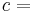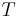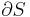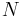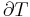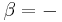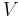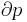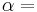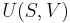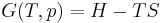Thermodynamic diagrams
Thermodynamic diagrams are diagrams used by scientists and engineers to represent the thermodynamic states of a material (typically fluid) and the consequences of manipulating this material. For instance, a temperature-entropy diagram (T-S diagram) may be used to demonstrate the behavior of a fluid as it is changed by a compressor.
Contents |
Overview
Especially in meteorology they are used to analyze the actual state of the atmosphere derived from the measurements of radiosondes, usually obtained with weather balloons. In such diagrams, temperature and humidity values (represented by the dew point) are displayed with respect to pressure. Thus the diagram gives at a first glance the actual atmospheric stratification and vertical water vapor distribution. Further analysis gives the actual base and top height of convective clouds or possible instabilities in the stratification.
By assuming the energy amount due to solar radiation it is possible to predict the 2 m (6.6 ft) temperature, humidity, and wind during the day, the development of the boundary layer of the atmosphere, the occurrence and development of clouds and the conditions for soaring flight during the day.
The main feature of thermodynamic diagrams is the equivalence between the area in the diagram and energy. When air changes pressure and temperature during a process and prescribes a closed curve within the diagram the area enclosed by this curve is proportional to the energy which has been gained or released by the air.
Types of thermodynamic diagrams
General purpose diagrams include:
- P-V diagram
- T-s diagram
- H-S (Mollier) diagram
- Psychrometric chart
- Cooling curve
- Indicator diagram
- Saturation vapor curve
Specific to weather services, there are mainly three different types of thermodynamic diagrams used:
These all are derived from the physical P-alpha-diagram which combines pressure and specific volume (alpha) as basic coordinates. The P-alpha-diagram shows a strong deformation of the grid for atmospheric conditions and is therefore not useful in atmospheric sciences. The three diagrams are constructed from the P-alpha-diagram by using appropriate coordinate transformations.
Not a thermodynamic diagram in a strict sense since it does not display the energy - area equivalence is the
Due to its simpler construction it is preferred in education.
Characteristics
Thermodynamic diagrams usually show a net of five different lines:
- isobars = lines of constant pressure
- isotherms = lines of constant temperature
- dry adiabats = lines of constant potential temperature representing the temperature of a rising parcel of dry air
- saturated adiabats or pseudoadiabats = lines representing the temperature of a rising parcel saturated with water vapour
- mixing ratio = lines representing the dewpoint of a rising parcel
The lapse rate, dry adiabatic lapse rate (DALR) and moist adiabatic lapse rate (MALR), are obtained. With the help of these lines, parameters such as cloud condensation level, level of free convection, onset of cloud formation. etc. can be derived from the soundings.
References
- The Physics of Atmospheres by John Houghton, Cambridge University Press 2002. Especially chapter 3.3. deals solely with the tephigram.
- German version of Handbook of meteorological soaring flight from the Organisation Scientifique et Technique Internationale du Vol à Voile (OSTIV) (chapter 2.3)
Further reading
- Handbook of meteorological forecasting for soaring flight WMO Technical Note No. 158. ISBN 92-63-10495-6 especially chapter 2.3.
External links
- radarmet.atmos.colostate.edu/../AT620_ch4.ppt A PowerPoint presentation with a very good mathematical description about the derivation of the different diagrams.
- www.met.tamu.edu/../aws-tr79-006.pdf A very large technical manual (164 pages) how to use the diagrams.
- www.comet.ucar.edu/../sld010.htm A course on how to use diagrams at comet the 'Cooperative Program for Operational Meteorology, Education and Training'.
- www.raob.com RAOB analysis software for radio soundings.
- www.ulweb.de/thermik/60Tempanalyse.ppt a PowerPoint presentation about the use of the Stuve diagram (in German).
- Tephigram page, University of Reading Blank colour and monochrome tephigrams as pdf from the Department of Meteorology, University of Reading.
- maths.ucd.ie/../blank_tephigram.pdf and .../Colour-Tephigram.pdf Blank b&w and color Tephigrams as pdf from UCD School of Mathematical sciences in Dublin.
- http://www.meteo.uni-koeln.de/meteo.php?show=En_We_We Radio soundings from all over the world from the 'Institut für Geophysik und Meteorologie' at the University of Cologne/Germany
- weather.uwyo.edu/upperair/sounding.html Radio soundings from all over the world from the Department of Atmospheric sciences at the University of Wyoming/USA
|
|||||||||||||||||