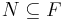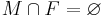STRIPS
|
In artificial intelligence, STRIPS (Stanford Research Institute Problem Solver) is an automated planner developed by Richard Fikes and Nils Nilsson in 1971. The same name was later used to refer to the formal language of the inputs to this planner. This language is the base for most of the languages for expressing automated planning problem instances in use today; such languages are commonly known as action languages. This article only describes the language, not the planner.
Definition
A STRIPS instance is composed of:
- An initial state;
- The specification of the goal states – situations which the planner is trying to reach;
- A set of actions. For each action, the following are included:
- preconditions (what must be established before the action is performed);
- postconditions (what is established after the action is performed).
Mathematically, a STRIPS instance is a quadruple 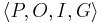 , in which each component has the following meaning:
, in which each component has the following meaning:
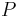 is a set of conditions (i.e., propositional variables);
is a set of conditions (i.e., propositional variables);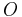 is a set of operators (i.e., actions); each operator is itself a quadruple
is a set of operators (i.e., actions); each operator is itself a quadruple 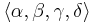 , each element being a set of conditions. These four sets specify, in order, which conditions must be true for the action to be executable, which ones must be false, which ones are made true by the action and which ones are made false;
, each element being a set of conditions. These four sets specify, in order, which conditions must be true for the action to be executable, which ones must be false, which ones are made true by the action and which ones are made false;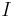 is the initial state, given as the set of conditions that are initially true (all others are assumed false);
is the initial state, given as the set of conditions that are initially true (all others are assumed false);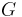 is the specification of the goal state; this is given as a pair
is the specification of the goal state; this is given as a pair 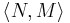 , which specify which conditions are true and false, respectively, in order for a state to be considered a goal state.
, which specify which conditions are true and false, respectively, in order for a state to be considered a goal state.
A plan for such a planning instance is a sequence of operators that can be executed from the initial state and that leads to a goal state.
Formally, a state is a set of conditions: a state is represented by the set of conditions that are true in it. Transitions between states are modeled by a transition function, which is a function mapping states into new states that result from the execution of actions. Since states are represented by sets of conditions, the transition function relative to the STRIPS instance 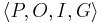 is a function
is a function
where 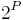 is the set of all subsets of
is the set of all subsets of 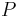 , and is therefore the set of all possible states.
, and is therefore the set of all possible states.
The transition function 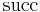 for a state
for a state 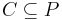 , can be defined as follows, using the simplifying assumption that actions can always be executed but have no effect if their preconditions are not met:
, can be defined as follows, using the simplifying assumption that actions can always be executed but have no effect if their preconditions are not met:
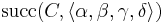 |
= 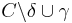 |
if 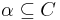 and and 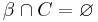 |
= 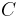 |
otherwise |
The function 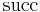 can be extended to sequences of actions by the following recursive equations:
can be extended to sequences of actions by the following recursive equations:
A plan for a STRIPS instance is a sequence of actions such that the state that results from executing the actions in order from the initial state satisfies the goal conditions. Formally, ![[a_1,a_2,\ldots,a_n]](/2012-wikipedia_en_all_nopic_01_2012/I/ce62aa9229bb66dc23d62f0b87aed5c2.png) is a plan for
is a plan for 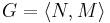 if
if ![F=\operatorname{succ}(I,[a_1,a_2,\ldots,a_n])](/2012-wikipedia_en_all_nopic_01_2012/I/3866809986a8a4879ad7c026357d5482.png) satisfies the following two conditions:
satisfies the following two conditions:
Extensions
The above language is actually the propositional version of STRIPS; in practice, conditions are often about objects: for example, that the position of a robot can be modeled by a predicate 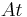 , and
, and 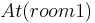 means that the robot is in Room1. In this case, actions can have free variables, which are implicitly existentially quantified. In other words, an action represents all possible propositional actions that can be obtained by replacing each free variable with a value.
means that the robot is in Room1. In this case, actions can have free variables, which are implicitly existentially quantified. In other words, an action represents all possible propositional actions that can be obtained by replacing each free variable with a value.
The initial state is considered fully known in the language described above: conditions that are not in 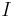 are all assumed false. This is often a limiting assumption, as there are natural examples of planning problems in which the initial state is not fully known. Extensions of STRIPS have been developed to deal with partially known initial states.
are all assumed false. This is often a limiting assumption, as there are natural examples of planning problems in which the initial state is not fully known. Extensions of STRIPS have been developed to deal with partially known initial states.
A sample STRIPS problem
A monkey is at location A in a lab. There is a box in location C. The monkey wants the bananas that are hanging from the ceiling in location B, but it needs to move the box and climb onto it in order to reach them.
Initial state: At(A), Level(low), BoxAt(C), BananasAt(B) Goal state: Have(Bananas)
Actions:
// move from X to Y
_Move(X, Y)_
Preconditions: At(X), Level(low)
Postconditions: not At(X), At(Y)
// climb up on the box
_ClimbUp(Location)_
Preconditions: At(Location), BoxAt(Location), Level(low)
Postconditions: Level(high), not Level(low)
// climb down from the box
_ClimbDown(Location)_
Preconditions: At(Location), BoxAt(Location), Level(high)
Postconditions: Level(low), not Level(high)
// move monkey and box from X to Y
_MoveBox(X, Y)_
Preconditions: At(X), BoxAt(X), Level(low)
Postconditions: BoxAt(Y), not BoxAt(X), At(Y), not At(X)
// take the bananas
_TakeBananas(Location)_
Preconditions: At(Location), BananasAt(Location), Level(high)
Postconditions: Have(bananas)
Complexity
Deciding the existence of a plan for a propositional STRIPS instance is PSPACE-complete. Various restrictions can be enforced on the instances to make the problem NP-complete[1]
See also
- Automated planning
- Hierarchical task network
- Planning Domain Definition Language (PDDL)
- Action description language (ADL)
- Sussman Anomaly
Notes
- ^ Bylander, T. The computational complexity of propositional STRIPS planning Artificial Intelligence, 1994, 69, 165-204.
References
- C. Bäckström and B. Nebel (1995). Complexity results for SAS+ planning. Computational Intelligence, 11:625-656.
- T. Bylander (1991). Complexity results for planning. In Proceedings of the Twelfth International Joint Conference on Artificial Intelligence (IJCAI'91), pages 274-279.
- R. Fikes and N. Nilsson (1971). STRIPS: a new approach to the application of theorem proving to problem solving. Artificial Intelligence, 2:189-208.
- Russell, Stuart J.; Norvig, Peter (2003), Artificial Intelligence: A Modern Approach (2nd ed.), Upper Saddle River, New Jersey: Prentice Hall, ISBN 0-13-790395-2, http://aima.cs.berkeley.edu/
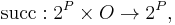
![\operatorname{succ}(C,[\ ]) = C](/2012-wikipedia_en_all_nopic_01_2012/I/39a4b82259cbfb2f18e34c9c7b4ca2f9.png)
![\operatorname{succ}(C,[a_1,a_2,\ldots,a_n])=\operatorname{succ}(\operatorname{succ}(C,a_1),[a_2,\ldots,a_n])](/2012-wikipedia_en_all_nopic_01_2012/I/e0fce75a0932679b17539ef067850c37.png)