Verlet list
A Verlet list (named after Loup Verlet) is a data structure in molecular dynamics simulations to efficiently maintain a list of all particles within a given cut-off distance of each other.[1]
This method may easily be applied to Monte Carlo simulations. For short-range interactions, a cut-off radius is typically used, beyond which particle interactions are considered "close enough" to zero to be safely ignored. For each particle, a Verlet list is constructed that lists all other particles within the potential cut-off distance, plus some extra distance so that the list may be used for several consecutive Monte Carlo "sweeps" before being updated. If we wish to use the same Verlet list n times before updating, then the cut-off distance for inclusion in the Verlet list should be 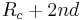 , where
, where 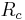 is the cut-off distance of the potential, and
is the cut-off distance of the potential, and 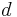 is the maximum Monte Carlo step of a single particle. Thus, we will spend of order
is the maximum Monte Carlo step of a single particle. Thus, we will spend of order  time to compute the Verlet lists (
time to compute the Verlet lists (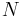 is the total number of particles), but are rewarded with
is the total number of particles), but are rewarded with  Monte Carlo "sweeps" of order
Monte Carlo "sweeps" of order 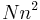 (instead of
(instead of 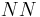 ). Optimizing our choice of
). Optimizing our choice of  , it can be shown that the
, it can be shown that the 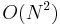 problem of Monte Carlo sweeps has been converted to an
problem of Monte Carlo sweeps has been converted to an 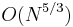 problem by using Verlet lists.
problem by using Verlet lists.
Using cell lists to identify the nearest neighbors in 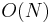 further reduces the computational cost.
further reduces the computational cost.
See also
References
- ^ Verlet, L. (1967). "Computer 'experiments' on classical fluids. I. Thermodynamical properties of Lennard-Jones molecules". Phys. Rev. 159: 98–103.
External links
- Constructing a Neighbour List — from Introduction to Atomistic Simulations course at the University of Helsinki.