Waterline
The term "waterline" generally refers to the line where the hull of a ship meets the water surface. It is also the name of a special marking, also known as the national Load Line or Plimsoll Line, to be positioned amidships, that indicates the draft of the ship and the legal limit to which a ship may be loaded for specific water types and temperatures. Temperature affects the level because warm water provides less buoyancy, being less dense than cold water. The salinity of the water also affects the level, fresh water being less dense than salty seawater. This marking was invented in the 1870s by Samuel Plimsoll.
For vessels with displacement hulls, the hull speed is determined by, amongst other things, the waterline length. In a sailing boat, the waterline length can change significantly as the boat heels, and can dynamically affect the speed of the boat.
In aircraft design, the term "waterline" refers to the vertical location of items on the aircraft. This is the (normally) "Z" axis of an XYZ coordinate system, the other two axes being the Fuselage Station (X) and Buttock Line (Y).
The purpose of a 'load line' is to ensure that a ship has sufficient freeboard (the height from the water line to the main deck) and thus sufficient reserve buoyancy (e.g., the enclosed volume created by the area between the waterline and the main deck). The freeboard of commercial vessels is measured between the lowest point of the uppermost continuous deck at side and the waterline and this must not be less than the freeboard marked on the Load Line Certificate issued to that ship. All commercial ships, other than in exceptional circumstances,[1] have a load line symbol painted amidships on each side of the ship. This symbol must also be permanently marked, so that if the paint wears off it remains visible. The load line makes it easy for anyone to determine if a ship has been overloaded. The exact location of the Load Line is calculated and/or verified by a Classification Society and that society issues the relevant certificates.
This symbol, also called an international load line or Plimsoll line, indicates the maximum safe draft, and therefore the minimum freeboard for the vessel in various operating conditions.[2]
The plimsoll mark is also used in chemistry as a symbol to denote a standard state.[3]
Contents |
History
The first official loading regulations are thought to date back to maritime legislation originating with the kingdom of Crete in 2,500 BC when vessels were required to pass loading and maintenance inspections. Roman sea regulations also contained similar regulations.
In the Middle Ages the Venetian Republic, the city of Genoa and the Hanseatic league required ships to show to a load line. In the case of Venice this was a cross marked on the side of the ship and of Genoa three horizontal lines.
The first 19th century loading recommendations were introduced by Lloyd's Register of British and Foreign Shipping in 1835, following discussions between shipowners, shippers and underwriters. Lloyds recommended freeboards as a function of the depth of the hold (three inches per foot of depth). These recommendations, used extensively until 1880, became known as "Lloyd's Rule".
In the 1860s, after increased loss of ships due to overloading, a British MP, Samuel Plimsoll, took up the load line cause. [4] A Royal Commission on unseaworthy ships was established in 1872, and in 1876 the United Kingdom Merchant Shipping Act made the load line mark compulsory, although the positioning of the mark was not fixed by law until 1894. In 1906, laws were passed requiring foreign ships visiting British ports to be marked with a load line. It was not until 1930 (The 1930 Load Line Convention) that there was international agreement for universal application of load line regulations.
In 1966 a Load Lines Convention was held in London which re-examined and amended the 1930 rules. The 1966 Convention has since seen amendments in 1971, 1975, 1979, 1983, 1995 and 2003.[5]
Standard load line marks
The original "Plimsoll Mark" was a circle with a horizontal line through it to show the maximum draft of a ship. Additional marks have been added over the years, allowing for different water densities and expected sea conditions.
Letters may also appear to the sides of the mark indicating the classification society that has surveyed the vessel's load line. The initials used include AB for the American Bureau of Shipping, LR for Lloyd's Register, GL for Germanischer Lloyd, BV for Bureau Veritas, IR for the Indian Register of Shipping, RI for the Registro Italiano Navale and NV for Det Norske Veritas. These letters should be approximately 115 millimetres in height and 75 millimetres in width.[6] The Load Line Length is referred to during and following load line calculations.
The letters on the Load line marks have the following meanings:
- TF – Tropical Fresh Water
- F – Fresh Water
- T – Tropical Seawater
- S – Summer Temperate Seawater
- W – Winter Temperate Seawater
- WNA – Winter North Atlantic
Fresh water is considered to have a density of 1000 kg/m³ and sea water 1025 kg/m³. Fresh water marks make allowance for the fact that the ship will float deeper in fresh water than salt water. A ship loaded to her Fresh Water mark in fresh water will float at her Summer Mark once she has passed into sea water. Similarly if loaded to her Tropical Fresh water mark she will float at her Tropical Mark once she passes in to sea water.
The Summer load line is the primary load line and it is from this mark that all other marks are derived. The position of the summer load line is calculated from the Load Line Rules and depends on many factors such as length of ship, type of ship, type and number of superstructures, amount of sheer, bow height and so on. The horizontal line through the circle of the Plimsoll mark is at the same level as the summer load line.
The Winter load line is one forty-eighth of the summer load draft below the summer load line.
The Tropical load line is one forty-eighth of the summer load draft above the summer load line.
The Fresh Water load line is an amount equal to 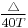 centimetres above the summer load line where
centimetres above the summer load line where  is the displacement in metric tonnes at the summer load draft and T is the metric tonnes per centimetre immersion at that draft.
is the displacement in metric tonnes at the summer load draft and T is the metric tonnes per centimetre immersion at that draft.
In any case where  cannot be ascertained the fresh water load line is at the same level as the tropical load line.
cannot be ascertained the fresh water load line is at the same level as the tropical load line.
The position of the Tropical Fresh load line relative to the tropical load line is found in the same way as the fresh water load line is to the summer load line.
The Winter North Atlantic load line is used by vessels not exceeding 100 metres in length when in certain areas of the North Atlantic Ocean during the winter period. When assigned it is 50 millimetres below the winter mark.[7]
Timber load line marks
Certain vessels are assigned Timber Freeboards but before these can be assigned certain additional conditions have to be met. One of these conditions is that the vessel must have a forecastle of at least 0.07 the length of the vessel and of not less than standard height, which is 1.8 metres for a vessel 75 metres or less in length and 2.3 metres for a vessel 125 metres or more in length with intermediate heights for intermediate lengths. A poop or raised quarter deck is also required if the length is less than 100 metres. The letter L prefixes the load line marks to indicate a timber load line.[8] Except for the Timber Winter North Atlantic freeboard the other freeboards are less than the standard freeboards. This allows these ships to carry additional timber as deck cargo, but with the facility to jettison this cargo.
The letters on the Timber Load line marks have the following meanings:
- LTF – Timber Tropical Fresh Water
- LF – Timber Fresh Water
- LT – Timber Tropical Seawater
- LS – Timber Summer Seawater
- LW – Timber Winter Seawater
- LWNA –Timber Winter North Atlantic
The Summer Timber load line is arrived at from the appropriate tables in the Load Line Rules. [9]
The Winter Timber load line is one thirty-sixth of the Summer Timber load draft below the Summer Timber load line.
The Tropical Timber load line is one forty-eighth of the Summer Timber load draft above the Summer timber load line.
The Timber Fresh and the Tropical Timber Fresh load lines are calculated in a similar way to the Fresh Water and Tropical Fresh water load lines except that the displacement used in the formula is that of the vessel at her Summer Timber load draft. If this cannot be ascertained then these marks will be one forty-eighth of the Timber Summer draft above the Timber Summer and Timber Tropical marks respectively.[10]
The Timber Winter North Atlantic load line is at the same level as the Winter North Atlantic load line
Subdivision load line marks
Passenger ships having spaces which are adapted for the accommodation of passengers and the carriage of cargo alternatively may have one or more additional load line marks corresponding to the subdivision drafts approved for the alternative conditions. These marks show C1 for the principal passenger condition, and C2, C3, etc., for the alternative conditions, however in no case shall any subdivision load line mark be placed above the deepest load line in salt water.[11]
See also
|
|
References
- ^ Statutory Instruments 1998 No. 2241 The Merchant Shipping (Load Line) Regulations 1998 Sections 5(1) and 5(3)
- ^ Notes on Cargo Work: Kemp and Young: ISBN 0853090408
- ^ Prigogine, I. & Defay, R. (1954) Chemical thermodynamics, p. xxiv
- ^ See Nicolette Jones, The Plimsoll Sensation. The Great Campaign to Save Lives at Sea, London, Little, Brown, 2006. ISBN 0316726122.
- ^ Précis of IMO web site. History of the Load Line.[1]
- ^ Statutory Instruments 1998 No. 2241 The Merchant Shipping (Load Line) Regulations 1998
- ^ Notes on Cargo Work: Kemp and Young: ISBN 0853090408
- ^ Notes on Cargo Work: Kemp and Young: ISBN 0853090408
- ^ The Merchant Shipping (Load Line) Regulations 1998, as amended by the Merchant Shipping (Load Line) (Amendment) Regulations 2000
- ^ Notes on Cargo Work: Kemp and Young: ISBN 0853090408
- ^ Merchant Shipping (Instructions to Surveyors) (Passenger Ships) Regulations (Hong Kong)
External links
- Historical background to the adoption of the Load Lines convention
- More historical background
- Online water density calculator
- IACS Unified Requirement L: Subdivision, Stability and Load Lines
|
|||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||