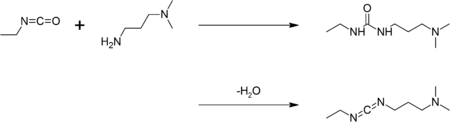1-Ethyl-3-(3-dimethylaminopropyl)carbodiimide
| 1-Ethyl-3-(3-dimethylaminopropyl)carbodiimide | |
|---|---|
 | |
| 3-(Ethyliminomethyleneamino)-N,N-dimethylpropan-1-amine | |
| Identifiers | |
| CAS number | 1892-57-5 |
| PubChem | 15908 |
| ChemSpider | 15119 |
| Jmol-3D images | Image 1 |
| |
| |
| Properties | |
| Molecular formula | C8H17N3 |
| Molar mass | 155.24 g mol−1 |
| Hazards | |
| MSDS | External MSDS (HCl salt) |
| Except where noted otherwise, data are given for materials in their standard state (at 25 °C (77 °F), 100 kPa) | |
| Infobox references | |
1-Ethyl-3-(3-dimethylaminopropyl)carbodiimide (EDC, EDAC or EDCI) is a water soluble carbodiimide usually obtained as the hydrochloride. It is typically employed in the 4.0-6.0 pH range. It is generally used as a carboxyl activating agent for the coupling of primary amines to yield amide bonds. Additionally, EDC can also be used to activate phosphate groups in order to form phosphomono-esters and phosphodiesters. Common uses for this carbodiimide include peptide synthesis, protein crosslinking to nucleic acids, but also in the preparation of immunoconjugates. EDC is often used in combination with N-hydroxysuccinimide (NHS) or sulfo-NHS to increase coupling efficiency by creating a more reactive amine- product.
EDC is also used in organic chemistry to couple a carboxylic acid to alcohol using DMAP as a catalyst.
Preparation
EDC is commercially available. It may be prepared by coupling ethyl isocyanate with N,N-dimethylpropane-1,3-diamine to give a urea, followed by dehydration:[1]
References
- ↑ Sheehan, John; Cruickshank, Philip; Boshart, Gregory (1961). "A Convenient Synthesis of Water-Soluble Carbodiimides". J. Org. Chem. 26 (7): 2525. doi:10.1021/jo01351a600.
Further reading
- López-Alonso, JP; Diez-Garcia, F; Font, J; Ribó, M; Vilanova, M; Scholtz, JM; González, C; Vottariello, F; Gotte, G; Libonati, M; Laurents, DV (2009). "Carbodiimide EDC Induces Cross-Links That Stabilize RNase A C-dimer against Dissociation: EDC Adducts Can Affect Protein Net Charge, Conformation and Activity". Bioconjug Chem. 20 (8): 1459. doi:10.1021/bc9001486.
- Nakajima, N; Ikada, Y (1995). "Mechanism of Amide Formation by Carbodiimide for Bioconjugation in Aqueous Media". Bioconjug Chem. 6: 123. doi:10.1021/bc00031a015.
- Skotnicki, S; Kearney, RM; Smith, AL (1994). "Synthesis of secorapamycin esters and amides". Tetrahedron Lett. 35 (21): 197. doi:10.1016/S0040-4039(00)76509-9.
External links
- EDCI coupling - Synthetic protocols from organic-reaction.com