. This colourless solid alkylated phenol and its derivatives are used industrially as UV stabilizer and an antioxidant for hydrocarbon-based products ranging from petrochemicals to plastics. Illustrative of its usefulness, it prevents gumming in aviation fuels.
Production
2,6-Di-tert-butylphenol is prepared by the reaction of phenol with isobutene catalysed by aluminium phenoxide: [1]
- C6H5OH + 2 CH2=C(CH3)2 → ((CH3)3C)2C6H3OH
In this way, approximately 2.5M kg/y are produced.
Applications
2,6-Di-tert-butylphenol is a precursor to more complex compounds used as antioxidants and light-protection agents. Representative derivatives include 3,5-di-tert-butyl-4-hydroxybenzyl chloride (CAS# 955-01-1), 3,5-di-tert-butyl-4-hydroxybenzyl alcohol (CAS# 88-26-6), and methyl-3-(3,5-di-tert-butyl-4-hydroxyphenyl)- propionate (CAS# 6386-38-5). Such derivatives are prepared from 2,6-di-tert-butylphenol by chloromethylation and hydroxymethylation using formaldehye and alkylation with acrylic acid.
Safety
The LD50 is 9200, indicating a low toxicity.[1]
Miscellaneous Regulations
U.S. Department of Transportation Code of Federal Regulations 49 CFR 172.101, Appendix B (20 Dec 2004). This substance is designated by the U.S. Department of Transportation (DOT) as a marine pollutant. Listed Name(s): 2,6-Di-tert-butylphenol.
See also
References
- ↑ 1.0 1.1 Helmut Fiege, Heinz-Werner Voges, Toshikazu Hamamoto, Sumio Umemura, Tadao Iwata, Hisaya Miki, Yasuhiro Fujita, Hans-Josef Buysch, Dorothea Garbe, Wilfried Paulus "Phenol Derivatives" Ullmann's Encyclopedia of Industrial Chemistry, Wiley-VCH, Weinheim, 2002. doi:10.1002/14356007.a19_313 Article Online Posting Date: June 15, 2000.
| ||||||||||||||
| |||||||||||