Önge language
| Onge | |
|---|---|
| Öñge | |
| Native to | India |
| Ethnicity | Onge people |
Native speakers | 94 (2006)[1] |
|
Ongan
| |
| Language codes | |
| ISO 639-3 | oon |
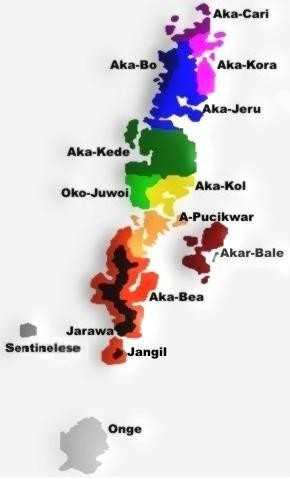 A map of tribal and language divisions in the Andaman Islands prior to the 1850s | |
The Onge or Öñge language ([ˈəŋɡe]; variously spelled Ongee, Eng, or Ung) is a language spoken by the Onge people in Little Andaman Island in India. It is one of two known Ongan languages.
Önge used to be spoken throughout Little Andaman as well as in smaller islands to the north - and possibly in the southern tip of South Andaman island. Since the middle of the 19th century, with the arrival of the British in the Andamans, and, after Indian independence, the massive inflow of Indian settlers from the mainland, the number of Onge speakers has steadily declined, although a moderate increase has been observed in recent years.[2] Currently, there are only 94 native speakers of Onge,[3] confined to a single settlement in the northeast of Little Andaman island (see map below), making it an endangered language.
Phonology
Vowels
| Front | Central | Back | |
| High | i | u | |
| Mid | e | ə | o |
| Low | a |
There is some vowel harmony: 1p pl. prefix et- becomes [ot-] when the vowel in the next syllable is /u/, e.g. et-eɟale 'our faces' but ot-oticule 'our heads'.[4]
Consonants
| Labial | Coronal | Palatal | Velar | |||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Stops | kʷ | b | t | d | c | ɟ | k | ɡ |
| Nasals | m | n | ɲ | ŋ | ||||
| Approximants | w | l (/r/) | j | |||||
/ʔ/? (c.f. Blevins (2007:161))
Blevins (2007:160-161) states that /c, ɟ/ are actually affricates, and that retroflexes may or may not be phonemic.
/kʷ/ delabializes to /k/ before /u, o/.[4]
Phonemic /d/ surfaces as [r] intervocalically, while arguably some words have phonemic /r/ which alternates with surface [r, l, j].[5]
Phonotactics
Words may be monosyllabic or longer, even in content words (unlike in the closely related Jarawa).[4] Words may begin with consonants or vowels, and maximal syllables are of the form CVC.[4] All Onge words end in vowels, except for imperatives, e.g. kaʔ 'give'.
Consonant-final stems in Jarawa often have cognates with final e in Onge, e.g. Jarawa iŋ, Onge iŋe 'water'; Jarawa inen, Onge inene 'foreigner'; Jarawa dag, Onge dage 'coconut'.[4] Historically these vowels must have been excrescent, as nonetymological word-final e doesn't surface when number markers are suffixed, and the definite article (-gi after etymological consonants, -i after etymological vowels, due to lenition) appears as -i after etymological e but as -gi after excrescent e, e.g. daŋe → daŋe-gi 'tree; dugout'; kue → kue-i 'pig'.[6]
NC clusters sometimes optionally reduce to single C, e.g. iɲɟo-~iɟo- 'to drink' (c.f. Jarawa -iɲɟo).[7]
Voiced obstruents may optionally nasalize in syllable onset when the coda is nasal, e.g. bone/mone 'resin, resin torch' (c.f. Jarawa pone 'resin, resin torch').[7]
Morphophonemics
Clusters across morpheme boundaries simplify to homorganic sequences, including geminates, which may occur after word final -e drops, e.g. daŋe 'tree, dugout canoe' → dandena 'two canoes'; umuge 'pigeon' → umulle 'pigeons'.[4]
References
Bibliography
- Blevins, Juliette (2007), "A Long Lost Sister of Proto-Austronesian? Proto-Ongan, Mother of Jarawa and Onge of the Andaman Islands", Oceanic Linguistics 46 (1): 154–198, doi:10.1353/ol.2007.0015