Stiction
Stiction (μs) is the static friction that needs to be overcome to enable relative motion of stationary objects in contact.[1][2] The term is a portmanteau of the term "static friction",[3] perhaps also influenced by the verb "stick".
Any solid objects pressing against each other (but not sliding) will require some threshold of force parallel to the surface of contact in order to overcome static cohesion. Stiction is a threshold, not a continuous force.
In situations where two surfaces with areas below the micrometer range come into close proximity (as in an accelerometer), they may adhere together. At this scale, electrostatic and/or Van der Waals and hydrogen bonding forces become significant. The phenomenon of two such surfaces being adhered together in this manner is also called stiction. Stiction may be related to hydrogen bonding or residual contamination.
Contents |
Demonstration
Place a wooden block near one end of a long wooden board. Leaving the far end of the board on the floor, lift the end with the block until the slope of the board is sufficient for the block to begin sliding downward without being pushed. Then lower the board slightly.
Placing the block again at the top, it will not begin to slide on its own. However, it will begin and continue to slide if given a small initial push. The push adds the necessary force to overcome stiction. Once the block is moving, it no longer requires the larger force.
Automobiles
Stiction is also the same threshold at which a rolling object would begin to slide over a surface rather than rolling at the expected rate (and in the case of a wheel, in the expected direction). In this case, it's called "rolling friction" or μr.
This is why driver training courses teach that if a car begins to slide sideways, the driver should try to steer in the same direction as the slide with no brakes. It gives the wheels a chance to regain static contact by rolling, which gives the driver some control again. An overenthusiastic driver may "squeal" the driving wheels trying to get a rapid start but this impressive display of noise and smoke is less effective than maintaining static contact with the road. Many stunt-driving techniques are also done by deliberately breaking and/or regaining this rolling friction.
A car on a slippery surface can slide a long way if the driver "locks" the wheels in stationary positions by pressing hard on the brakes. Anti-lock braking systems use wheel speed sensors and vehicle speed sensors to determine if any of the wheels have stopped turning. The ABS Module then briefly releases pressure to that wheel to allow the wheel to begin turning again. Anti-lock brakes can be much more effective than cadence braking which is essentially a non-automatic technique for doing the same thing.
Examples
Surface micromachining
Stiction or adhesion between the substrate (usually silicon based) and the microstructure occurs during the isotropic wet etching of the sacrificial layer. The capillary forces due to the surface tension of the liquid between the microstructure and substrate during drying of the wet etchant cause the two surfaces to adhere together. Separating the two surfaces is often complicated due to the fragile nature of the microstructure. Stiction is often circumvented by the use of a sublimating fluid (often supercritical 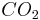 , which has extremely low surface tension) drying process where the liquid phase is bypassed.
, which has extremely low surface tension) drying process where the liquid phase is bypassed. 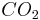 displaces the rinsing fluid and is heated past the supercritical point. As the chamber pressure is slowly released the
displaces the rinsing fluid and is heated past the supercritical point. As the chamber pressure is slowly released the 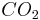 sublimates thereby preventing stiction.
sublimates thereby preventing stiction.
Hard disk drives
In the context of hard disk drives, stiction refers to the tendency of read/write heads to stick to the platters. Stiction as a result of smoothness and is exacerbated by humidity and other liquids condensing at the head-disk interface. Once the heads have stuck to the platters, the disk can be prevented from spinning up and can cause physical damage to the media and the slider. Other forces considered as responsible for stiction include electrostatic forces.
In the early models of hard disk drives stiction was known to cause read/write heads to stick the platters of the hard drive due to the breakdown of lubricants used to coat the platters. During the late 1980s and early 1990s as the size of hard drive platters decreased from the older 8" and 5.25" sizes to 3.5" and smaller, manufacturers continued to use the same calendering processes and lubricants used on the older, larger drives. The much tighter space caused much higher internal operating temperatures in these newer smaller drives, often leading to an accelerated breakdown of the surface lubricants into their much stickier components. When the drive was powered off and would cool down(say at the end of the day when a user went home and shut off their PC), these now-broken-down lubricants would become quite viscous and sticky, sometimes causing the read/write heads to literally stick to the platter. One response to this problem was to remove the affected drive and strike it gently but firmly on the side, then try to start it while connected to but not necessarily fitted inside the machine. This might break the heads free for long enough to spin up the drive and recover the data from it without powering it down once started; it would continue to run indefinitely, but might not start again if powered down. Instead of tapping the drive, rotating it sharply by hand could start it.
Modern hard drives have mostly solved the stiction problem by using ramps to "unload" the heads from the disk surface on power-down. These ramps ensure the heads are not touching the platters, which not only prevents stiction but also keeps abrasion from kicking up microscopic particulates that can later contaminate the drive mechanism. Parking the heads in this manner also allows the voice coil actuator to be shut down to save power, so the heads are also frequently unloaded when the drive is idle. A competing solution is based on laser textured landing zones near the ID of the platter where no data is stored. The heads are parked in that zone and the actuator is latched until the next start-up. The landing zone consists of a controlled array of nanometer-level 'bumps' on the disk surface produced during manufacturing of the disk using a local substrate melting process employing suitable laser-based equipment. The method was pioneered by IBM around 1995 and is still widely in use in most desktop and server class HDDs.
Digital storage tapes
Stiction may also manifest itself on computer tapes (9 track tape etc.). The magnetic surface of the tape would be heated against the read head in the tape deck, and when the tape stopped moving would cool slightly and "glue" onto the read head. This could be avoided by configuring the software so that the tape could be read continuously. Discussion by data recovery firm
Amateur astronomy
The term "stiction" has come into use in amateur astronomy circles to describe a characteristic of Dobsonian style altazimuth telescope mounts. These mounts can resist initial movement by the user, making it difficult to track an object in the sky. There is backlash; breaking this resistance requires enough force to cause the observer to overshoot the object.
Stereolithography
Typically the phenomenon occurs when “green” epoxy photopolymer components are left in direct contact with each other. If left long enough it appears that “cross-linking” of the polymer takes place in the region of contact. This effectively “welds” or more appropriately “glues” the parts together. This issue can have a significant impact on models where testing of kinematics are required. To avoid stiction in stereolithography clean and more importantly “fully” cure all geometry prior to assembly.
Game show
In the TV Series Takeshi's Castle, contestants must run over numerous rollers to reach the other side without falling. Depending on the athlete's balance and weight, some are able to scale across without creating too much rolling movement, whilst others break the stiction point, create the rolling motion, and fall early on.