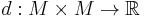Ultrametric space
In mathematics, an ultrametric space is a special kind of metric space in which the triangle inequality is replaced with d(x, z) ≤ max{d(x, y), d(y, z)}. Sometimes the associated metric is also called a non-Archimedean metric or super-metric. Although some of the theorems for ultrametric spaces may seem strange at a first glance, they appear naturally in many applications.
Contents |
Formal definition
Formally, an ultrametric space is a set of points  with an associated distance function (also called a metric)
with an associated distance function (also called a metric)
(where R is the set of real numbers), such that for all x, y, z in M, one has:
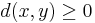
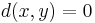 iff
iff 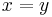
 (symmetry)
(symmetry)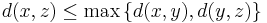 (strong triangle or ultrametric inequality).
(strong triangle or ultrametric inequality).
The last property can be made stronger using the Krull sharpening[1] to:
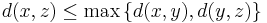 with equality if
with equality if 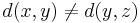
For simplicity, let us use the norms instead of the distances in the proof; we want to prove that if 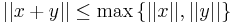 , then the equality occurs if
, then the equality occurs if 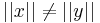 . Without loss of generality, let's assume that
. Without loss of generality, let's assume that 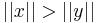 . This implies that
. This implies that 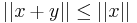 . But we can also compute
. But we can also compute 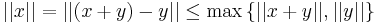 . Now, the value of
. Now, the value of 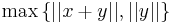 cannot be
cannot be 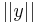 , for if that is the case, we have
, for if that is the case, we have 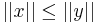 contrary to the initial assumption. Thus,
contrary to the initial assumption. Thus, 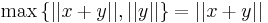 , and
, and 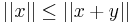 . Using the initial inequality, we have
. Using the initial inequality, we have 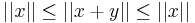 and therefore
and therefore 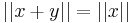 .
.
Properties
From the above definition, one can conclude several typical properties of ultrametrics. For example, in an ultrametric space, for all x, y, z in M and r, s in R:
- Every triangle is isosceles, i.e. d(x,y) = d(y,z) or d(x,z) = d(y,z) or d(x,y) = d(z,x).
In the following, the concept and notation of an (open) ball is the same as in the article about metric spaces, i.e.
- B(x; r) = { y ∈ M | d(x, y) < r } .
- Every point inside a ball is its center, i.e. if d(x,y) < r then B(x; r) = B(y; r).
- Intersecting balls are contained in each other, i.e. if B(x; r) ∩ B(y; s) is non-empty then either B(x; r) ⊆ B(y; s) or B(y; s) ⊆ B(x; r).
- All balls are both open and closed sets in the induced topology. That is, open balls are also closed, and closed balls (replace < with ≤) are also open.
- The set of all open balls with radius r and center in a closed ball of radius r > 0 forms a partition of the latter, and the mutual distance of two distinct open balls is again equal to r.
Proving these statements is an instructive exercise. Note that, by the second statement, a ball may have several center points that have non-zero distance. The intuition behind such seemingly strange effects is that, due to the strong triangle inequality, distances in ultrametrics do not add up.
Examples
- The discrete metric is an ultrametric.
- Consider the set of words of arbitrary length (finite or infinite) over some alphabet Σ. Define the distance between two different words to be 2-n, where n is the first place at which the words differ. The resulting metric is an ultrametric.
- The p-adic numbers form a complete ultrametric space.
- If r=(rn) is a sequence of real numbers decreasing to zero, then |x|r := lim supn→∞ |xn|rn induces an ultrametric on the space of all complex sequences for which it is finite. (Note that this is not a seminorm since it lacks homogeneity. — If the rn are allowed to be zero, one should use here the rather unusual convention that 00=0.)
- If G is an edge-weighted undirected graph, all edge weights are positive, and d(u,v) is the weight of the minimax path between u and v (that is, the largest weight of an edge, on a path chosen to minimize this largest weight), then the vertices of the graph, with distance measured by d, form an ultrametric space, and all finite ultrametric spaces may be represented in this way.[2]
Applications
A contraction mapping may then be thought of as a way of approximating the final result of a computation (which can be guaranteed to exist by the Banach fixed point theorem). Similar ideas can be found in domain theory. P-adic analysis makes heavy use of the ultrametric nature of the p-adic metric.
Applications are also known in solid-state physics, namely in the treatment of spin glasses by the replica-theory of Giorgio Parisi and coworkers,[3] and also in the theory of aperiodic solids.[4]
Ultrametric distances are also utilized in taxonomy and phylogenetic tree construction using the UPGMA and WPGMA methods.[4]
References
- ^ Planet Math: Non Archimedean Triangle Inequality
- ^ Leclerc, Bruno (1981), "Description combinatoire des ultramétriques" (in French), Centre de Mathématique Sociale. École Pratique des Hautes Études. Mathématiques et Sciences Humaines (73): 5–37, 127, MR623034.
- ^ Mezard, M; Parisi, G; and Virasoro, M: SPIN GLASS THEORY AND BEYOND, World Scientific, 1986. ISBN 978-9971-5-0116-7
- ^ a b Rammal, R.; Toulouse, G., Virasoro, M. (1986). "Ultrametricity for physicists". Reviews of Modern Physics 58 (3): 765–788. doi:10.1103/RevModPhys.58.765. http://rmp.aps.org/abstract/RMP/v58/i3/p765_1. Retrieved 20 June 2011.
Further reading
- Kaplansky, I. (1977), Set Theory and Metric Spaces, AMS Chelsea Publishing, ISBN 0-8218-2694-8.