Β-Santalol
From Wikipedia, the free encyclopedia
| β-Santalol | ||
|---|---|---|
 | ||
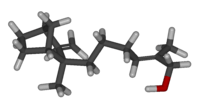 | ||
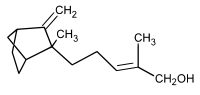
| IUPAC name (2Z)-2-Methyl-5-[2-methyl-3-methylene-bicyclo[2.2.1]hept-2-yl]pent-2-en-1-ol | ||
| Identifiers | ||
| CAS number | 77-42-9 | |
| EC number | 201-027-2 | |
| Jmol-3D images | Image 1 | |
| ||
| Properties | ||
| Molecular formula | C15H24O | |
| Molar mass | 220.34 g/mol | |
| Appearance | Liquid | |
| Density | 0.9717 g/cm3 | |
| Boiling point | 177 °C; 351 °F; 450 K | |
| Solubility in water | practically insoluble | |
| Solubility in ethanol | soluble | |
| Solubility in diethyl ether | soluble | |
| Chiral rotation [α]D | −87.1° | |
| Refractive index (nD) | 1.5100 | |
| Related compounds | ||
| Related terpeness | α-Santalol | |
| Except where noted otherwise, data are given for materials in their standard state (at 25 °C (77 °F), 100 kPa) | ||
| Infobox references | ||
β-Santalol is an organic compound that is classified as a sesquiterpene. It comprises about 20% of the oil of sandalwood, the major component being α-santalol. As of 2002, about 60 tons of sandalwood oil are produced annually by steam distillation of the heartwood of Santalum album.[1]
References
- ↑ Karl-Georg Fahlbusch, Franz-Josef Hammerschmidt, Johannes Panten, Wilhelm Pickenhagen, Dietmar Schatkowski, Kurt Bauer, Dorothea Garbe, Horst Surburg "Flavors and Fragrances" in Ullmann's Encyclopedia of Industrial Chemistry, Wiley-VCH, Weinheim: 2002. Published online: 15 January 2003; doi:10.1002/14356007.a11_141.
This article is issued from Wikipedia. The text is available under the Creative Commons Attribution/Share Alike; additional terms may apply for the media files.