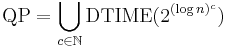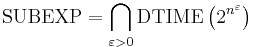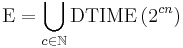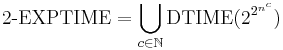Time complexity
In computer science, the time complexity of an algorithm quantifies the amount of time taken by an algorithm to run as a function of the size of the input to the problem. The time complexity of an algorithm is commonly expressed using big O notation, which suppresses multiplicative constants and lower order terms. When expressed this way, the time complexity is said to be described asymptotically, i.e., as the input size goes to infinity. For example, if the time required by an algorithm on all inputs of size n is at most 5n3 + 3n, the asymptotic time complexity is O(n3).
Time complexity is commonly estimated by counting the number of elementary operations performed by the algorithm, where an elementary operation takes a fixed amount of time to perform. Thus the amount of time taken and the number of elementary operations performed by the algorithm differ by at most a constant factor.
Since an algorithm may take a different amount of time even on inputs of the same size, the most commonly used measure of time complexity, the worst-case time complexity of an algorithm, denoted as T(n), is the maximum amount of time taken on any input of size n. Time complexities are classified by the nature of the function T(n). For instance, an algorithm with T(n) = O(n) is called a linear time algorithm, and an algorithm with T(n) = O(2n) is said to be an exponential time algorithm.
Table of common time complexities
The following table summarises some classes of commonly encountered time complexities. In the table, poly(x) = xO(1), i.e., polynomial in x.
| Name | Complexity class | Running time (T(n)) | Examples of running times | Examples of algorithms |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| constant time | O(1) | 10 | Determining if a number is even or odd | |
| inverse Ackermann | O(α(n)) | Amortized time per operation using a disjoint set | ||
| iterated logarithmic | O(log* n) | Distributed coloring of cycles | ||
| log-logarithmic | O(log log n) | Amortized time per operation using a bounded priority queue[1] | ||
| logarithmic time | DLOGTIME | O(log n) | log n, log(n2) | Binary search |
| polylogarithmic time | poly(log n) | (log n)2 | ||
| fractional power | O(nc) where 0 < c < 1 | n1/2, n2/3 | Searching in a kd-tree | |
| linear time | O(n) | n | Finding the smallest item in an unsorted array | |
| "n log star n" | O(n log* n) | Seidel's polygon triangulation algorithm. | ||
| linearithmic time | O(n log n) | n log n, log n! | Fastest possible comparison sort | |
| quadratic time | O(n2) | n2 | Bubble sort; Insertion sort | |
| cubic time | O(n3) | n3 | Naive multiplication of two n×n matrices. Calculating partial correlation. | |
| polynomial time | P | 2O(log n) = poly(n) | n, n log n, n10 | Karmarkar's algorithm for linear programming; AKS primality test |
| quasi-polynomial time | QP | 2poly(log n) | nlog log n, nlog n | Best-known O(log2 n)-approximation algorithm for the directed Steiner tree problem. |
| sub-exponential time (first definition) |
SUBEXP | O(2nε) for all ε > 0 | O(2log nlog log n) | Assuming complexity theoretic conjectures, BPP is contained in SUBEXP.[2] |
| sub-exponential time (second definition) |
2o(n) | 2n1/3 | Best-known algorithm for integer factorization and graph isomorphism | |
| exponential time | E | 2O(n) | 1.1n, 10n | Solving the traveling salesman problem using dynamic programming |
| exponential time | EXPTIME | 2poly(n) | 2n, 2n2 | |
| factorial time | O(n!) | n! | Solving the traveling salesman problem via brute-force search | |
| double exponential time | 2-EXPTIME | 22poly(n) | 23n | Deciding the truth of a given statement in Presburger arithmetic |
Constant time
An algorithm is said to be constant time (also written as O(1) time) if the value of T(n) is bounded by a value that does not depend on the size of the input. For example, accessing any single element in an array takes constant time as only one operation has to be performed to locate it. However, finding the minimal value in an unordered array is not a constant time operation as a scan over each element in the array is needed in order to determine the minimal value. Hence it is a linear time operation, taking O(n) time. If the number of elements is known in advance and does not change, however, such an algorithm can still be said to run in constant time.
Despite the name "constant time", the running time does not have to be independent of the problem size, but an upper bound for the running time has to be bounded independently of the problem size. For example, the task "exchange the values of a and b if necessary so that a≤b" is called constant time even though the time may depend on whether or not it is already true that a ≤ b. However, there is some constant t such that the time required is always at most t.
Here are some examples of code fragments that run in constant time:
int index = 5;
int item = list[index];
if (condition true) then
perform some operation that runs in constant time
else
perform some other operation that runs in constant time
for i = 1 to 100
for j = 1 to 200
perform some operation that runs in constant time
If T(n) is O(any constant value), this is equivalent to and stated in standard notation as T(n) being O(1).
Logarithmic time
An algorithm is said to take logarithmic time if T(n) = O(log n). Due to the use of the binary numeral system by computers, the logarithm is frequently base 2 (that is, log2 n, sometimes written lg n). However, by the change of base equation for logarithms, loga n and logb n differ only by a constant multiplier, which in big-O notation is discarded; thus O(log n) is the standard notation for logarithmic time algorithms regardless of the base of the logarithm.
Algorithms taking logarithmic time are commonly found in operations on binary trees or when using binary search.
Polylogarithmic time
An algorithm is said to run in polylogarithmic time if T(n) = O((log n)k), for some constant k. For example, matrix chain ordering can be solved in polylogarithmic time on a Parallel Random Access Machine.[3]
Sub-linear time
An algorithm is said to run in sub-linear time (often spelled sublinear time) if T(n) = o(n). In particular this includes algorithms with the time complexities defined above, as well as others such as the O(n½) Grover's search algorithm.
For an algorithm to be exact and yet run in sub-linear time, it needs to use parallel processing (as the NC1 matrix determinant calculation does) or non-classical processing (as Grover's search does), or alternatively have guaranteed assumptions on the input structure (as the logarithmic time binary search and many tree maintenance algorithms do). Otherwise, a sub-linear time algorithm would not be able to read or learn the entire input prior to providing its output.
The specific term sublinear time algorithm is usually reserved to algorithms that are unlike the above in that they are run over classical serial machine models and are not allowed prior assumptions on the input.[4] They are however allowed to be randomized, and indeed must be randomized for all but the most trivial of tasks.
As such an algorithm must provide an answer without reading the entire input, its particulars heavily depend on the access allowed to the input. Usually for an input that is represented as a binary string b1,...,bk it is assumed that the algorithm can in time O(1) request and obtain the value of bi for any i.
Sublinear time algorithms are typically randomized, and provide only approximate solutions. In fact, the property of a binary string having only zeros (and no ones) can be easily proved not to be decidable by a (non-approximate) sublinear time algorithm. Sublinear time algorithms arise naturally in the investigation of property testing.
Linear time
An algorithm is said to take linear time, or O(n) time, if its time complexity is O(n). Informally, this means that for large enough input sizes the running time increases linearly with the size of the input. For example, a procedure that adds up all elements of a list requires time proportional to the length of the list. This description is slightly inaccurate, since the running time can significantly deviate from a precise proportionality, especially for small values of n.
Linear time is often viewed as a desirable attribute for an algorithm. Much research has been invested into creating algorithms exhibiting (nearly) linear time or better. This research includes both software and hardware methods. In the case of hardware, some algorithms which, mathematically speaking, can never achieve linear time with standard computation models are able to run in linear time. There are several hardware technologies which exploit parallelism to provide this. An example is content-addressable memory. This concept of linear time is used in string matching algorithms such as the Boyer-Moore Algorithm and Ukkonen's Algorithm.
Linearithmic/quasilinear time
A linearithmic function (portmanteau of linear and logarithmic) is a function of the form n · log n (i.e., a product of a linear and a logarithmic term). An algorithm is said to run in linearithmic time if T(n) = O(n log n). Compared to other functions, a linearithmic function is ω(n), o(n1+ε) for every ε > 0, and Θ(n · log n). Thus, a linearithmic term grows faster than a linear term but slower than any polynomial in n with exponent strictly greater than 1.
An algorithm is said to run in quasilinear time if T(n) = O(n logk n) for any constant k. Quasilinear time algorithms are also o(n1+ε) for every ε > 0, and thus run faster than any polynomial in n with exponent strictly greater than 1.
In many cases, the n · log n running time is simply the result of performing a Θ(log n) operation n times. For example, Binary tree sort creates a Binary tree by inserting each element of the n-sized array one by one. Since the insert operation on a self-balancing binary search tree takes O(log n) time, the entire algorithm takes linearithmic time.
Comparison sorts require at least linearithmic number of comparisons in the worst case because log(n!) = Θ(n log n), by Stirling's approximation. They also frequently arise from the recurrence relation T(n) = 2 T(n/2) + O(n).
Some famous algorithms that run in linearithmic time include:
- Comb sort, in the average and worst case
- Quicksort in the average case
- Heapsort, merge sort, introsort, binary tree sort, smoothsort, patience sorting, etc. in the worst case
- Fast Fourier transforms
- Monge array calculation
Sub-quadratic time
An algorithm is said to be subquadratic time if T(n) = o(n2).
For example, most naïve comparison-based sorting algorithms are quadratic (e.g. insertion sort), but more advanced algorithms can be found that are subquadratic (e.g. Shell sort). No general-purpose sorts run in linear time, but the change from quadratic to sub-quadratic is of great practical importance.
Polynomial time
An algorithm is said to be of polynomial time if its running time is upper bounded by a polynomial expression in the size of the input for the algorithm, i.e., T(n) = O(nk) for some constant k.[5][6] Problems for which a polynomial time algorithm exists belong to the complexity class P, which is central in the field of computational complexity theory. Cobham's thesis states that polynomial time is a synonym for "tractable", "feasible", "efficient", or "fast".[7]
Some examples of polynomial time algorithms:
- The quicksort sorting algorithm on n integers performs at most
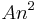 operations for some constant A. Thus it runs in time
operations for some constant A. Thus it runs in time 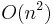 and is a polynomial time algorithm.
and is a polynomial time algorithm. - All the basic arithmetic operations (addition, subtraction, multiplication, division, and comparison) can be done in polynomial time.
- Maximum matchings in graphs can be found in polynomial time.
Strongly and weakly polynomial time
In some contexts, especially in optimization, one differentiates between strongly polynomial time and weakly polynomial time algorithms. These two concepts are only relevant if the inputs to the algorithms consist of integers.
Strongly polynomial time is defined in the arithmetic model of computation. In this model of computation the basic arithmetic operations (addition, subtraction, multiplication, division, and comparison) take a unit time step to perform, regardless of the sizes of the operands. The algorithm runs in strongly polynomial time if [8]
- the number of operations in the arithmetic model of computation is bounded by a polynomial in the number of integers in the input instance; and
- the space used by the algorithm is bounded by a polynomial in the size of the input.
Any algorithm with these two properties can be converted to a polynomial time algorithm by replacing the arithmetic operations by suitable algorithms for performing the arithmetic operations on a Turing machine. If the second of the above requirement is not met, then this is not true anymore. Given the integer 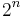 (which takes up space proportional to n), it is possible to compute
(which takes up space proportional to n), it is possible to compute 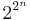 with n multiplications using repeated squaring. However, the space used to represent
with n multiplications using repeated squaring. However, the space used to represent 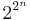 is proportional to
is proportional to 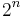 , and thus exponential rather than polynomial in the space used to represent the input. Hence, it is not possible to carry out this computation in polynomial time on a Turing machine, but it is possible to compute it by polynomially many arithmetic operations.
, and thus exponential rather than polynomial in the space used to represent the input. Hence, it is not possible to carry out this computation in polynomial time on a Turing machine, but it is possible to compute it by polynomially many arithmetic operations.
There are algorithms which run in polynomial time in the Turing machine model but not in the arithmetic model. The Euclidean algorithm for computing the greatest common divisor of two integers is one example. Given two integers a and b the running time of the algorithm is bounded by 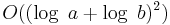 . This is polynomial in the size of a binary representation of a and b as the size of such a representation is roughly
. This is polynomial in the size of a binary representation of a and b as the size of such a representation is roughly 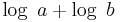 . However, the algorithm does not run in strongly polynomial time as the running time depends on the magnitudes of a and b and not only on the number of integers in the input (which is constant in this case, there is always only two integers in the input).
. However, the algorithm does not run in strongly polynomial time as the running time depends on the magnitudes of a and b and not only on the number of integers in the input (which is constant in this case, there is always only two integers in the input).
An algorithm which runs in polynomial time but which is not strongly polynomial is said to run in weakly polynomial time.[9] A well-known example of a problem for which a weakly polynomial-time algorithm is known, but is not known to admit a strongly polynomial-time algorithm, is linear programming. Weakly polynomial-time should not be confused with pseudo-polynomial time.
Complexity classes
The concept of polynomial time leads to several complexity classes in computational complexity theory. Some important classes defined using polynomial time are the following.
- P: The complexity class of decision problems that can be solved on a deterministic Turing machine in polynomial time.
- NP: The complexity class of decision problems that can be solved on a non-deterministic Turing machine in polynomial time.
- ZPP: The complexity class of decision problems that can be solved with zero error on a probabilistic Turing machine in polynomial time.
- RP: The complexity class of decision problems that can be solved with 1-sided error on a probabilistic Turing machine in polynomial time.
- BPP: The complexity class of decision problems that can be solved with 2-sided error on a probabilistic Turing machine in polynomial time.
- BQP: The complexity class of decision problems that can be solved with 2-sided error on a quantum Turing machine in polynomial time.
P is the smallest time-complexity class on a deterministic machine which is robust in terms of machine model changes. (For example, a change from a single-tape Turing machine to a multi-tape machine can lead to a quadratic speedup, but any algorithm that runs in polynomial time under one model also does so on the other.) Any given abstract machine will have a complexity class corresponding to the problems which can be solved in polynomial time on that machine.
Superpolynomial time
An algorithm is said to take superpolynomial time if T(n) is not bounded above by any polynomial. It is ω(nc) time for all constants c, where n is the input parameter, typically the number of bits in the input.
For example, an algorithm that runs for 2n steps on an input of size n requires superpolynomial time (more specifically, exponential time).
An algorithm that uses exponential resources is clearly superpolynomial, but some algorithms are only very weakly superpolynomial. For example, the Adleman–Pomerance–Rumely primality test runs for nO(log log n) time on n-bit inputs; this grows faster than any polynomial for large enough n, but the input size must become impractically large before it cannot be dominated by a polynomial with small degree.
An algorithm that has been proven to require superpolynomial time cannot be solved in polynomial time, and so is known to lie outside the complexity class P. Cobham's thesis conjectures that these algorithms are impractical, and in many cases they are. Since the P versus NP problem is unresolved, no algorithm for a NP-complete problem is currently known to run in polynomial time.
Quasi-polynomial time
Quasi-polynomial time algorithms are algorithms which run slower than polynomial time, yet not so slow as to be exponential time. The worst case running time of a quasi-polynomial time algorithm is 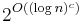 for some fixed c. The best-known classical algorithm for integer factorization, the general number field sieve, which runs in time about
for some fixed c. The best-known classical algorithm for integer factorization, the general number field sieve, which runs in time about 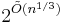 is not quasi-polynomial since the running time cannot be expressed as
is not quasi-polynomial since the running time cannot be expressed as 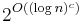 for some fixed c. If the constant "c" in the definition of quasi-polynomial time algorithms is equal to 1, we get a polynomial time algorithm, and if it less than 1, we get a sub-linear time algorithm.
for some fixed c. If the constant "c" in the definition of quasi-polynomial time algorithms is equal to 1, we get a polynomial time algorithm, and if it less than 1, we get a sub-linear time algorithm.
Quasi-polynomial time algorithms typically arise in reductions from an NP-hard problem to another problem. For example, one can take an instance of an NP hard problem, say 3SAT, and convert it to an instance of another problem B, but the size of the instance becomes 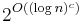 . In that case, this reduction does not prove that problem B is NP-hard; this reduction only shows that there is no polynomial time algorithm for B unless there is a quasi-polynomial time algorithm for 3SAT (and thus all of NP). Similarly, there are some problems for which we know quasi-polynomial time algorithms, but no polynomial time algorithm is known. Such problems arise in approximation algorithms; a famous example is the directed Steiner tree problem, for which there is a quasi-polynomial time approximation algorithm achieving an approximation factor of
. In that case, this reduction does not prove that problem B is NP-hard; this reduction only shows that there is no polynomial time algorithm for B unless there is a quasi-polynomial time algorithm for 3SAT (and thus all of NP). Similarly, there are some problems for which we know quasi-polynomial time algorithms, but no polynomial time algorithm is known. Such problems arise in approximation algorithms; a famous example is the directed Steiner tree problem, for which there is a quasi-polynomial time approximation algorithm achieving an approximation factor of 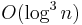 (n being the number of vertices), but showing the existence of such a polynomial time algorithm is an open problem.
(n being the number of vertices), but showing the existence of such a polynomial time algorithm is an open problem.
The complexity class QP consists of all problems which have quasi-polynomial time algorithms. It can be defined in terms of DTIME as follows.[10]
Relation to NP-complete problems
In complexity theory, the unsolved P versus NP problem asks if all problems in NP have polynomial-time algorithms. All the best-known algorithms for NP-complete problems like 3SAT etc. take exponential time. Indeed, it is conjectured for many natural NP-complete problems that they do not have sub-exponential time algorithms. Here "sub-exponential time" is taken to mean the second definition presented above. (On the other hand, many graph problems represented in the natural way by adjacency matrices are solvable in subexponential time simply because the size of the input is square of the number of vertices.) This conjecture (for the k-SAT problem) is known as the exponential time hypothesis.[11] Since it is conjectured that NP-complete problems do not have quasi-polynomial time algorithms, some inapproximability results in the field of approximation algorithms make the assumption that NP-complete problems do not have quasi-polynomial time algorithms. For example, see the known inapproximability results for the set cover problem.
Sub-exponential time
The term sub-exponential time is used to express that the running time of some algorithm may grow faster than any polynomial but is still significantly smaller than an exponential. In this sense, problems that have sub-exponential time algorithms are somewhat more tractable than those that only have exponential algorithms. The precise definition of "sub-exponential" is not generally agreed upon,[12] and we list the two most widely used ones below.
First definition
A problem is said to be sub-exponential time solvable if it can be solved in running times whose logarithms grow smaller than any given polynomial. More precisely, a problem is in sub-exponential time if for every ε > 0 there exists an algorithm which solves the problem in time O(2nε). The set of all such problems is the complexity class SUBEXP which can be defined in terms of DTIME as follows.[2][13][14][15]
Note that this notion of sub-exponential is non-uniform in terms of ε in the sense that ε is not part of the input and each ε may have its own algorithm for the problem.
Second definition
Some authors define sub-exponential time as running times in 2o(n).[11][16][17] This definition allows larger running times than the first definition of sub-exponential time. An example of such a sub-exponential time algorithm is the best-known classical algorithm for integer factorization, the general number field sieve, which runs in time about 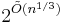 , where the length of the input is n. Another example is the best-known algorithm for the graph isomorphism problem, which runs in time 2O(√(n log n)).
, where the length of the input is n. Another example is the best-known algorithm for the graph isomorphism problem, which runs in time 2O(√(n log n)).
Note that it makes a difference whether the algorithm is allowed to be sub-exponential in the size of the instance, the number of vertices, or the number of edges. In parameterized complexity, this difference is made explicit by considering pairs 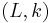 of decision problems and parameters k. SUBEPT is the class of all parameterized problems that run in time sub-exponential in k and polynomial in the input size n:[18]
of decision problems and parameters k. SUBEPT is the class of all parameterized problems that run in time sub-exponential in k and polynomial in the input size n:[18]
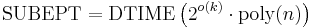 .
.
More precisely, SUBEPT is the class of all parameterized problems 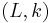 for which there is a computable function
for which there is a computable function 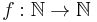 with
with 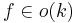 and an algorithm that decides L in time
and an algorithm that decides L in time 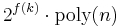 .
.
Exponential time hypothesis
The exponential time hypothesis (ETH) is that 3SAT, the satisfiability problem of Boolean formulas in conjunctive normal form with at most three literals per clause and with n variables, cannot be solved in time 2o(n). More precisely, the hypothesis is that there is some absolute constant c>0 such that 3SAT cannot be decided in time 2cn by any deterministic Turing machine. With m denoting the number of clauses, ETH is equivalent to the hypothesis that kSAT cannot be solved in time 2o(m) for any integer k≥3.[19] The exponential time hypothesis implies P ≠ NP.
Exponential time
An algorithm is said to be exponential time, if T(n) is upper bounded by 2poly(n), where poly(n) is some polynomial in n. More formally, an algorithm is exponential time if T(n) is bounded by O(2nk) for some constant k. Problems which admit exponential time algorithms on a deterministic Turing machine form the complexity class known as EXP.
Sometimes, exponential time is used to refer to algorithms that have T(n) = 2O(n), where the exponent is at most a linear function of n. This gives rise to the complexity class E.
Double exponential time
An algorithm is said to be double exponential time if T(n) is upper bounded by 22poly(n), where poly(n) is some polynomial in n. Such algorithms belong to the complexity class 2-EXPTIME.
Well-known double exponential time algorithms include:
- Decision procedures for Presburger arithmetic
- Computing a Gröbner basis (in the worst case)
- Quantifier elimination on real closed fields takes at least doubly exponential time (but is not even known to be computable in ELEMENTARY)
See also
References
- ^ Mehlhorn, Kurt; Naher, Stefan (1990). "Bounded ordered dictionaries in O(log log N) time and O(n) space". Information Processing Letters 35 (4): 183. doi:10.1016/0020-0190(90)90022-P.
- ^ a b Babai, László; Fortnow, Lance; Nisan, N.; Wigderson, Avi (1993). "BPP has subexponential time simulations unless EXPTIME has publishable proofs". Computational Complexity (Berlin, New York: Springer-Verlag) 3 (4): 307–318. doi:10.1007/BF01275486.
- ^ Bradford, Phillip G.; Rawlins, Gregory J. E.; Shannon, Gregory E. (1998). "Efficient Matrix Chain Ordering in Polylog Time". SIAM Journal on Computing (Philadelphia: Society for Industrial and Applied Mathematics) 27 (2): 466–490. doi:10.1137/S0097539794270698. ISSN 1095-7111.
- ^ Kumar, Ravi; Rubinfeld, Ronitt (2003). "Sublinear time algorithms". SIGACT News 34 (4): 57–67. http://www.cs.princeton.edu/courses/archive/spr04/cos598B/bib/kumarR-survey.pdf.
- ^ Papadimitriou, Christos H. (1994). Computational complexity. Reading, Mass.: Addison-Wesley. ISBN 0-201-53082-1.
- ^ Sipser, Michael (2006). Introduction to the Theory of Computation. Course Technology Inc. ISBN 0-619-21764-2.
- ^ Cobham, Alan (1965). "The intrinsic computational difficulty of functions". Proc. Logic, Methodology, and Philosophy of Science II. North Holland.
- ^ Grötschel, Martin; László Lovász, Alexander Schrijver (1988). "Complexity, Oracles, and Numerical Computation". Geometric Algorithms and Combinatorial Optimization. Springer. ISBN 038713624X.
- ^ Schrijver, Alexander (2003). "Preliminaries on algorithms and Complexity". Combinatorial Optimization: Polyhedra and Efficiency. 1. Springer. ISBN 3540443894.
- ^ Complexity Zoo: Class QP: Quasipolynomial-Time
- ^ a b Impagliazzo, R.; Paturi, R. (2001). "On the complexity of k-SAT". Journal of Computer and System Sciences (Elsevier) 62 (2): 367–375. doi:10.1006/jcss.2000.1727. ISSN 1090-2724.
- ^ Aaronson, Scott (5 April 2009). "A not-quite-exponential dilemma". Shtetl-Optimized. http://scottaaronson.com/blog/?p=394. Retrieved 2 December 2009.
- ^ Complexity Zoo: Class SUBEXP: Deterministic Subexponential-Time
- ^ Moser, P. (2003). "Baire's Categories on Small Complexity Classes". Lecture Notes in Computer Science (Berlin, New York: Springer-Verlag): 333–342. ISSN 0302-9743.
- ^ Miltersen, P.B. (2001). "DERANDOMIZING COMPLEXITY CLASSES". Handbook of Randomized Computing (Kluwer Academic Pub): 843.
- ^ Kuperberg, Greg (2005). "A Subexponential-Time Quantum Algorithm for the Dihedral Hidden Subgroup Problem". SIAM Journal on Computing (Philadelphia: Society for Industrial and Applied Mathematics) 35 (1): 188. ISSN 1095-7111.
- ^ Oded Regev (2004). "A Subexponential Time Algorithm for the Dihedral Hidden Subgroup Problem with Polynomial Space". arXiv:quant-ph/0406151v1 [quant-ph].
- ^ Flum, Jörg; Grohe, Martin (2006). Parameterized Complexity Theory. Springer. p. 417. ISBN 978-3-540-29952-3. http://www.springer.com/east/home/generic/search/results?SGWID=5-40109-22-141358322-0. Retrieved 2010-03-05.
- ^ Impagliazzo, R.; Paturi, R.; Zane, F. (2001). "Which problems have strongly exponential complexity?". Journal of Computer and System Sciences 63 (4): 512–530. doi:10.1006/jcss.2001.1774.