1,3-Dioxetanedione
From Wikipedia, the free encyclopedia
| 1,3-Dioxetanedione | ||
|---|---|---|
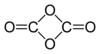 | ||
| 1,3-Dioxetane-2,4-dione[1] | ||
| Identifiers | ||
| PubChem | 17801328 | |
| Jmol-3D images | Image 1 | |
| ||
| ||
| Properties | ||
| Molecular formula | C2O4 | |
| Molar mass | 88.02 g mol−1 | |
| Except where noted otherwise, data are given for materials in their standard state (at 25 °C (77 °F), 100 kPa) | ||
| Infobox references | ||
The chemical compound 1,3-dioxetanedione, or 1,3-dioxacyclobutane-2,4-dione is a hypothetical oxide of carbon with formula C2O4. It can be considered a cyclic dimer of carbon dioxide (CO2) or as a double ketone of 1,3-dioxetane (1,3-dioxacyclobutane).
Theoretical calculations indicate that the compound is extremely unstable at room temperature (half-life of less than 1.1 μs); but may be stable at −196 °C.[2]
References
- ↑ "CID 17801328 - Compound Summary". PubChem Compound. USA: National Center for Biotechnology Information. 4 December 2007. Identification and Related Records. Retrieved 7 October 2011.
- ↑ Errol Lewars (1996), Polymers and oligomers of carbon dioxide: ab initio and semiempirical calculations. Journal of Molecular Structure: THEOCHEM, Volume 363, Number 1, pp. 1–15.
| ||||||||||||||
This article is issued from Wikipedia. The text is available under the Creative Commons Attribution/Share Alike; additional terms may apply for the media files.